The LiMAx test: a new liver function test for predicting postoperative outcome in liver surgery
- PMID: 20495659
- PMCID: PMC2826673
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1477-2574.2009.00151.x
The LiMAx test: a new liver function test for predicting postoperative outcome in liver surgery
Abstract
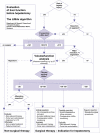
Background: Liver failure has remained a major cause of mortality after hepatectomy, but it is difficult to predict preoperatively. This study describes the introduction into clinical practice of the new LiMAx test and provides an algorithm for its use in the clinical management of hepatic tumours.
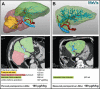
Methods: Patients with hepatic tumours and indications for hepatectomy were investigated perioperatively with the LiMAx test. In one patient, analysis of liver volume was carried out with preoperative three-dimensional virtual resection.
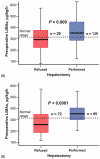
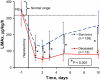
Results: A total of 329 patients with hepatic tumours were evaluated for hepatectomy. Blinded preoperative LiMAx values were significantly higher before resection (n= 139; mean 351 microg/kg/h, range 285-451 microg/kg/h) than before refusal (n= 29; mean 299 microg/kg/h, range 223-376 microg/kg/h; P= 0.009). In-hospital mortality rates were 38.1% (8/21 patients), 10.5% (2/19 patients) and 1.0% (1/99 patients) for postoperative LiMAx of <80 microg/kg/h, 80-100 microg/kg/h and >100 microg/kg/h, respectively (P < 0.0001). A decision tree was developed to avoid critical values and its prospective preoperative application revealed a reduction in mortality from 9.4% to 3.4% (P= 0.019).
Discussion: The LiMAx test can validly determine liver function capacity and is feasible in every clinical situation. Combination with virtual resection could enable the calculation of residual liver function. The LiMAx decision tree algorithm for hepatectomy might significantly improve preoperative evaluation and postoperative outcome in liver surgery.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Prediction of postoperative outcome after hepatectomy with a new bedside test for maximal liver function capacity.Ann Surg. 2009 Jul;250(1):119-25. doi: 10.1097/SLA.0b013e3181ad85b5. Ann Surg. 2009. PMID: 19561474
-
Reductions in post-hepatectomy liver failure and related mortality after implementation of the LiMAx algorithm in preoperative work-up: a single-centre analysis of 1170 hepatectomies of one or more segments.HPB (Oxford). 2015 Jul;17(7):651-8. doi: 10.1111/hpb.12424. HPB (Oxford). 2015. PMID: 26058324 Free PMC article.
-
[Enhancing safety in liver surgery using a new diagnostic tool for evaluation of actual liver function capacity - The LiMAx test].Dtsch Med Wochenschr. 2014 Feb;139(8):387-91. doi: 10.1055/s-0033-1360061. Epub 2014 Feb 11. Dtsch Med Wochenschr. 2014. PMID: 24519118 Review. German. No abstract available.
-
Safety validation of decision trees for hepatocellular carcinoma.World J Gastroenterol. 2015 Aug 21;21(31):9394-402. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i31.9394. World J Gastroenterol. 2015. PMID: 26309366 Free PMC article.
-
New perspectives in the assessment of future remnant liver.Dig Surg. 2014;31(4-5):255-68. doi: 10.1159/000364836. Epub 2014 Oct 14. Dig Surg. 2014. PMID: 25322678 Review.
Cited by
-
Regeneration of Liver Function Capacity After Partial Liver Resection is Impaired in Case of Postoperative Bile Leakage.World J Surg. 2016 Sep;40(9):2221-8. doi: 10.1007/s00268-016-3524-z. World J Surg. 2016. PMID: 27164934
-
[Intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma - current perspectives and treatment algorithm].Chirurg. 2018 Nov;89(11):858-864. doi: 10.1007/s00104-018-0718-y. Chirurg. 2018. PMID: 30182267 Review. German.
-
Hyperspectral Imaging (HSI) in anatomic left liver resection.Int J Surg Case Rep. 2019;62:108-111. doi: 10.1016/j.ijscr.2019.08.025. Epub 2019 Aug 31. Int J Surg Case Rep. 2019. PMID: 31493663 Free PMC article.
-
Noninvasive Evaluation of Liver Function in Morbidly Obese Patients.Gastroenterol Res Pract. 2019 Feb 3;2019:4307462. doi: 10.1155/2019/4307462. eCollection 2019. Gastroenterol Res Pract. 2019. PMID: 30863439 Free PMC article.
-
[Preoperative imaging/operation planning for liver surgery].Chirurg. 2015 Dec;86(12):1167-79; quiz 1180-1. doi: 10.1007/s00104-015-0107-8. Chirurg. 2015. PMID: 26606924 Review. German.
References
-
- Clavien PA, Petrowsky H, DeOliveira ML, Graf R. Strategies for safer liver surgery and partial liver transplantation. N Engl J Med. 2007;356:1545–1559. - PubMed
-
- Schneider PD. Preoperative assessment of liver function. Surg Clin North Am. 2004;84:355–373. - PubMed
-
- Mullin EJ, Metcalfe MS, Maddern GJ. How much liver resection is too much? Am J Surg. 2005;190:87–97. - PubMed
-
- van den Broek MA, Olde Damink SW, Dejong CH, Lang H, Malago M, Jalan R, et al. Liver failure after partial hepatic resection: definition, pathophysiology, risk factors and treatment. Liver Int. 2008;28:767–780. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

