Mechanisms, regulation and consequences of protein SUMOylation
- PMID: 20462400
- PMCID: PMC3310159
- DOI: 10.1042/BJ20100158
Mechanisms, regulation and consequences of protein SUMOylation
Abstract
The post-translational modification SUMOylation is a major regulator of protein function that plays an important role in a wide range of cellular processes. SUMOylation involves the covalent attachment of a member of the SUMO (small ubiquitin-like modifier) family of proteins to lysine residues in specific target proteins via an enzymatic cascade analogous to, but distinct from, the ubiquitination pathway. There are four SUMO paralogues and an increasing number of proteins are being identified as SUMO substrates. However, in many cases little is known about how SUMOylation of these targets is regulated. Compared with the ubiquitination pathway, relatively few components of the conjugation machinery have been described and the processes that specify individual SUMO paralogue conjugation to defined substrate proteins are an active area of research. In the present review, we briefly describe the SUMOylation pathway and present an overview of the recent findings that are beginning to identify some of the mechanisms that regulate protein SUMOylation.
Figures
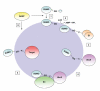
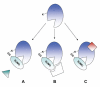
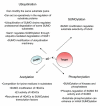
Similar articles
-
Regulation of the sumoylation system in gene expression.Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2008 Jun;20(3):288-93. doi: 10.1016/j.ceb.2008.03.014. Epub 2008 May 28. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2008. PMID: 18468876 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Molecular mechanisms in SUMO conjugation.Biochem Soc Trans. 2020 Feb 28;48(1):123-135. doi: 10.1042/BST20190357. Biochem Soc Trans. 2020. PMID: 31872228 Review.
-
E2-mediated small ubiquitin-like modifier (SUMO) modification of thymine DNA glycosylase is efficient but not selective for the enzyme-product complex.J Biol Chem. 2014 May 30;289(22):15810-9. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M114.572081. Epub 2014 Apr 21. J Biol Chem. 2014. PMID: 24753249 Free PMC article.
-
The post-translational modification, SUMOylation, and cancer (Review).Int J Oncol. 2018 Apr;52(4):1081-1094. doi: 10.3892/ijo.2018.4280. Epub 2018 Feb 22. Int J Oncol. 2018. PMID: 29484374 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Current Status of SUMOylation Inhibitors.Curr Med Chem. 2021;28(20):3892-3912. doi: 10.2174/0929867327666200810135039. Curr Med Chem. 2021. PMID: 32778019 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Stepwise phosphorylation and SUMOylation of PIDD1 drive PIDDosome assembly in response to DNA repair failure.Nat Commun. 2024 Oct 24;15(1):9195. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-53412-0. Nat Commun. 2024. PMID: 39448602 Free PMC article.
-
SUMOylation is developmentally regulated and required for cell pairing during conjugation in Tetrahymena thermophila.Eukaryot Cell. 2015 Feb;14(2):170-81. doi: 10.1128/EC.00252-14. Epub 2014 Dec 19. Eukaryot Cell. 2015. PMID: 25527524 Free PMC article.
-
Modulation of Tau Pathology in Alzheimer's Disease by Dietary Bioactive Compounds.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jan 9;25(2):831. doi: 10.3390/ijms25020831. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38255905 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Phosphorylation-dependent SUMOylation of the transcription factor NF-E2.PLoS One. 2012;7(9):e44608. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0044608. Epub 2012 Sep 10. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22970264 Free PMC article.
-
SUMOylation and DeSUMOylation: Tug of War of Pain Signaling.Mol Neurobiol. 2024 Sep 14. doi: 10.1007/s12035-024-04478-w. Online ahead of print. Mol Neurobiol. 2024. PMID: 39276308 Review.
References
-
- Tanaka K, Nishide J, Okazaki K, Kato H, Niwa O, Nakagawa T, Matsuda H, Kawamukai M, Murakami Y. Characterization of a fission yeast SUMO-1 homologue, pmt3p, required for multiple nuclear events, including the control of telomere length and chromosome segregation. Mol. Cell. Biol. 1999;19:8660–8672. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Giaever G, Chu AM, Ni L, Connelly C, Riles L, Veronneau S, Dow S, Lucau-Danila A, Anderson K, Andre B, et al. Functional profiling of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae genome. Nature. 2002;418:387–391. - PubMed
-
- Shen Z, Pardington-Purtymun PE, Comeaux JC, Moyzis RK, Chen DJ. UBL1, a human ubiquitin-like protein associating with human RAD51/RAD52 proteins. Genomics. 1996;36:271–279. - PubMed
-
- Boddy MN, Howe K, Etkin LD, Solomon E, Freemont PS. PIC 1, a novel ubiquitin-like protein which interacts with the PML component of a multiprotein complex that is disrupted in acute promyelocytic leukaemia. Oncogene. 1996;13:971–982. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

