Aberrant IgG galactosylation precedes disease onset, correlates with disease activity, and is prevalent in autoantibodies in rheumatoid arthritis
- PMID: 20506563
- PMCID: PMC4118465
- DOI: 10.1002/art.27533
Aberrant IgG galactosylation precedes disease onset, correlates with disease activity, and is prevalent in autoantibodies in rheumatoid arthritis
Abstract
Objective: To examine the association between aberrant IgG galactosylation and disease parameters in rheumatoid arthritis (RA).
Methods: Analysis of N-glycan in serum samples from multiple cohorts was performed. The IgG N-glycan content and the timing of N-glycan aberrancy relative to disease onset were compared in healthy subjects and in patients with RA. Correlations between aberrant galactosylation and disease activity were assessed in the RA cohorts. The impact of disease activity, sex, age, anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide (anti-CCP) antibody titer, disease duration, and C-reactive protein level on aberrant galactosylation was determined using multivariate analysis. The N-glycan content was also compared between epitope affinity-purified autoantibodies and the remaining IgG repertoire in RA patients.
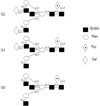
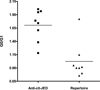
Results: Our results confirm the aberrant galactosylation of IgG in RA patients as compared with healthy controls (mean +/- SD 1.36 +/- 0.43 versus 1.01 +/- 0.23; P < 0.0001). We observed a significant correlation between levels of aberrant IgG galactosylation and disease activity (Spearman's rho = 0.37, P < 0.0001). This correlation was higher in women (Spearman's rho = 0.60, P < 0.0001) than in men (Spearman's rho = 0.16, P = 0.10). Further, aberrant IgG galactosylation substantially predated the onset of arthritis and the diagnosis of RA (3.5 years) and resided selectively in the anticitrullinated antigen fraction.
Conclusion: Our findings identify aberrant IgG galactosylation as a dysregulated component of the humoral immune response in RA that begins prior to disease onset, associates with disease activity in a sex-specific manner, and resides preferentially in autoantibodies.
Figures
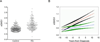
Similar articles
-
ACPA IgG galactosylation associates with disease activity in pregnant patients with rheumatoid arthritis.Ann Rheum Dis. 2018 Aug;77(8):1130-1136. doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2018-212946. Epub 2018 Apr 3. Ann Rheum Dis. 2018. PMID: 29615411
-
Low galactosylation of IgG associates with higher risk for future diagnosis of rheumatoid arthritis during 10 years of follow-up.Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis. 2018 Jun;1864(6 Pt A):2034-2039. doi: 10.1016/j.bbadis.2018.03.018. Epub 2018 Mar 20. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis. 2018. PMID: 29572115
-
Anti-citrullinated protein antibodies acquire a pro-inflammatory Fc glycosylation phenotype prior to the onset of rheumatoid arthritis.Ann Rheum Dis. 2015 Jan;74(1):234-41. doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2013-203565. Epub 2013 Oct 8. Ann Rheum Dis. 2015. PMID: 24106048
-
Hypogalactosylation of immunoglobulin G in rheumatoid arthritis: relationship to HLA-DRB1 shared epitope, anticitrullinated protein antibodies, rheumatoid factor, and correlation with inflammatory activity.Arthritis Res Ther. 2018 Mar 14;20(1):44. doi: 10.1186/s13075-018-1540-0. Arthritis Res Ther. 2018. PMID: 29540200 Free PMC article.
-
Glycosylation of random IgG distinguishes seropositive and seronegative rheumatoid arthritis.Autoimmunity. 2018 May;51(3):111-117. doi: 10.1080/08916934.2018.1468886. Epub 2018 May 7. Autoimmunity. 2018. PMID: 29733234
Cited by
-
Pharmacogenomics of intravenous immunoglobulin response in Kawasaki disease.Front Immunol. 2024 Jan 8;14:1287094. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1287094. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 38259468 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of Estradiol on Immunoglobulin G Glycosylation: Mapping of the Downstream Signaling Mechanism.Front Immunol. 2021 May 25;12:680227. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.680227. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34113353 Free PMC article.
-
Changes in antigen-specific IgG1 Fc N-glycosylation upon influenza and tetanus vaccination.Mol Cell Proteomics. 2012 Apr;11(4):M111.014563. doi: 10.1074/mcp.M111.014563. Epub 2011 Dec 19. Mol Cell Proteomics. 2012. PMID: 22184099 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Mucosa-Environment Interactions in the Pathogenesis of Rheumatoid Arthritis.Cells. 2019 Jul 10;8(7):700. doi: 10.3390/cells8070700. Cells. 2019. PMID: 31295951 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Plasma N-glycans in colorectal cancer risk.Sci Rep. 2018 Jun 5;8(1):8655. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-26805-7. Sci Rep. 2018. PMID: 29872119 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Schellekens GA, Visser H, de Jong BA, van den Hoogen FH, Hazes JM, Breedveld FC, et al. The diagnostic properties of rheumatoid arthritis antibodies recognizing a cyclic citrullinated peptide. Arthritis and rheumatism. 2000;43(1):155–163. - PubMed
-
- Corrigall VM, Bodman-Smith MD, Fife MS, Canas B, Myers LK, Wooley P, et al. The human endoplasmic reticulum molecular chaperone BiP is an autoantigen for rheumatoid arthritis and prevents the induction of experimental arthritis. J Immunol. 2001;166(3):1492–1498. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- AI-50864/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- T32-AR-07534/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- U19-AI-050864/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- K23-AR-051461/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R21 AI061479/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- K23 AR051461/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- M01-RR-000425/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- T32-AR-007534-23/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- T32-AR-07530-25/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- T32 AR007530/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R21-AI-61479/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U19 AI050864/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- K24 AR055989/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AR051394/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- M01-RR-00069/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- K23 AR051461-03/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- P30-AR-053503/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- AR-51394/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- K23 AR051461-05/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- K23 AR051461-02/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- K24-AR-055989/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- K23 AR051461-04/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- T32 AR007534/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- U19-AI-50864/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- K23 AR051461-01/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01-AR-051394/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

