Effect of intrathecal glycine and related amino acids on the allodynia and hyperalgesic action of strychnine or bicuculline in mice
- PMID: 20498816
- PMCID: PMC2872893
- DOI: 10.4097/kjae.2010.58.1.76
Effect of intrathecal glycine and related amino acids on the allodynia and hyperalgesic action of strychnine or bicuculline in mice
Abstract
Background: The intrathecal (IT) administration of glycine or GABA(A) receptor antagonist result in a touch evoked allodynia through disinhibition in the spinal cord. Glycine is an inhibitory neurotransmitter that appears to be important in sensory processing in the spinal cord. This study was aimed to evaluate the effect of glycine-related amino acids on antagonizing the effects of IT strychnine (STR) or bicuculline (BIC) when each amino acid was administered in combination with STR or BIC.
Methods: A total of 174 male ICR mice were randomized to receive an IT injection of equimolar dose of glycine, betaine, beta-alanine, or taurine in combination with STR or BIC. Agitation in response to innocuous stimulation with a von Frey filament after IT injection was assessed. The pain index in hot-plate test were observed after IT injection. The effect of IT muscimol in combination with STR or BIC were also observed.
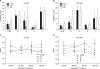
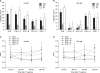
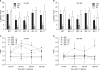
Results: The allodynia induced by STR was relieved by high dose of glycine or betaine. But, allodynia induced by BIC was not relieved by any amino acid. Whereas the STR-induced thermal hyperalgesia was only relieved by high dose of taurine at 120 min after IT injection, the BIC-induced one was relieved by not only high dose of taurine at 120 min but also low dose of glycine or betaine at 60 min after IT injection. The BIC-induced allodynia and thermal hyperalgesia was relieved by IT muscimol.
Conclusions: This study suggests that IT glycine and related amino acids can reduce the allodynic and hyperalgesic action of STR or BIC in mice.
Keywords: Allodynia; Bicuculline; Glycine; Neuropathic pain model; Strychnine; Thermal hyperalgesia.
Figures
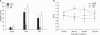
Similar articles
-
[Concurrent characterization of spinal amino acid release and touch-evoked allodynia produced by spinal glycine or GABAA receptor antagonists].Masui. 1996 Apr;45(4):439-44. Masui. 1996. PMID: 8725598 Japanese.
-
Coadministration of intrathecal strychnine and bicuculline effects synergistic allodynia in the rat: an isobolographic analysis.J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2001 Mar;296(3):756-61. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2001. PMID: 11181903
-
Intracisternal or intrathecal glycine, taurine, or muscimol inhibit bicuculline-induced allodynia and thermal hyperalgesia in mice.Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2010 Aug;31(8):907-14. doi: 10.1038/aps.2010.82. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2010. PMID: 20686515 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of spinal amino acid release and touch-evoked allodynia produced by spinal glycine or GABA(A) receptor antagonist.Neuroscience. 2000;95(3):781-6. doi: 10.1016/s0306-4522(99)00461-3. Neuroscience. 2000. PMID: 10670445
-
Implications of intrathecal pertussis toxin animal model on the cellular mechanisms of neuropathic pain syndrome.Acta Anaesthesiol Sin. 2003 Dec;41(4):187-96. Acta Anaesthesiol Sin. 2003. PMID: 14768516 Review.
Cited by
-
Taurine enhances antinociception produced by a COX-2 inhibitor in an inflammatory pain model.Inflammation. 2013 Jun;36(3):658-64. doi: 10.1007/s10753-012-9589-4. Inflammation. 2013. PMID: 23307337
-
Modulation of Glycine Receptor-Mediated Pain Signaling in vitro and in vivo by Glucose.Front Mol Neurosci. 2019 Nov 22;12:280. doi: 10.3389/fnmol.2019.00280. eCollection 2019. Front Mol Neurosci. 2019. PMID: 31824259 Free PMC article.
-
Pharmacology of intracisternal or intrathecal glycine, muscimol, and baclofen in strychnine-induced thermal hyperalgesia of mice.J Korean Med Sci. 2011 Oct;26(10):1371-7. doi: 10.3346/jkms.2011.26.10.1371. Epub 2011 Oct 1. J Korean Med Sci. 2011. PMID: 22022192 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of Glycine Re-Uptake: A Potential Approach for Treating Pain by Augmenting Glycine-Mediated Spinal Neurotransmission and Blunting Central Nociceptive Signaling.Biomolecules. 2021 Jun 10;11(6):864. doi: 10.3390/biom11060864. Biomolecules. 2021. PMID: 34200954 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Onaka M, Minami T, Nishihara I, Ito S. Involvement of glutamate receptors in strychnine- and bicuculline-induced allodynia in conscious mice. Anesthesiology. 1996;84:1215–1222. - PubMed
-
- Chen Y, Dai TJ, Zeng YM. Strychnine-sensitive glycine receptors mediate analgesia induced by emulsified inhalation anaethetics in thermal nociception but not in chemical nociception. Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol. 2007;100:165–169. - PubMed
-
- Loomis CW, Khandwala H, Osmond G, Hefferan MP. Co-administration of intrathecal strychnine and bicuculline effects synergistic allodynia in the rat: an isobolographic analysis. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2001;296:756–761. - PubMed
-
- Ishikawa T, Marsala M, Sakabe T, Yaksh TL. Characterization of spinal amino acid release and touch-evoked allodynia produced by spinal glycine or GABAA receptor antagonist. Neuroscience. 2000;95:781–786. - PubMed
-
- Khandwala H, Loomis CW. Milacemide, a glycine pro-drug, inhibits strychnine-allodynia without affecting normal nociception in the rat. Pain. 1998;77:87–95. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

