Morphological and proteomic analysis of early stage of osteoblast differentiation in osteoblastic progenitor cells
- PMID: 20483354
- PMCID: PMC4580249
- DOI: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2010.05.011
Morphological and proteomic analysis of early stage of osteoblast differentiation in osteoblastic progenitor cells
Abstract
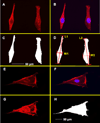
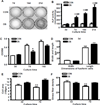
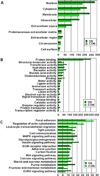
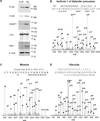
Bone remodeling relies on a dynamic balance between bone formation and resorption, mediated by osteoblasts and osteoclasts, respectively. Under certain stimuli, osteoprogenitor cells may differentiate into premature osteoblasts and further into mature osteoblasts. This process is marked by increased alkaline phosphatase (ALP) activity and mineralized nodule formation. In this study, we induced osteoblast differentiation in mouse osteoprogenitor MC3T3-E1 cells and divided the process into three stages. In the first stage (day 3), the MC3T3-E1 cell under osteoblast differentiation did not express ALP or deposit a mineralized nodule. In the second stage, the MC3T3-E1 cell expressed ALP but did not form a mineralized nodule. In the third stage, the MC3T3-E1 cell had ALP activity and formed mineralized nodules. In the present study, we focused on morphological and proteomic changes of MC3T3-E1 cells in the early stage of osteoblast differentiation - a period when premature osteoblasts transform into mature osteoblasts. We found that mean cell area and mean stress fiber density were increased in this stage due to enhanced cell spreading and decreased cell proliferation. We further analyzed the proteins in the signaling pathway of regulation of the cytoskeleton using a proteomic approach and found upregulation of IQGAP1, gelsolin, moesin, radixin, and Cfl1. After analyzing the focal adhesion signaling pathway, we found the upregulation of FLNA, LAMA1, LAMA5, COL1A1, COL3A1, COL4A6, and COL5A2 as well as the downregulation of COL4A1, COL4A2, and COL4A4. In conclusion, the signaling pathway of regulation of the cytoskeleton and focal adhesion play critical roles in regulating cell spreading and actin skeleton formation in the early stage of osteoblast differentiation.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Integrin mediated adhesion of osteoblasts to connective tissue growth factor (CTGF/CCN2) induces cytoskeleton reorganization and cell differentiation.PLoS One. 2015 Feb 25;10(2):e0115325. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0115325. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 25714841 Free PMC article.
-
Role of serum in the developmental expression of alkaline phosphatase in MC3T3-E1 osteoblasts.J Cell Physiol. 1994 Mar;158(3):467-75. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041580311. J Cell Physiol. 1994. PMID: 8126070
-
Akt activation is required for TGF-β1-induced osteoblast differentiation of MC3T3-E1 pre-osteoblasts.PLoS One. 2014 Dec 3;9(12):e112566. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0112566. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 25470129 Free PMC article.
-
Sonic hedgehog regulates osteoblast function by focal adhesion kinase signaling in the process of fracture healing.PLoS One. 2013 Oct 4;8(10):e76785. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0076785. eCollection 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 24124594 Free PMC article.
-
Nanotopographical control of human osteoprogenitor differentiation.Curr Stem Cell Res Ther. 2007 May;2(2):129-38. doi: 10.2174/157488807780599220. Curr Stem Cell Res Ther. 2007. PMID: 18220898 Review.
Cited by
-
Mesh Ti6Al4V Material Manufactured by Selective Laser Melting (SLM) as a Promising Intervertebral Fusion Cage.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Apr 3;23(7):3985. doi: 10.3390/ijms23073985. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35409345 Free PMC article.
-
Human Mesenchymal Stem Cell Morphology and Migration on Microtextured Titanium.Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2016 May 10;4:41. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2016.00041. eCollection 2016. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2016. PMID: 27243001 Free PMC article.
-
Use of Polyphenol Tannic Acid to Functionalize Titanium with Strontium for Enhancement of Osteoblast Differentiation and Reduction of Osteoclast Activity.Polymers (Basel). 2019 Jul 29;11(8):1256. doi: 10.3390/polym11081256. Polymers (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31362449 Free PMC article.
-
Enhancing osteogenic differentiation in adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells with Near Infra-Red and Green Photobiomodulation.Regen Ther. 2023 Nov 10;24:602-616. doi: 10.1016/j.reth.2023.11.003. eCollection 2023 Dec. Regen Ther. 2023. PMID: 38034860 Free PMC article.
-
The secreted protein DEL-1 activates a β3 integrin-FAK-ERK1/2-RUNX2 pathway and promotes osteogenic differentiation and bone regeneration.J Biol Chem. 2020 May 22;295(21):7261-7273. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA120.013024. Epub 2020 Apr 12. J Biol Chem. 2020. PMID: 32280065 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Komori T. Regulation of osteoblast differentiation by transcription factors. J Cell Biochem. 2006;99:1233–1239. - PubMed
-
- Day TF, Guo X, Garrett-Beal L, Yang Y. Wnt/beta-catenin signaling in mesenchymal progenitors controls osteoblast and chondrocyte differentiation during vertebrate skeletogenesis. Dev Cell. 2005;8:739–750. - PubMed
-
- Quarles LD, Yohay DA, Lever LW, Caton R, Wenstrup RJ. Distinct proliferative and differentiated stages of murine MC3T3-E1 cells in culture: an in vitro model of osteoblast development. J Bone Miner Res. 1992;7:683–692. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

