Nuclear receptor CAR represses TNFalpha-induced cell death by interacting with the anti-apoptotic GADD45B
- PMID: 20404936
- PMCID: PMC2853562
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0010121
Nuclear receptor CAR represses TNFalpha-induced cell death by interacting with the anti-apoptotic GADD45B
Abstract
Background: Phenobarbital (PB) is the most well-known among numerous non-genotoxic carcinogens that cause the development of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). PB activates nuclear xenobiotic receptor Constitutive Active/Androstane Receptor (CAR; NR1I3) and this activation is shown to determine PB promotion of HCC in mice. The molecular mechanism of CAR-mediated tumor promotion, however, remains elusive at the present time. Here we have identified Growth Arrest and DNA Damage-inducible 45beta (GADD45B) as a novel CAR target, through which CAR represses cell death.
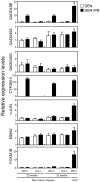
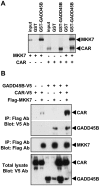
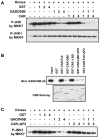
Methodology/principal findings: PB activation of nuclear xenobiotic receptor CAR is found to induce the Gadd45b gene in mouse liver throughout the development of HCC as well as in liver tumors. Given the known function of GADD45B as a factor that represses Mitogen-activated protein Kinase Kinase 7 - c-Jun N-terminal Kinase (MKK7-JNK) pathway-mediated apoptosis, we have now demonstrated that CAR interacts with GADD45B to repress Tumor Necrosis Factor alpha ( TNFalpha)-induced JNK1 phosphorylation as well as cell death. Primary hepatocytes, prepared from Car(+/+), Car(-/-), Gadd45b(+/+) and Gadd45b(-/-) mice, were treated with TNFalpha and Actinomycin D to induce phosphorylation of JNK1 and cell death. Co-treatment with the CAR activating ligand TCPOBOP (1,4 bis[2-(3,5-dichloropyridyloxy)]benzene) has resulted in repression of both phosphorylation and cell death in the primary hepatocytes from Car(+/+) but not Car(-/-) mice. Repression by TCPOBOP was not observed in those prepared from Gadd45b(-/-) mice. In vitro protein-protein interaction and phosphorylation assays have revealed that CAR interacts with MKK7 and represses the MKK7-mediated phosphorylation of JNK1.
Conclusions/significance: CAR can form a protein complex with GADD45B, through which CAR represses MKK7-mediated phosphorylation of JNK1. In addition to activating the Gadd45b gene, CAR may repress death of mouse primary hepatocytes by forming a GADD45B complex and repressing MKK7-mediated phosphorylation of JNK1. The present finding that CAR can repress cell death via its interaction with GADD45B provides an insight for further investigations into the CAR-regulated molecular mechanism by which PB promotes development of HCC.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
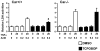

Similar articles
-
Nuclear Receptor CAR Suppresses GADD45B-p38 MAPK Signaling to Promote Phenobarbital-induced Proliferation in Mouse Liver.Mol Cancer Res. 2018 Aug;16(8):1309-1318. doi: 10.1158/1541-7786.MCR-18-0118. Epub 2018 May 1. Mol Cancer Res. 2018. PMID: 29716964
-
The antiapoptotic factor growth arrest and DNA-damage-inducible 45 beta regulates the nuclear receptor constitutive active/androstane receptor-mediated transcription.Drug Metab Dispos. 2008 Jul;36(7):1189-93. doi: 10.1124/dmd.108.020628. Epub 2008 Mar 24. Drug Metab Dispos. 2008. PMID: 18362160 Free PMC article.
-
Extracellular signal-regulated kinase is an endogenous signal retaining the nuclear constitutive active/androstane receptor (CAR) in the cytoplasm of mouse primary hepatocytes.Mol Pharmacol. 2007 May;71(5):1217-21. doi: 10.1124/mol.107.034538. Epub 2007 Feb 21. Mol Pharmacol. 2007. PMID: 17314319 Free PMC article.
-
Gadd45 in the liver: signal transduction and transcriptional mechanisms.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2013;793:69-80. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4614-8289-5_5. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2013. PMID: 24104474 Review.
-
Mode of action and human relevance analysis for nuclear receptor-mediated liver toxicity: A case study with phenobarbital as a model constitutive androstane receptor (CAR) activator.Crit Rev Toxicol. 2014 Jan;44(1):64-82. doi: 10.3109/10408444.2013.835786. Epub 2013 Nov 4. Crit Rev Toxicol. 2014. PMID: 24180433 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Gadd45b is a novel mediator of neuronal apoptosis in ischemic stroke.Int J Biol Sci. 2015 Feb 8;11(3):353-60. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.9813. eCollection 2015. Int J Biol Sci. 2015. PMID: 25678854 Free PMC article.
-
Phosphorylation of vaccinia-related kinase 1 at threonine 386 transduces glucose stress signal in human liver cells.Biosci Rep. 2020 Apr 30;40(4):BSR20200498. doi: 10.1042/BSR20200498. Biosci Rep. 2020. PMID: 32266931 Free PMC article.
-
Phenobarbital indirectly activates the constitutive active androstane receptor (CAR) by inhibition of epidermal growth factor receptor signaling.Sci Signal. 2013 May 7;6(274):ra31. doi: 10.1126/scisignal.2003705. Sci Signal. 2013. PMID: 23652203 Free PMC article.
-
Xenobiotic metabolism, disposition, and regulation by receptors: from biochemical phenomenon to predictors of major toxicities.Toxicol Sci. 2011 Mar;120 Suppl 1(Suppl 1):S49-75. doi: 10.1093/toxsci/kfq338. Epub 2010 Nov 8. Toxicol Sci. 2011. PMID: 21059794 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nuclear receptors and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2016 Sep;1859(9):1083-1099. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagrm.2016.03.002. Epub 2016 Mar 4. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2016. PMID: 26962021 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Sueyoshi T, Kawamoto T, Zelko I, Honkakoski P, Negishi M. The repressed nuclear receptor CAR responds to phenobarbital in activating the human CYP2B6 gene. J Biol Chem. 1999;274:6043–6046. - PubMed
-
- Rosenfeld JM, Vargas R, Jr, Xie W, Evans RM. Genetic profiling defines the xenobiotic gene network controlled by the nuclear receptor pregnane X receptor. Mol Endocrinol. 2003;17:1268–1282. - PubMed
-
- Ueda A, Hamadeh HK, Webb HK, Yamamoto Y, Sueyoshi T, et al. Diverse roles of the nuclear orphan receptor CAR in regulating hepatic genes in response to phenobarbital. Mol Pharmacol. 2002;61:1–6. - PubMed
-
- Wei P, Zhang J, Egan-Hafley M, Liang S, Moore DD. The nuclear receptor CAR mediates specific xenobiotic induction of drug metabolism. Nature. 2000;407:920–923. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

