In situ proximity ligation detection of c-Jun/AP-1 dimers reveals increased levels of c-Jun/Fra1 complexes in aggressive breast cancer cell lines in vitro and in vivo
- PMID: 20511396
- PMCID: PMC2938117
- DOI: 10.1074/mcp.M110.000943
In situ proximity ligation detection of c-Jun/AP-1 dimers reveals increased levels of c-Jun/Fra1 complexes in aggressive breast cancer cell lines in vitro and in vivo
Abstract
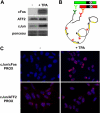
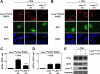
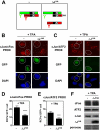
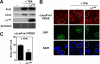
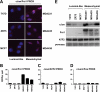
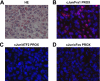
Genetic and biochemical studies have shown that selective interactions between the Jun, Fos, and activating transcription factor (ATF) components of transcription factor activating protein 1 (AP-1) exhibit specific and critical functions in the regulation of cell proliferation, differentiation, and survival. For instance, the ratio between c-Jun/c-Fos and c-Jun/ATF2 dimers in the cell can be a determining factor in the cellular response to oncogenic or apoptotic stimuli. Until recently, no methods were available to detect endogenous AP-1 complexes in cells and tissues in situ. Here, we validated the proximity ligation assay (PLA) for its ability to specifically visualize and quantify changes in endogenous c-Jun/c-Fos, c-Jun/ATF2, and c-Jun/Fra1 complexes by using, among others, partner-selective c-Jun mutants. Furthermore, we examined the levels of c-Jun/AP-1 dimers in cell lines representing different types of human breast cancer and found that aggressive basal-like breast cancer cells can be discriminated from much less invasive luminal-like cells by PLA detection of c-Jun/Fra1 rather than of c-Jun/ATF2 and c-Jun/c-Fos. Also in tumor tissue derived from highly metastatic basal-like MDA-MB231 cells, high levels of c-Jun/Fra1 complexes were detected. Together, these results demonstrate that in situ PLA is a powerful diagnostic tool to analyze and quantify the amounts of biologically critical AP-1 dimers in fixed cells and tissue material.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Promoter specificity and biological activity of tethered AP-1 dimers.Mol Cell Biol. 2002 Jul;22(13):4952-64. doi: 10.1128/MCB.22.13.4952-4964.2002. Mol Cell Biol. 2002. PMID: 12052899 Free PMC article.
-
Specific interactions between Smad proteins and AP-1 components determine TGFβ-induced breast cancer cell invasion.Oncogene. 2013 Aug 1;32(31):3606-15. doi: 10.1038/onc.2012.370. Epub 2012 Aug 27. Oncogene. 2013. PMID: 22926518
-
Restriction to Fos family members of Trip6-dependent coactivation and glucocorticoid receptor-dependent trans-repression of activator protein-1.Mol Endocrinol. 2008 Aug;22(8):1767-80. doi: 10.1210/me.2007-0574. Epub 2008 Jun 5. Mol Endocrinol. 2008. PMID: 18535250 Free PMC article.
-
Distinct roles of Jun : Fos and Jun : ATF dimers in oncogenesis.Oncogene. 2001 Apr 30;20(19):2453-64. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1204239. Oncogene. 2001. PMID: 11402340 Review.
-
AP-1 (Fos/Jun) transcription factors in hematopoietic differentiation and apoptosis.Int J Oncol. 1998 Mar;12(3):685-700. doi: 10.3892/ijo.12.3.685. Int J Oncol. 1998. PMID: 9472112 Review.
Cited by
-
Methods for analysis of the cancer microenvironment and their potential for disease prediction, monitoring and personalized treatments.EPMA J. 2012 Mar 22;3(1):7. doi: 10.1007/s13167-012-0140-3. EPMA J. 2012. PMID: 22738217 Free PMC article.
-
Shear stress induces Gαq/11 activation independently of G protein-coupled receptor activation in endothelial cells.Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2017 Apr 1;312(4):C428-C437. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00148.2016. Epub 2017 Feb 1. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2017. PMID: 28148497 Free PMC article.
-
Barriers to transmission of transcriptional noise in a c-fos c-jun pathway.Mol Syst Biol. 2013;9:687. doi: 10.1038/msb.2013.45. Mol Syst Biol. 2013. PMID: 24022005 Free PMC article.
-
TRPA1-FGFR2 binding event is a regulatory oncogenic driver modulated by miRNA-142-3p.Nat Commun. 2017 Oct 16;8(1):947. doi: 10.1038/s41467-017-00983-w. Nat Commun. 2017. PMID: 29038531 Free PMC article.
-
MALINC1 an Immune-Related Long Non-Coding RNA Associated with Early-Stage Breast Cancer Progression.Cancers (Basel). 2022 Jun 7;14(12):2819. doi: 10.3390/cancers14122819. Cancers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35740485 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Shaulian E., Karin M. (2002) AP-1 as a regulator of cell life and death. Nat. Cell Biol. 4, E131–E136 - PubMed
-
- Shaulian E., Karin M. (2001) AP-1 in cell proliferation and survival. Oncogene 20, 2390–2400 - PubMed
-
- Karin M., Liu Z., Zandi E. (1997) AP-1 function and regulation. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 9, 240–246 - PubMed
-
- van Dam H., Castellazzi M. (2001) Distinct roles of Jun:Fos and Jun:ATF dimers in oncogenesis. Oncogene 20, 2453–2464 - PubMed
-
- Diefenbacher M., Sekula S., Heilbock C., Maier J. V., Litfin M., van Dam H., Castellazzi M., Herrlich P., Kassel O. (2008) Restriction to Fos family members of Trip6-dependent coactivation and glucocorticoid receptor-dependent trans-repression of activator protein-1. Mol. Endocrinol. 22, 1767–1780 - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

