The miR-17-92 microRNA polycistron regulates MLL leukemia stem cell potential by modulating p21 expression
- PMID: 20406979
- PMCID: PMC2862107
- DOI: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-09-3268
The miR-17-92 microRNA polycistron regulates MLL leukemia stem cell potential by modulating p21 expression
Abstract
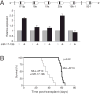
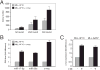
Despite advances in defining the critical molecular determinants for leukemia stem cell (LSC) generation and maintenance, little is known about the roles of microRNAs in LSC biology. Here, we identify microRNAs that are differentially expressed in LSC-enriched cell fractions (c-kit(+)) in a mouse model of MLL leukemia. Members of the miR-17 family were notably more abundant in LSCs compared with their normal counterpart granulocyte-macrophage progenitors and myeloblast precursors. Expression of miR-17 family microRNAs was substantially reduced concomitant with leukemia cell differentiation and loss of self-renewal, whereas forced expression of a polycistron construct encoding miR-17-19b miRNAs significantly shortened the latency for MLL leukemia development. Leukemias expressing increased levels of the miR-17-19b construct displayed a higher frequency of LSCs, more stringent block of differentiation, and enhanced proliferation associated with reduced expression of p21, a cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor previously implicated as a direct target of miR-17 microRNAs. Knockdown of p21 in MLL-transformed cells phenocopied the overexpression of the miR-17 polycistron, including a significant decrease in leukemia latency, validating p21 as a biologically relevant and direct in vivo target of the miR-17 polycistron in MLL leukemia. Expression of c-myc, a crucial upstream regulator of the miR-17 polycistron, correlated with miR-17-92 levels, enhanced self-renewal, and LSC potential. Thus, microRNAs quantitatively regulate LSC self-renewal in MLL-associated leukemia in part by modulating the expression of p21, a known regulator of normal stem cell function.
(c)2010 AACR.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
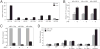



Similar articles
-
Meis1 is an essential and rate-limiting regulator of MLL leukemia stem cell potential.Genes Dev. 2007 Nov 1;21(21):2762-74. doi: 10.1101/gad.1602107. Epub 2007 Oct 17. Genes Dev. 2007. PMID: 17942707 Free PMC article.
-
MiR-495 is a tumor-suppressor microRNA down-regulated in MLL-rearranged leukemia.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012 Nov 20;109(47):19397-402. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1217519109. Epub 2012 Nov 6. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012. PMID: 23132946 Free PMC article.
-
Bortezomib suppresses self-renewal and leukemogenesis of leukemia stem cell by NF-ĸB-dependent inhibition of CDK6 in MLL-rearranged myeloid leukemia.J Cell Mol Med. 2021 Mar;25(6):3124-3135. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.16377. Epub 2021 Feb 17. J Cell Mol Med. 2021. PMID: 33599085 Free PMC article.
-
Learning from mouse models of MLL fusion gene-driven acute leukemia.Biochim Biophys Acta Gene Regul Mech. 2020 Aug;1863(8):194550. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagrm.2020.194550. Epub 2020 Apr 19. Biochim Biophys Acta Gene Regul Mech. 2020. PMID: 32320749 Review.
-
Dysregulation of haematopoietic stem cell regulatory programs in acute myeloid leukaemia.J Mol Med (Berl). 2017 Jul;95(7):719-727. doi: 10.1007/s00109-017-1535-3. Epub 2017 Apr 20. J Mol Med (Berl). 2017. PMID: 28429049 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Aberrant microRNA expression and its implications in the pathogenesis of leukemias.Cell Oncol (Dordr). 2012 Oct;35(5):317-34. doi: 10.1007/s13402-012-0095-3. Epub 2012 Sep 7. Cell Oncol (Dordr). 2012. PMID: 22956261 Review.
-
Crosstalk among Epigenetic Pathways Regulates Neurogenesis.Front Neurosci. 2012 May 8;6:59. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2012.00059. eCollection 2012. Front Neurosci. 2012. PMID: 22586361 Free PMC article.
-
Novel agent nitidine chloride induces erythroid differentiation and apoptosis in CML cells through c-Myc-miRNAs axis.PLoS One. 2015 Feb 3;10(2):e0116880. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0116880. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 25647305 Free PMC article.
-
Hoxb8 regulates expression of microRNAs to control cell death and differentiation.Cell Death Differ. 2013 Oct;20(10):1370-80. doi: 10.1038/cdd.2013.92. Epub 2013 Jul 19. Cell Death Differ. 2013. PMID: 23872792 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNA-17-5p post-transcriptionally regulates p21 expression in irradiated betel quid chewing-related oral squamous cell carcinoma cells.Strahlenther Onkol. 2013 Aug;189(8):675-83. doi: 10.1007/s00066-013-0347-9. Epub 2013 Jun 20. Strahlenther Onkol. 2013. PMID: 23780339
References
-
- Berezikov E, Guryev V, van de Belt J, Wienholds E, Plasterk RH, Cuppen E. Phylogenetic shadowing and computational identification of human microRNA genes. Cell. 2005;120(1):21–4. - PubMed
-
- Olsen PH, Ambros V. The lin-4 regulatory RNA controls developmental timing in Caenorhabditis elegans by blocking LIN-14 protein synthesis after the initiation of translation. Dev Biol. 1999;216(2):671–80. - PubMed
-
- Wightman B, Ha I, Ruvkun G. Posttranscriptional regulation of the heterochronic gene lin-14 by lin-4 mediates temporal pattern formation in C. elegans. Cell. 1993;75(5):855–62. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

