Human cytomegalovirus IE72 protein interacts with the transcriptional repressor hDaxx to regulate LUNA gene expression during lytic infection
- PMID: 20444888
- PMCID: PMC2898242
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.02231-09
Human cytomegalovirus IE72 protein interacts with the transcriptional repressor hDaxx to regulate LUNA gene expression during lytic infection
Abstract
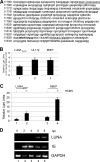
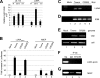
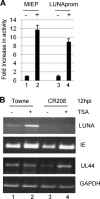
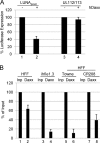
A putative latency-associated transcript (LUNA) complementary to the human cytomegalovirus (HCMV) UL81-82 region previously identified in seropositive donors' monocytes is also expressed during lytic infection. Thus, the LUNA promoter is active during both lytic and latent infection. Consequently, the mechanisms regulating this promoter may provide further insight into factors that determine whether the outcome of HCMV infection is latent or lytic. By transfection, the LUNA promoter exhibited low but reproducible activity. Substantial activation by virus infection suggested that a viral factor was important for LUNA expression during lytic infection. IE72, a known transactivator of viral promoters, activated the LUNA promoter in cotransfection assays. Furthermore, coinfection with wild-type HCMV but not an IE72 deletion virus (CR208) also activated the LUNA promoter. Finally, diminished LUNA gene expression in CR208 virus-infected cells supported a role for IE72 in LUNA gene expression. The initial regulation of herpesvirus immediate-early gene expression is associated with proteins found at cellular nuclear domain 10 (ND10) bodies, such as PML, hDaxx, and ATRX. hDaxx transfection repressed LUNA promoter activity. Furthermore, we observed binding of hDaxx to the LUNA promoter, which was abrogated by IE72 gene expression via direct interaction. Finally, we show that small interfering RNA (siRNA) knockdown of the hDaxx interaction partner ATRX rescued LUNA gene expression in CR208-infected cells. Overall, these data show that hDaxx/ATRX-mediated repression of LUNA during lytic infection absolutely requires IE72 gene expression. It also suggests that the targeting of cellular factors by IE72 is important throughout the different phases of HCMV gene expression during productive infection.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Role of the cellular protein hDaxx in human cytomegalovirus immediate-early gene expression.J Gen Virol. 2006 May;87(Pt 5):1113-1121. doi: 10.1099/vir.0.81566-0. J Gen Virol. 2006. PMID: 16603511
-
Human cytomegalovirus protein pp71 displaces the chromatin-associated factor ATRX from nuclear domain 10 at early stages of infection.J Virol. 2008 Dec;82(24):12543-54. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01215-08. Epub 2008 Oct 15. J Virol. 2008. PMID: 18922870 Free PMC article.
-
Human Daxx-mediated repression of human cytomegalovirus gene expression correlates with a repressive chromatin structure around the major immediate early promoter.J Biol Chem. 2006 Dec 8;281(49):37652-60. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M604273200. Epub 2006 Oct 11. J Biol Chem. 2006. PMID: 17035242
-
Chromatin-mediated regulation of cytomegalovirus gene expression.Virus Res. 2011 May;157(2):134-43. doi: 10.1016/j.virusres.2010.09.019. Epub 2010 Sep 25. Virus Res. 2011. PMID: 20875471 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Intrinsic cellular defense mechanisms targeting human cytomegalovirus.Virus Res. 2011 May;157(2):128-33. doi: 10.1016/j.virusres.2010.10.002. Epub 2010 Oct 8. Virus Res. 2011. PMID: 20934469 Review.
Cited by
-
Regulation of human cytomegalovirus transcription in latency: beyond the major immediate-early promoter.Viruses. 2013 Jun 3;5(6):1395-413. doi: 10.3390/v5061395. Viruses. 2013. PMID: 23736881 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Inhibition of human cytomegalovirus immediate-early gene expression by cyclin A2-dependent kinase activity.J Virol. 2012 Sep;86(17):9369-83. doi: 10.1128/JVI.07181-11. Epub 2012 Jun 20. J Virol. 2012. PMID: 22718829 Free PMC article.
-
Single-cell analysis of Daxx and ATRX-dependent transcriptional repression.J Cell Sci. 2012 Nov 15;125(Pt 22):5489-501. doi: 10.1242/jcs.110148. Epub 2012 Sep 12. J Cell Sci. 2012. PMID: 22976303 Free PMC article.
-
A Tale of Usurpation and Subversion: SUMO-Dependent Integrity of Promyelocytic Leukemia Nuclear Bodies at the Crossroad of Infection and Immunity.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021 Aug 27;9:696234. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.696234. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021. PMID: 34513832 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Human cytomegalovirus manipulation of latently infected cells.Viruses. 2013 Nov 21;5(11):2803-24. doi: 10.3390/v5112803. Viruses. 2013. PMID: 24284875 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Ahn, J. H., and G. S. Hayward. 2000. Disruption of PML-associated nuclear bodies by IE1 correlates with efficient early stages of viral gene expression and DNA replication in human cytomegalovirus infection. Virology 274:39-55. - PubMed
-
- Arvin, A. M., P. Fast, M. Myers, S. Plotkin, and R. Rabinovich. 2004. Vaccine development to prevent cytomegalovirus disease: report from the National Vaccine Advisory Committee. Clin. Infect. Dis. 39:233-239. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

