Pluronic-modified superoxide dismutase 1 attenuates angiotensin II-induced increase in intracellular superoxide in neurons
- PMID: 20493251
- PMCID: PMC2998907
- DOI: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2010.04.039
Pluronic-modified superoxide dismutase 1 attenuates angiotensin II-induced increase in intracellular superoxide in neurons
Abstract
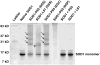
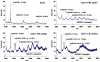
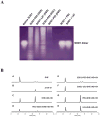
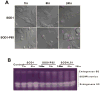
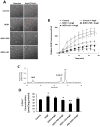
Overexpressing superoxide dismutase 1 (SOD1; also called Cu/ZnSOD), an intracellular superoxide (O(2)(*-))-scavenging enzyme, in central neurons inhibits angiotensin II (AngII) intraneuronal signaling and normalizes cardiovascular dysfunction in diseases associated with enhanced AngII signaling in the brain, including hypertension and heart failure. However, the blood-brain barrier and neuronal cell membranes impose a tremendous impediment for the delivery of SOD1 to central neurons, which hinders the potential therapeutic impact of SOD1 treatment on these diseases. To address this, we developed conjugates of SOD1 with poly(ethylene oxide)-poly(propylene oxide)-poly(ethylene oxide) block copolymer (Pluronic) (SOD1-P85 and SOD1-L81), which retained significant SOD1 enzymatic activity. The modified SOD1 effectively scavenged xanthine oxidase/hypoxanthine-derived O(2)(*-), as determined by HPLC and the measurement of 2-hydroxyethidium. Using catecholaminergic neurons, we observed an increase in neuronal uptake of SOD1-Pluronic after 1, 6, or 24h, compared to neurons treated with pure SOD1 or PEG-SOD1. Importantly, without inducing neuronal toxicity, SOD1-Pluronic conjugates significantly inhibited AngII-induced increases in intraneuronal O(2)(*-) levels. These data indicate that SOD1-Pluronic conjugates penetrate neuronal cell membranes, which results in elevated intracellular levels of functional SOD1. Pluronic conjugation may be a new delivery system for SOD1 into central neurons and therapeutically beneficial for AngII-related cardiovascular diseases.
Published by Elsevier Inc.
Figures
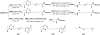
Similar articles
-
Conjugates of superoxide dismutase 1 with amphiphilic poly(2-oxazoline) block copolymers for enhanced brain delivery: synthesis, characterization and evaluation in vitro and in vivo.Mol Pharm. 2013 Jan 7;10(1):360-77. doi: 10.1021/mp300496x. Epub 2012 Dec 17. Mol Pharm. 2013. PMID: 23163230 Free PMC article.
-
Over-expressed copper/zinc superoxide dismutase localizes to mitochondria in neurons inhibiting the angiotensin II-mediated increase in mitochondrial superoxide.Redox Biol. 2013 Nov 18;2:8-14. doi: 10.1016/j.redox.2013.11.002. eCollection 2013. Redox Biol. 2013. PMID: 24363997 Free PMC article.
-
The attenuation of central angiotensin II-dependent pressor response and intra-neuronal signaling by intracarotid injection of nanoformulated copper/zinc superoxide dismutase.Biomaterials. 2010 Jul;31(19):5218-26. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2010.03.026. Epub 2010 Apr 7. Biomaterials. 2010. PMID: 20378166 Free PMC article.
-
Mitochondrial mechanisms of neuronal rescue by F-68, a hydrophilic Pluronic block co-polymer, following acute substrate deprivation.Neurochem Int. 2017 Oct;109:126-140. doi: 10.1016/j.neuint.2017.04.007. Epub 2017 Apr 19. Neurochem Int. 2017. PMID: 28433663 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pluronic block copolymers for gene delivery.Adv Genet. 2005;53:231-61. Adv Genet. 2005. PMID: 16240996 Review.
Cited by
-
HPLC-based monitoring of products formed from hydroethidine-based fluorogenic probes--the ultimate approach for intra- and extracellular superoxide detection.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2014 Feb;1840(2):739-44. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagen.2013.05.008. Epub 2013 May 10. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2014. PMID: 23668959 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nanoformulated SOD1 ameliorates the combined NASH and alcohol-associated liver disease partly via regulating CYP2E1 expression in adipose tissue and liver.Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2020 Mar 1;318(3):G428-G438. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.00217.2019. Epub 2020 Jan 13. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2020. PMID: 31928222 Free PMC article.
-
Brain delivery of proteins via their fatty acid and block copolymer modifications.J Drug Target. 2013 Dec;21(10):940-55. doi: 10.3109/1061186X.2013.847098. J Drug Target. 2013. PMID: 24160902 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Endothelial targeting of antibody-decorated polymeric filomicelles.ACS Nano. 2011 Sep 27;5(9):6991-9. doi: 10.1021/nn2015453. Epub 2011 Aug 23. ACS Nano. 2011. PMID: 21838300 Free PMC article.
-
Catalase and superoxide dismutase conjugated with platelet-endothelial cell adhesion molecule antibody distinctly alleviate abnormal endothelial permeability caused by exogenous reactive oxygen species and vascular endothelial growth factor.J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2011 Jul;338(1):82-91. doi: 10.1124/jpet.111.180620. Epub 2011 Apr 7. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2011. PMID: 21474567 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Inagi R. Oxidative stress in cardiovascular disease: a new avenue toward future therapeutic approaches. Recent patents on cardiovascular drug discovery. 2006;1:151–159. - PubMed
-
- Muzykantov VR. Targeting of superoxide dismutase and catalase to vascular endothelium. J Control Release. 2001;71:1–21. - PubMed
-
- Hirooka Y. Role of reactive oxygen species in brainstem in neural mechanisms of hypertension. Auton Neurosci. 2008;142:20–24. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

