Selective visualization of cyclooxygenase-2 in inflammation and cancer by targeted fluorescent imaging agents
- PMID: 20430759
- PMCID: PMC2864539
- DOI: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-09-2664
Selective visualization of cyclooxygenase-2 in inflammation and cancer by targeted fluorescent imaging agents
Abstract
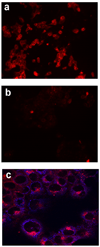
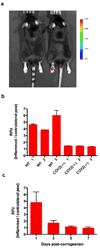
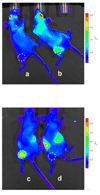
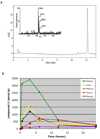
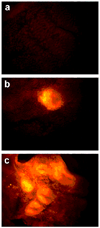
Effective diagnosis of inflammation and cancer by molecular imaging is challenging because of interference from nonselective accumulation of the contrast agents in normal tissues. Here, we report a series of novel fluorescence imaging agents that efficiently target cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2), which is normally absent from cells, but is found at high levels in inflammatory lesions and in many premalignant and malignant tumors. After either i.p. or i.v. injection, these reagents become highly enriched in inflamed or tumor tissue compared with normal tissue and this accumulation provides sufficient signal for in vivo fluorescence imaging. Further, we show that only the intact parent compound is found in the region of interest. COX-2-specific delivery was unambiguously confirmed using animals bearing targeted deletions of COX-2 and by blocking the COX-2 active site with high-affinity inhibitors in both in vitro and in vivo models. Because of their high specificity, contrast, and detectability, these fluorocoxibs are ideal candidates for detection of inflammatory lesions or early-stage COX-2-expressing human cancers, such as those in the esophagus, oropharynx, and colon.
(c)2010 AACR.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Fluorocoxib A loaded nanoparticles enable targeted visualization of cyclooxygenase-2 in inflammation and cancer.Biomaterials. 2016 Jun;92:71-80. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2016.03.028. Epub 2016 Mar 21. Biomaterials. 2016. PMID: 27043768 Free PMC article.
-
Design, synthesis, and structure-activity relationship studies of fluorescent inhibitors of cycloxygenase-2 as targeted optical imaging agents.Bioconjug Chem. 2013 Apr 17;24(4):712-23. doi: 10.1021/bc300693w. Epub 2013 Mar 28. Bioconjug Chem. 2013. PMID: 23488616 Free PMC article.
-
Fluorophore-labeled cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitors for the imaging of cyclooxygenase-2 overexpression in cancer: synthesis and biological studies.ChemMedChem. 2014 Jan;9(1):109-16, 240. doi: 10.1002/cmdc.201300355. Epub 2013 Oct 31. ChemMedChem. 2014. PMID: 24376205
-
Radiolabeled COX-2 inhibitors for non-invasive visualization of COX-2 expression and activity--a critical update.Molecules. 2013 May 29;18(6):6311-55. doi: 10.3390/molecules18066311. Molecules. 2013. PMID: 23760031 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Carcinogenesis and cyclooxygenase: the potential role of COX-2 inhibition in upper aerodigestive tract cancer.Oral Oncol. 2003 Sep;39(6):537-46. doi: 10.1016/s1368-8375(03)00035-6. Oral Oncol. 2003. PMID: 12798395 Review.
Cited by
-
Meloxicam prevents COX-2-mediated post-surgical inflammation but not pain following laparotomy in mice.Eur J Pain. 2016 Feb;20(2):231-40. doi: 10.1002/ejp.712. Epub 2015 Apr 23. Eur J Pain. 2016. PMID: 25908253 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular imaging of cyclooxygenase-2 in canine transitional cell carcinomas in vitro and in vivo.Cancer Prev Res (Phila). 2013 May;6(5):466-76. doi: 10.1158/1940-6207.CAPR-12-0358. Epub 2013 Mar 26. Cancer Prev Res (Phila). 2013. PMID: 23531445 Free PMC article.
-
Fluorocoxib A loaded nanoparticles enable targeted visualization of cyclooxygenase-2 in inflammation and cancer.Biomaterials. 2016 Jun;92:71-80. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2016.03.028. Epub 2016 Mar 21. Biomaterials. 2016. PMID: 27043768 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular Imaging of Inflammation in Osteoarthritis Using a Water-Soluble Fluorocoxib.ACS Med Chem Lett. 2020 Feb 24;11(10):1875-1880. doi: 10.1021/acsmedchemlett.9b00512. eCollection 2020 Oct 8. ACS Med Chem Lett. 2020. PMID: 33062167 Free PMC article.
-
Detection of tyrosine kinase inhibitors-induced COX-2 expression in bladder cancer by fluorocoxib A.Oncotarget. 2019 Aug 27;10(50):5168-5180. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.27125. eCollection 2019 Aug 27. Oncotarget. 2019. PMID: 31497247 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Weissleder R, Ntziachristos V. Shedding light onto live molecular targets. NatMed. 2003;9:123–128. - PubMed
-
- Tanabe K, Zhang Z, Ito T, Hatta H, Nishimoto S. Current molecular design of intelligent drugs and imaging probes targeting tumor-specific microenvironments. OrgBiomolChem. 2007;5:3745–3757. - PubMed
-
- Crofford LJ. COX-1 and COX-2 tissue expression: implications and predictions. The JRheumatol. 1997;49:15–19. - PubMed
-
- Dannenberg AJ, Lippman SM, Mann JR, Subbaramaiah K, DuBois RN. Cyclooxygenase-2 and epidermal growth factor receptor: pharmacologic targets for chemoprevention. JClinOncol. 2005;23:254–266. - PubMed
-
- Marnett LJ. The COXIB Experience: A Look in the Rear-View Mirror. AnnuRevPharmacolToxicol. 2009;49:265–290. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- U54 CA136465/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA89450/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U54 CA136465-02/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA126588/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U24 CA126588/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA111469/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U54 CA105296/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA68485/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA105296/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA060867/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- GM72048/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- CA60867/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA089450-10/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA089450/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA068485/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA86283/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA111469/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P20 GM072048/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

