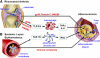
Toll-like receptor signaling: a potential link among rheumatoid arthritis, systemic lupus, and atherosclerosis
- PMID: 20484668
- PMCID: PMC2908942
- DOI: 10.1189/jlb.0310126
Toll-like receptor signaling: a potential link among rheumatoid arthritis, systemic lupus, and atherosclerosis
Figures
Similar articles
-
Atherosclerosis in rheumatoid arthritis and systemic lupus erythematosus.Curr Opin Lipidol. 2008 Aug;19(4):338-43. doi: 10.1097/MOL.0b013e328304b65f. Curr Opin Lipidol. 2008. PMID: 18607179 Review.
-
Altered lipoprotein metabolism in chronic inflammatory states: proinflammatory high-density lipoprotein and accelerated atherosclerosis in systemic lupus erythematosus and rheumatoid arthritis.Arthritis Res Ther. 2008;10(4):213. doi: 10.1186/ar2471. Epub 2008 Aug 29. Arthritis Res Ther. 2008. PMID: 18828865 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Toll-like receptor--a potent driving force behind rheumatoid arthritis.J Clin Exp Hematop. 2011;51(2):77-92. doi: 10.3960/jslrt.51.77. J Clin Exp Hematop. 2011. PMID: 22104306 Review.
-
Roles of B Cell-Intrinsic TLR Signals in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus.Int J Mol Sci. 2015 Jun 9;16(6):13084-105. doi: 10.3390/ijms160613084. Int J Mol Sci. 2015. PMID: 26068236 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[Connective tissue metabolism in systemic lupus erythematosus, systemic scleroderma and rheumatoid arthritis].Revmatologiia (Mosk). 1988 Apr-Jun;(2):72-8. Revmatologiia (Mosk). 1988. PMID: 3051281 Review. Russian. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
The inflammatory role of phagocyte apoptotic pathways in rheumatic diseases.Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2016 Aug 23;12(9):543-58. doi: 10.1038/nrrheum.2016.132. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2016. PMID: 27549026 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Immune Effects of Macrophages in Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Bibliometric Analysis From 2000 to 2021.Front Immunol. 2022 Sep 12;13:903771. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.903771. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 36172378 Free PMC article.
-
The deubiquitinase A20 mediates feedback inhibition of interleukin-17 receptor signaling.Sci Signal. 2013 Jun 4;6(278):ra44. doi: 10.1126/scisignal.2003699. Sci Signal. 2013. PMID: 23737552 Free PMC article.
-
Distinct NF-κB and MAPK Activation Thresholds Uncouple Steady-State Microbe Sensing from Anti-pathogen Inflammatory Responses.Cell Syst. 2016 Jun 22;2(6):378-90. doi: 10.1016/j.cels.2016.04.016. Epub 2016 May 26. Cell Syst. 2016. PMID: 27237739 Free PMC article.
-
Activated TLR signaling in atherosclerosis among women with lower Framingham risk score: the multi-ethnic study of atherosclerosis.PLoS One. 2011;6(6):e21067. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0021067. Epub 2011 Jun 16. PLoS One. 2011. PMID: 21698167 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Haque S, Mirjafari H, Bruce I N. Atherosclerosis in rheumatoid arthritis and systemic lupus erythematosus. Curr Opin Lipidol. 2008;19:338–343. - PubMed
-
- Akira S, Uematsu S, Takeuchi O. Pathogen recognition and innate immunity. Cell. 2006;124:783–801. - PubMed
-
- Akira S, Takeda K. Toll-like receptor signaling. Nat Rev Immunol. 2004;4:499–511. - PubMed
-
- de Vos A F, Pater J M, van den Pangaart P S, de Kruif M D, van 't Veer C, van der Poll T. In vivo lipopolysaccharide exposure of human blood leukocytes induces cross-tolerance to multiple TLR ligands. J Immunol. 2009;183:533–542. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

