Prolonged effects of short-term anti-CD20 B cell depletion therapy in murine systemic lupus erythematosus
- PMID: 20506300
- PMCID: PMC2920998
- DOI: 10.1002/art.27515
Prolonged effects of short-term anti-CD20 B cell depletion therapy in murine systemic lupus erythematosus
Abstract
Objective: Although B cells are implicated in the pathogenesis of systemic lupus erythematosus, the role of B cell depletion (BCD) as a treatment is controversial, given the variable benefit in human disease. This study was undertaken to test the effects of BCD therapy in a murine lupus model to better understand the mechanisms, heterogeneity, and effects on disease outcomes.
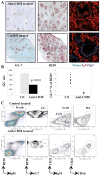
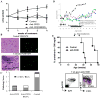
Methods: (NZB x NZW)F(1) female mice with varying degrees of disease severity were treated with an anti-mouse CD20 (anti-mCD20) antibody (IgG2a), BR3-Fc fusion protein (for BAFF blockade), or control anti-human CD20 monoclonal antibody (approximately 10 mg/kg each). Tissue samples were harvested and analyzed by flow cytometry. The development and extent of nephritis were assessed by monitoring proteinuria (using a urine dipstick) and by immunohistochemical analysis of the kidneys. Serum immunoglobulin levels were measured by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay.
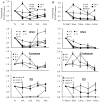
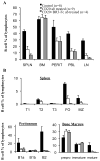
Results: After a single injection of anti-mCD20, BCD was more efficient in the peripheral blood, lymph nodes, and spleen compared with the bone marrow and peritoneum of normal mice as well as younger mice with lupus. Since depletion of the marginal zone and peritoneal B cells was incomplete and variable, particularly in older mice with established nephritis, a strategy of sequential weekly dosing was subsequently used, which improved the extent of depletion. BAFF blockade further enhanced depletion in the spleen and lymph nodes. Early BCD therapy delayed disease onset, whereas BCD therapy in mice with advanced disease reduced the progression of nephritis. These effects were long-lasting, even after B cell reconstitution occurred, and were associated with a reduction in T cell activation but no significant change in autoantibody production.
Conclusion: The lasting benefit of a short course of BCD therapy in lupus-prone mice with an intact immune system and established disease highlights the validity of this treatment approach.
Figures


Similar articles
-
CD20-Mimotope Peptide Active Immunotherapy in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus and a Reappraisal of Vaccination Strategies in Rheumatic Diseases.Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 2017 Apr;52(2):217-233. doi: 10.1007/s12016-016-8551-x. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 2017. PMID: 27216429 Review.
-
Dual B cell immunotherapy is superior to individual anti-CD20 depletion or BAFF blockade in murine models of spontaneous or accelerated lupus.Arthritis Rheumatol. 2015 Jan;67(1):215-24. doi: 10.1002/art.38907. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2015. PMID: 25303150 Free PMC article.
-
Protective and pathogenic roles for B cells during systemic autoimmunity in NZB/W F1 mice.J Immunol. 2010 May 1;184(9):4789-800. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.0902391. Epub 2010 Apr 5. J Immunol. 2010. PMID: 20368280 Free PMC article.
-
An acquired defect in IgG-dependent phagocytosis explains the impairment in antibody-mediated cellular depletion in Lupus.J Immunol. 2011 Oct 1;187(7):3888-94. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1101629. Epub 2011 Aug 26. J Immunol. 2011. PMID: 21873531 Free PMC article.
-
[Molecular targets and their regulation in systemic lupus erythematosus and lupus nephritis].Nihon Jinzo Gakkai Shi. 2012;54(5):598-602. Nihon Jinzo Gakkai Shi. 2012. PMID: 22991839 Review. Japanese. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
The pathogenesis of systemic lupus erythematosus-an update.Curr Opin Immunol. 2012 Dec;24(6):651-7. doi: 10.1016/j.coi.2012.10.004. Epub 2012 Nov 3. Curr Opin Immunol. 2012. PMID: 23131610 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Bortezomib Plus Continuous B Cell Depletion Results in Sustained Plasma Cell Depletion and Amelioration of Lupus Nephritis in NZB/W F1 Mice.PLoS One. 2015 Aug 7;10(8):e0135081. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0135081. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26252021 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanisms of tissue injury in lupus nephritis.Arthritis Res Ther. 2011;13(6):250. doi: 10.1186/ar3528. Epub 2011 Dec 21. Arthritis Res Ther. 2011. PMID: 22192660 Free PMC article. Review.
-
CD20-Mimotope Peptide Active Immunotherapy in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus and a Reappraisal of Vaccination Strategies in Rheumatic Diseases.Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 2017 Apr;52(2):217-233. doi: 10.1007/s12016-016-8551-x. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 2017. PMID: 27216429 Review.
-
Local CD34-positive capillaries decrease in mouse models of kidney disease associating with the severity of glomerular and tubulointerstitial lesions.BMC Nephrol. 2017 Sep 4;18(1):280. doi: 10.1186/s12882-017-0694-3. BMC Nephrol. 2017. PMID: 28870174 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Chan O, Shlomchik MJ. A new role for B cells in systemic autoimmunity: B cells promote spontaneous T cell activation in MRL-lpr/lpr mice. J Immunol. 1998;160(1):51–9. - PubMed
-
- Anolik JH. B cell biology and dysfunction in SLE. Bull NYU Hosp Jt Dis. 2007;65(3):182–6. - PubMed
-
- Leandro MJ, Edwards JC, Cambridge G, Ehrenstein MR, Isenberg DA. An open study of B lymphocyte depletion in systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 2002;46(10):2673–7. - PubMed
-
- Looney RJ, Anolik JH, Campbell D, Felgar RE, Young F, Arend LJ, et al. B cell depletion as a novel treatment for systemic lupus erythematosus: a phase I/II dose-escalation trial of rituximab. Arthritis Rheum. 2004;50(8):2580–9. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

