Differences in hippocampal CREB phosphorylation in trace fear conditioning of two inbred mouse strains
- PMID: 20501325
- PMCID: PMC3219426
- DOI: 10.1016/j.brainres.2010.05.048
Differences in hippocampal CREB phosphorylation in trace fear conditioning of two inbred mouse strains
Abstract
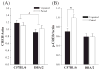
The effects of genetic background on fear trace conditioning were evaluated in relation to phosphorylated levels of cAMP response element-binding protein (CREB) in the hippocampus using two different inbred strains of mice, C57BL/6 and DBA/2. The male mice received a trace fear conditioning protocol and unpaired control groups were included to assess nonassociative effects on test performance. Both C57BL/6 and DBA/2 mice with paired training displayed higher freezing responses during testing than those with unpaired training, respectively. The C57BL/6 mice with paired training also displayed higher freezing responses to the tone-CS during testing than the DBA/2 mice with paired training. Because much evidence implicates the hippocampus as an important neural substrate for trace fear conditioning, the engagement of the hippocampus was examined after testing by measuring levels of CREB and phosphorylated CREB (pCREB). The results revealed that hippocampal CREB levels in both strains of mice were not significantly altered according to the type of training (unpaired vs. paired). However, the hippocampal pCREB levels were significantly higher in the paired training group than the unpaired control group in C57BL/6 mice, but not in DBA/2 mice. These findings indicate that hippocampal pCREB is closely tied to this form of associative conditioning only in C57BL/6 mice and that different neural substrates may support trace conditioning in C57BL/6 and DBA/2 strains.
Copyright 2010 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Learning strategy selection in the water maze and hippocampal CREB phosphorylation differ in two inbred strains of mice.Learn Mem. 2008 Mar 19;15(4):183-8. doi: 10.1101/lm.783108. Print 2008 Apr. Learn Mem. 2008. PMID: 18353993 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic background differences and nonassociative effects in mouse trace fear conditioning.Learn Mem. 2007 Sep 5;14(9):597-605. doi: 10.1101/lm.614807. Print 2007 Sep. Learn Mem. 2007. PMID: 17823243 Free PMC article.
-
DBA/2 and C57BL/6 mice differ in contextual fear but not auditory fear conditioning.Behav Neurosci. 1994 Aug;108(4):810-7. doi: 10.1037//0735-7044.108.4.810. Behav Neurosci. 1994. PMID: 7986374
-
Foreground contextual fear memory consolidation requires two independent phases of hippocampal ERK/CREB activation.Learn Mem. 2006 May-Jun;13(3):349-58. doi: 10.1101/lm.80206. Epub 2006 May 16. Learn Mem. 2006. PMID: 16705140 Free PMC article.
-
Trace fear conditioning: a role for context?Arch Ital Biol. 2004 May;142(3):251-63. Arch Ital Biol. 2004. PMID: 15260379 Review.
Cited by
-
Differences in the Flexibility of Switching Learning Strategies and CREB Phosphorylation Levels in Prefrontal Cortex, Dorsal Striatum and Hippocampus in Two Inbred Strains of Mice.Front Behav Neurosci. 2016 Sep 16;10:176. doi: 10.3389/fnbeh.2016.00176. eCollection 2016. Front Behav Neurosci. 2016. PMID: 27695401 Free PMC article.
-
Pten haploinsufficiency causes desynchronized growth of brain areas involved in sensory processing.iScience. 2022 Jan 19;25(2):103796. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2022.103796. eCollection 2022 Feb 18. iScience. 2022. PMID: 35198865 Free PMC article.
-
Developing and validating trace fear conditioning protocols in C57BL/6 mice.J Neurosci Methods. 2014 Jan 30;222:111-7. doi: 10.1016/j.jneumeth.2013.11.005. Epub 2013 Nov 20. J Neurosci Methods. 2014. PMID: 24269252 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of the performance of DBA/2 and C57BL/6 mice in transitive inference and foreground and background contextual fear conditioning.Behav Neurosci. 2012 Apr;126(2):249-57. doi: 10.1037/a0027048. Epub 2012 Feb 6. Behav Neurosci. 2012. PMID: 22309443 Free PMC article.
-
Dysregulation of Npas4 and Inhba expression and an altered excitation-inhibition balance are associated with cognitive deficits in DBA/2 mice.Learn Mem. 2022 Jan 18;29(2):55-70. doi: 10.1101/lm.053527.121. Print 2022 Feb. Learn Mem. 2022. PMID: 35042829 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ammassari-Teule M, Passino E, Restivo L, de Marsanich B. Fear conditioning in C57/BL/6 and DBA/2 mice: variability in nucleus accumbens function according to the strain predisposition to show contextual- or cue-based responding. Eur J Neurosci. 2000;12:4467–4474. - PubMed
-
- Anagnostaras SG, Gale GD, Fanselow MS. Hippocampus and contextual fear conditioning: recent controversies and advances. Hippocampus. 2001;11:8–17. - PubMed
-
- Balogh SA, Wehner JM. Inbred mouse strain differences in the establishment of long-term fear memory. Behav Brain Res. 2003;140:97–106. - PubMed
-
- Balogh SA, Radcliffe RA, Logue SF, Wehner JM. Contextual and cued fear conditioning in C57BL/6J and DBA/2J mice: context discrimination and the effects of retention interval. Behav Neurosci. 2002;116:947–957. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

