The anti-aging gene KLOTHO is a novel target for epigenetic silencing in human cervical carcinoma
- PMID: 20482749
- PMCID: PMC2885346
- DOI: 10.1186/1476-4598-9-109
The anti-aging gene KLOTHO is a novel target for epigenetic silencing in human cervical carcinoma
Abstract
Background: Klotho was originally characterized as an anti-aging gene that predisposed Klotho-deficient mice to a premature aging-like syndrome. Recently, KLOTHO was reported to function as a secreted Wnt antagonist and as a tumor suppressor. Epigenetic gene silencing of secreted Wnt antagonists is considered a common event in a wide range of human malignancies. Abnormal activation of the canonical Wnt pathway due to epigenetic deregulation of Wnt antagonists is thought to play a crucial role in cervical tumorigenesis. In this study, we examined epigenetic silencing of KLOTHO in human cervical carcinoma.
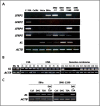
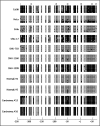
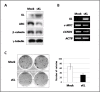
Results: Loss of KLOTHO mRNA was observed in several cervical cancer cell lines and in invasive carcinoma samples, but not during the early, preinvasive phase of primary cervical tumorigenesis. KLOTHO mRNA was restored after treatment with either the DNA demethylating agent 2'-deoxy-5-azacytidine or histone deacetylase inhibitor trichostatin A. Methylation-specific PCR and bisulfite genomic sequencing analysis of the promoter region of KLOTHO revealed CpG hypermethylation in non-KLOTHO-expressing cervical cancer cell lines and in 41% (9/22) of invasive carcinoma cases. Histone deacetylation was also found to be the major epigenetic silencing mechanism for KLOTHO in the SiHa cell line. Ectopic expression of the secreted form of KLOTHO restored anti-Wnt signaling and anti-clonogenic activity in the CaSki cell line including decreased active beta-catenin levels, suppression of T-cell factor/beta-catenin target genes, such as c-MYC and CCND1, and inhibition of colony growth.
Conclusions: Epigenetic silencing of KLOTHO may occur during the late phase of cervical tumorigenesis, and consequent functional loss of KLOTHO as the secreted Wnt antagonist may contribute to aberrant activation of the canonical Wnt pathway in cervical carcinoma.
Figures


Similar articles
-
WIF1 is a frequent target for epigenetic silencing in squamous cell carcinoma of the cervix.Carcinogenesis. 2011 Nov;32(11):1625-33. doi: 10.1093/carcin/bgr193. Epub 2011 Aug 26. Carcinogenesis. 2011. PMID: 21873353 Free PMC article.
-
Epigenetic silencing of the tumor suppressor klotho in human breast cancer.Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2012 Jun;133(2):649-57. doi: 10.1007/s10549-011-1824-4. Epub 2011 Oct 22. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2012. PMID: 22042362
-
Frequent epigenetic inactivation of Wnt inhibitory factor-1 in human gastrointestinal cancers.Oncogene. 2005 Nov 24;24(53):7946-52. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1208910. Oncogene. 2005. PMID: 16007117
-
Klotho: a tumor suppressor and modulator of the Wnt/β-catenin pathway in human hepatocellular carcinoma.Lab Invest. 2016 Feb;96(2):197-205. doi: 10.1038/labinvest.2015.86. Epub 2015 Aug 3. Lab Invest. 2016. PMID: 26237271 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Role of Alpha-Klotho as a Universal Tumor Suppressor.Vitam Horm. 2016;101:197-214. doi: 10.1016/bs.vh.2016.03.001. Epub 2016 Apr 6. Vitam Horm. 2016. PMID: 27125743 Review.
Cited by
-
Suppression of Klotho expression by protein-bound uremic toxins is associated with increased DNA methyltransferase expression and DNA hypermethylation.Kidney Int. 2012 Apr;81(7):640-50. doi: 10.1038/ki.2011.445. Epub 2012 Jan 11. Kidney Int. 2012. PMID: 22237753 Free PMC article.
-
Klotho gene silencing promotes pathology in the mdx mouse model of Duchenne muscular dystrophy.Hum Mol Genet. 2016 Jun 15;25(12):2465-2482. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddw111. Epub 2016 May 6. Hum Mol Genet. 2016. PMID: 27154199 Free PMC article.
-
Vitamin D, reactive oxygen species and calcium signalling in ageing and disease.Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2016 Aug 5;371(1700):20150434. doi: 10.1098/rstb.2015.0434. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2016. PMID: 27377727 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Klotho, an anti-senescence related gene, is frequently inactivated through promoter hypermethylation in colorectal cancer.Tumour Biol. 2011 Aug;32(4):729-35. doi: 10.1007/s13277-011-0174-5. Epub 2011 Apr 27. Tumour Biol. 2011. PMID: 21523445
-
Identification of novel small molecules that elevate Klotho expression.Biochem J. 2012 Jan 1;441(1):453-61. doi: 10.1042/BJ20101909. Biochem J. 2012. PMID: 21939436 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

