Hemorrhagic shock activates lung endothelial reduced nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NADPH) oxidase via neutrophil NADPH oxidase
- PMID: 20418360
- PMCID: PMC3095934
- DOI: 10.1165/rcmb.2009-0408OC
Hemorrhagic shock activates lung endothelial reduced nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NADPH) oxidase via neutrophil NADPH oxidase
Abstract
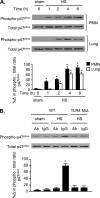
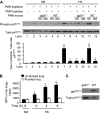
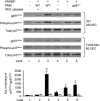
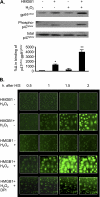
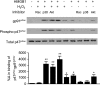
The vascular endothelium plays an important role in the regulation of inflammatory responses after trauma and hemorrhage. Interactions of neutrophils with endothelial cells (ECs) contribute to the activation of specific EC responses involved in innate immunity. We have previously reported that oxidants derived from the neutrophil reduced nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NADPH) oxidase is a critical regulator to EC activation. Our objective was to test the role of neutrophil NADPH oxidase-derived oxidants in mediating and enhancing hemorrhagic shock (HS)-induced activation of lung endothelial NADPH oxidase. Mice were subjected to HS and neutrophil depletion. The mice were also replenished with the neutrophil from NADPH oxidase-deficient mice. The resultant activation of lung NADPH oxidase was analyzed. The in vivo studies were also recapitulated with in vitro neutrophil-EC coculture system. HS induces NADPH oxidase activation in neutrophils and lung through high-mobility group box 1/Toll-like receptor 4-dependent signaling. In neutropenic mice, shock-induced NADPH oxidase activation in the lung was reduced significantly, but was restored upon repletion with neutrophils obtained from wild-type mice subjected to shock, but not with neutrophils from shock mice lacking the gp91(phox) subunit of NADPH oxidase. The findings were recapitulated in mouse lung vascular ECs cocultured with neutrophils. The data further demonstrate that neutrophil-derived oxidants are key factors mediating augmented High mobility group box 1 (HMGB1)-induced endothelial NADPH oxidase activation through a Rac1-dependent, but p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase-independent, pathway. Oxidant signaling by neutrophil NADPH oxidase is an important determinant of activation of endothelial NADPH oxidase after HS.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Hemorrhagic shock augments lung endothelial cell activation: role of temporal alterations of TLR4 and TLR2.Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2009 Dec;297(6):R1670-80. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.00445.2009. Epub 2009 Oct 14. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2009. PMID: 19828841 Free PMC article.
-
Hemorrhagic shock induces NAD(P)H oxidase activation in neutrophils: role of HMGB1-TLR4 signaling.J Immunol. 2007 May 15;178(10):6573-80. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.178.10.6573. J Immunol. 2007. PMID: 17475888
-
TLR4 signaling induces TLR2 expression in endothelial cells via neutrophil NADPH oxidase.J Clin Invest. 2003 Oct;112(8):1234-43. doi: 10.1172/JCI18696. J Clin Invest. 2003. PMID: 14561708 Free PMC article.
-
The roles of NADPH oxidase in modulating neutrophil effector responses.Mol Oral Microbiol. 2019 Apr;34(2):27-38. doi: 10.1111/omi.12252. Epub 2019 Feb 7. Mol Oral Microbiol. 2019. PMID: 30632295 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Priming of the neutrophil NADPH oxidase activation: role of p47phox phosphorylation and NOX2 mobilization to the plasma membrane.Semin Immunopathol. 2008 Jul;30(3):279-89. doi: 10.1007/s00281-008-0118-3. Epub 2008 Jun 7. Semin Immunopathol. 2008. PMID: 18536919 Review.
Cited by
-
PARP-1 inhibitor, DPQ, attenuates LPS-induced acute lung injury through inhibiting NF-κB-mediated inflammatory response.PLoS One. 2013 Nov 21;8(11):e79757. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0079757. eCollection 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 24278171 Free PMC article.
-
Oxidative stress and inflammation are differentially affected by atorvastatin, pravastatin, rosuvastatin, and simvastatin on lungs from mice exposed to cigarette smoke.Inflammation. 2014 Oct;37(5):1355-65. doi: 10.1007/s10753-014-9860-y. Inflammation. 2014. PMID: 24609836
-
Innate immunity and immunotherapy for hemorrhagic shock.Front Immunol. 2022 Aug 25;13:918380. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.918380. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 36091025 Free PMC article. Review.
-
PARP inhibitor, olaparib ameliorates acute lung and kidney injury upon intratracheal administration of LPS in mice.Mol Cell Biochem. 2015 Feb;400(1-2):153-62. doi: 10.1007/s11010-014-2271-4. Epub 2014 Nov 18. Mol Cell Biochem. 2015. PMID: 25404465
-
Tissue damage negatively regulates LPS-induced macrophage necroptosis.Cell Death Differ. 2016 Sep 1;23(9):1428-47. doi: 10.1038/cdd.2016.21. Epub 2016 Mar 4. Cell Death Differ. 2016. PMID: 26943325 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Daniel TO, Abrahamson D. Endothelial signal integration in vascular assembly. Annu Rev Physiol 2000;62:649–671. - PubMed
-
- Iivanainen E, Kahari VM, Heino J, Elenius K. Endothelial cell–matrix interactions. Microsc Res Tech 2003;60:13–22. - PubMed
-
- Abdelrahman M, Mazzon E, Bauer M, Bauer I, Delbosc S, Cristol JP, Patel NS, Cuzzocrea S, Thiemermann C. Inhibitors of NADPH oxidase reduce the organ injury in hemorrhagic shock. Shock 2005;23:107–114. - PubMed
-
- Akgur FM, Brown MF, Zibari GB, McDonald JC, Epstein CJ, Ross CR, Granger DN. Role of superoxide in hemorrhagic shock-induced P-selectin expression. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 2000;279:H791–H797. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

