Regulation of IkappaBalpha function and NF-kappaB signaling: AEBP1 is a novel proinflammatory mediator in macrophages
- PMID: 20396415
- PMCID: PMC2855089
- DOI: 10.1155/2010/823821
Regulation of IkappaBalpha function and NF-kappaB signaling: AEBP1 is a novel proinflammatory mediator in macrophages
Abstract
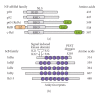
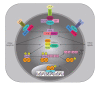
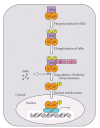
NF-kappaB comprises a family of transcription factors that are critically involved in various inflammatory processes. In this paper, the role of NF-kappaB in inflammation and atherosclerosis and the regulation of the NF-kappaB signaling pathway are summarized. The structure, function, and regulation of the NF-kappaB inhibitors, IkappaBalpha and IkappaBbeta, are reviewed. The regulation of NF-kappaB activity by glucocorticoid receptor (GR) signaling and IkappaBalpha sumoylation is also discussed. This paper focuses on the recently reported regulatory function that adipocyte enhancer-binding protein 1 (AEBP1) exerts on NF-kappaB transcriptional activity in macrophages, in which AEBP1 manifests itself as a potent modulator of NF-kappaB via physical interaction with IkappaBalpha and a critical mediator of inflammation. Finally, we summarize the regulatory roles that recently identified IkappaBalpha-interacting proteins play in NF-kappaB signaling. Based on its proinflammatory roles in macrophages, AEBP1 is anticipated to serve as a therapeutic target towards the treatment of various inflammatory conditions and disorders.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Adipocyte enhancer-binding protein-1 promotes macrophage inflammatory responsiveness by up-regulating NF-kappaB via IkappaBalpha negative regulation.Mol Biol Cell. 2007 Mar;18(3):930-42. doi: 10.1091/mbc.e06-03-0217. Epub 2007 Jan 3. Mol Biol Cell. 2007. PMID: 17202411 Free PMC article.
-
Adipocyte enhancer-binding protein 1 (AEBP1) (a novel macrophage proinflammatory mediator) overexpression promotes and ablation attenuates atherosclerosis in ApoE (-/-) and LDLR (-/-) mice.Mol Med. 2011 Sep-Oct;17(9-10):1056-64. doi: 10.2119/molmed.2011.00141. Epub 2011 Jun 14. Mol Med. 2011. PMID: 21687917 Free PMC article.
-
Adipocyte enhancer-binding protein 1 is a potential novel atherogenic factor involved in macrophage cholesterol homeostasis and inflammation.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006 Feb 14;103(7):2346-51. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0508139103. Epub 2006 Feb 6. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006. PMID: 16461908 Free PMC article.
-
PPARgamma1 and LXRalpha face a new regulator of macrophage cholesterol homeostasis and inflammatory responsiveness, AEBP1.Nucl Recept Signal. 2010 Apr 16;8:e004. doi: 10.1621/nrs.08004. Nucl Recept Signal. 2010. PMID: 20419060 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Molecular mechanisms of system control of NF-kappaB signaling by IkappaBalpha.Biochemistry. 2010 Mar 2;49(8):1560-7. doi: 10.1021/bi901948j. Biochemistry. 2010. PMID: 20055496 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Lactation defect with impaired secretory activation in AEBP1-null mice.PLoS One. 2011;6(11):e27795. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0027795. Epub 2011 Nov 16. PLoS One. 2011. PMID: 22114697 Free PMC article.
-
SUMOylation targeting mitophagy in cardiovascular diseases.J Mol Med (Berl). 2022 Nov;100(11):1511-1538. doi: 10.1007/s00109-022-02258-4. Epub 2022 Sep 26. J Mol Med (Berl). 2022. PMID: 36163375 Review.
-
Identification of the possible therapeutic targets in the insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor pathway in a cohort of Egyptian hepatocellular carcinoma complicating chronic hepatitis C type 4.Drug Target Insights. 2020 Apr 8;14:1-11. doi: 10.33393/dti.2020.1548. eCollection 2020. Drug Target Insights. 2020. PMID: 33132693 Free PMC article.
-
PCB 126 induces monocyte/macrophage polarization and inflammation through AhR and NF-κB pathways.Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2019 Mar 15;367:71-81. doi: 10.1016/j.taap.2019.02.006. Epub 2019 Feb 13. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2019. PMID: 30768972 Free PMC article.
-
AEBP1 promotes epithelial-mesenchymal transition of gastric cancer cells by activating the NF-κB pathway and predicts poor outcome of the patients.Sci Rep. 2018 Aug 10;8(1):11955. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-29878-6. Sci Rep. 2018. PMID: 30097586 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Baeuerle PA. Pro-inflammatory signaling: last pieces in the NF-κB puzzle? Current Biology. 1998;8(1):R19–R22. - PubMed
-
- Shoelson SE, Lee J, Yuan M. Inflammation and the IKKβ/IκB/NF-κB axis in obesity- and diet-induced insulin resistance. The International Journal of Obesity. 2003;27(supplement 3):S49–S52. - PubMed
-
- Clevers H. At the crossroads of inflammation and cancer. Cell. 2004;118(6):671–674. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

