Pak1 regulates branching morphogenesis in 3D MDCK cell culture by a PIX and beta1-integrin-dependent mechanism
- PMID: 20457839
- PMCID: PMC2904258
- DOI: 10.1152/ajpcell.00543.2009
Pak1 regulates branching morphogenesis in 3D MDCK cell culture by a PIX and beta1-integrin-dependent mechanism
Abstract
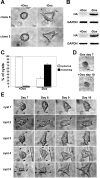
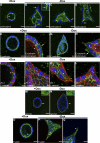
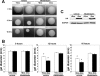
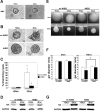
Branching morphogenesis is a fundamental process in the development of the kidney. This process gives rise to a network of ducts, which form the collecting system. Defective branching can lead to a multitude of kidney disorders including agenesis and reduced nephron number. The formation of branching tubules involves changes in cell shape, cell motility, and reorganization of the cytoskeleton. However, the exact intracellular mechanisms involved are far from understood. We have used the three-dimensional (3D) Madin-Darby canine kidney (MDCK) cell culture system to study how p21-activated kinase 1 (Pak1), which is an important regulator of the cytoskeleton, modulates branching. Our data reveal that Pak1 plays a crucial role in regulating branching morphogenesis. Expression of a dominant-negative Pak1 mutant (DN-Pak1) in MDCK cysts resulted in the spontaneous formation of extensions and branching tubules. Cellular contractility and levels of phosphorylated myosin light chain (pMLC) were increased in DN-Pak1 cells in collagen. Expression of a DN-Pak1 mutant that does not bind to PIX (DN-Pak1-DeltaPIX) failed to form extensions in collagen and did not have increased contractility. This shows that the DN-Pak1 mutant requires PIX binding to generate extensions and increased contractility in 3D culture. Furthermore, a beta1-integrin function-blocking antibody (AIIB2) inhibited the formation of branches and blocked the increased contractility in DN-Pak1 cysts. Taken together, our work shows that DN-Pak1-induced branching morphogenesis requires PIX binding and beta1-integrin signaling.
Figures


Comment in
-
Branching morphogenesis: Rac signaling "PIX" tubulogenesis. Focus on "Pak1 regulates branching morphogenesis in 3D MDCK cell culture by a PIX and beta1-integrin-dependent mechanism".Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2010 Jul;299(1):C7-10. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00145.2010. Epub 2010 Apr 28. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2010. PMID: 20427711 No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Branching morphogenesis: Rac signaling "PIX" tubulogenesis. Focus on "Pak1 regulates branching morphogenesis in 3D MDCK cell culture by a PIX and beta1-integrin-dependent mechanism".Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2010 Jul;299(1):C7-10. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00145.2010. Epub 2010 Apr 28. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2010. PMID: 20427711 No abstract available.
-
Pak1 and PIX regulate contact inhibition during epithelial wound healing.EMBO J. 2003 Aug 15;22(16):4155-65. doi: 10.1093/emboj/cdg398. EMBO J. 2003. PMID: 12912914 Free PMC article.
-
Pak1 regulates the orientation of apical polarization and lumen formation by distinct pathways.PLoS One. 2012;7(7):e41039. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0041039. Epub 2012 Jul 18. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22815903 Free PMC article.
-
Cellular mechanisms regulating epithelial morphogenesis and cancer invasion.Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2010 Oct;22(5):640-50. doi: 10.1016/j.ceb.2010.08.019. Epub 2010 Sep 9. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2010. PMID: 20832275 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Multiscale dynamics of branching morphogenesis.Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2019 Oct;60:99-105. doi: 10.1016/j.ceb.2019.04.008. Epub 2019 Jun 7. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2019. PMID: 31181348 Review.
Cited by
-
Dia1-dependent adhesions are required by epithelial tissues to initiate invasion.J Cell Biol. 2018 Apr 2;217(4):1485-1502. doi: 10.1083/jcb.201703145. Epub 2018 Feb 5. J Cell Biol. 2018. PMID: 29437785 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting P21-Activated Kinase-1 for Metastatic Prostate Cancer.Cancers (Basel). 2023 Apr 11;15(8):2236. doi: 10.3390/cancers15082236. Cancers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37190165 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Making Heads or Tails of It: Cell-Cell Adhesion in Cellular and Supracellular Polarity in Collective Migration.Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2017 Nov 1;9(11):a027854. doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a027854. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2017. PMID: 28246177 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Polarity in mammalian epithelial morphogenesis.Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2013 Feb 1;5(2):a013789. doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a013789. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2013. PMID: 23378592 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Distinct roles of cadherin-6 and E-cadherin in tubulogenesis and lumen formation.Mol Biol Cell. 2011 Jun 15;22(12):2031-41. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E11-01-0038. Epub 2011 Apr 20. Mol Biol Cell. 2011. PMID: 21508319 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bokoch GM. Biology of the p21-activated kinases. Annu Rev Biochem 72: 743–781, 2003 - PubMed
-
- Bright MD, Garner AP, Ridley AJ. PAK1 and PAK2 have different roles in HGF-induced morphological responses. Cell Signal 21: 1738–1747, 2009 - PubMed
-
- Cantley LG, Barros EJ, Gandhi M, Rauchman M, Nigam SK. Regulation of mitogenesis, motogenesis, and tubulogenesis by hepatocyte growth factor in renal collecting duct cells. Am J Physiol Renal Fluid Electrolyte Physiol 267: F271–F280, 1994 - PubMed
-
- Caplan MJ, Stow JL, Newman AP, Madri J, Anderson HC, Farquhar MG, Palade GE, Jamieson JD. Dependence on pH of polarized sorting of secreted proteins. Nature 329: 632–635, 1987 - PubMed
-
- Cheng HY, Lin YY, Yu CY, Chen JY, Shen KF, Lin WL, Liao HK, Chen YJ, Liu CH, Pang VF, Jou TS. Molecular identification of canine podocalyxin-like protein 1 as a renal tubulogenic regulator. J Am Soc Nephrol 16: 1612–1622, 2005 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

