Iron-sulfur (Fe-S) cluster assembly: the SufBCD complex is a new type of Fe-S scaffold with a flavin redox cofactor
- PMID: 20460376
- PMCID: PMC2906325
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M110.127449
Iron-sulfur (Fe-S) cluster assembly: the SufBCD complex is a new type of Fe-S scaffold with a flavin redox cofactor
Abstract
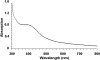
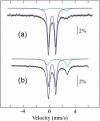
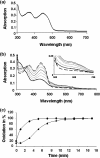
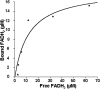
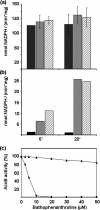
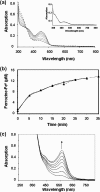
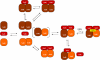
Assembly of iron-sulfur (Fe-S) clusters and maturation of Fe-S proteins in vivo require complex machineries. In Escherichia coli, under adverse stress conditions, this process is achieved by the SUF system that contains six proteins as follows: SufA, SufB, SufC, SufD, SufS, and SufE. Here, we provide a detailed characterization of the SufBCD complex whose function was so far unknown. Using biochemical and spectroscopic analyses, we demonstrate the following: (i) the complex as isolated exists mainly in a 1:2:1 (B:C:D) stoichiometry; (ii) the complex can assemble a [4Fe-4S] cluster in vitro and transfer it to target proteins; and (iii) the complex binds one molecule of flavin adenine nucleotide per SufBC(2)D complex, only in its reduced form (FADH(2)), which has the ability to reduce ferric iron. These results suggest that the SufBC(2)D complex functions as a novel type of scaffold protein that assembles an Fe-S cluster through the mobilization of sulfur from the SufSE cysteine desulfurase and the FADH(2)-dependent reductive mobilization of iron.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Interplay between oxygen and Fe-S cluster biogenesis: insights from the Suf pathway.Biochemistry. 2014 Sep 23;53(37):5834-47. doi: 10.1021/bi500488r. Epub 2014 Sep 11. Biochemistry. 2014. PMID: 25153801 Free PMC article. Review.
-
SufD and SufC ATPase activity are required for iron acquisition during in vivo Fe-S cluster formation on SufB.Biochemistry. 2010 Nov 2;49(43):9402-12. doi: 10.1021/bi1011546. Biochemistry. 2010. PMID: 20857974 Free PMC article.
-
The SufBCD protein complex is the scaffold for iron-sulfur cluster assembly in Thermus thermophiles HB8.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2014 Jan 10;443(2):376-81. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2013.11.131. Epub 2013 Dec 11. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2014. PMID: 24333431
-
The SufBCD Fe-S scaffold complex interacts with SufA for Fe-S cluster transfer.Biochemistry. 2009 Nov 10;48(44):10644-53. doi: 10.1021/bi901518y. Biochemistry. 2009. PMID: 19810706 Free PMC article.
-
The SUF system: an ABC ATPase-dependent protein complex with a role in Fe-S cluster biogenesis.Res Microbiol. 2019 Nov-Dec;170(8):426-434. doi: 10.1016/j.resmic.2019.08.001. Epub 2019 Aug 14. Res Microbiol. 2019. PMID: 31419582 Review.
Cited by
-
A new role for heme, facilitating release of iron from the bacterioferritin iron biomineral.J Biol Chem. 2011 Feb 4;286(5):3473-83. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.175034. Epub 2010 Nov 23. J Biol Chem. 2011. PMID: 21106523 Free PMC article.
-
Peptide Selenocysteine Substitutions Reveal Direct Substrate-Enzyme Interactions at Auxiliary Clusters in Radical S-Adenosyl-l-methionine Maturases.J Am Chem Soc. 2023 May 10;145(18):10167-10177. doi: 10.1021/jacs.3c00831. Epub 2023 Apr 27. J Am Chem Soc. 2023. PMID: 37104670 Free PMC article.
-
Escherichia coli SufE sulfur transfer protein modulates the SufS cysteine desulfurase through allosteric conformational dynamics.J Biol Chem. 2013 Dec 20;288(51):36189-200. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M113.525709. Epub 2013 Nov 6. J Biol Chem. 2013. PMID: 24196966 Free PMC article.
-
Interplay between oxygen and Fe-S cluster biogenesis: insights from the Suf pathway.Biochemistry. 2014 Sep 23;53(37):5834-47. doi: 10.1021/bi500488r. Epub 2014 Sep 11. Biochemistry. 2014. PMID: 25153801 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Fe-S cluster assembly in the supergroup Excavata.J Biol Inorg Chem. 2018 Jun;23(4):521-541. doi: 10.1007/s00775-018-1556-6. Epub 2018 Apr 5. J Biol Inorg Chem. 2018. PMID: 29623424 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Johnson D. C., Dean D. R., Smith A. D., Johnson M. K. (2005) Annu. Rev. Biochem. 74, 247–281 - PubMed
-
- Fontecave M., Ollagnier-de-Choudens S. (2008) Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 474, 226–237 - PubMed
-
- Tokumoto U., Kitamura S., Fukuyama K., Takahashi Y. (2004) J. Biochem. 136, 199–209 - PubMed
-
- Lill R., Mühlenhoff U. (2008) Annu. Rev. Biochem. 77, 669–700 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

