Serine dephosphorylation of receptor protein tyrosine phosphatase alpha in mitosis induces Src binding and activation
- PMID: 20385765
- PMCID: PMC2876684
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.01202-09
Serine dephosphorylation of receptor protein tyrosine phosphatase alpha in mitosis induces Src binding and activation
Abstract
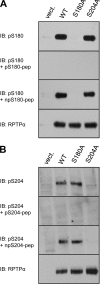
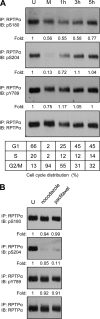
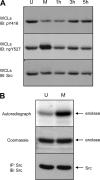
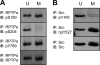
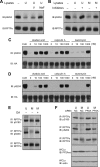
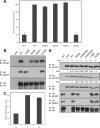
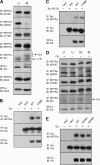
Receptor protein tyrosine phosphatase alpha (RPTPalpha) is the mitotic activator of the protein tyrosine kinase Src. RPTPalpha serine hyperphosphorylation was proposed to mediate mitotic activation of Src. We raised phosphospecific antibodies to the two main serine phosphorylation sites, and we discovered that RPTPalpha Ser204 was almost completely dephosphorylated in mitotic NIH 3T3 and HeLa cells, whereas Ser180 and Tyr789 phosphorylation were only marginally reduced in mitosis. Concomitantly, Src pTyr527 and pTyr416 were dephosphorylated, resulting in 2.3-fold activation of Src in mitosis. Using inhibitors and knockdown experiments, we demonstrated that dephosphorylation of RPTPalpha pSer204 in mitosis was mediated by PP2A. Mutation of Ser204 to Ala did not activate RPTPalpha, and intrinsic catalytic activity of RPTPalpha was not affected in mitosis. Interestingly, binding of endogenous Src to RPTPalpha was induced in mitosis. GRB2 binding to RPTPalpha, which was proposed to compete with Src binding to RPTPalpha, was only modestly reduced in mitosis, which could not account for enhanced Src binding. Moreover, we demonstrate that Src bound to mutant RPTPalpha-Y789F, lacking the GRB2 binding site, and mutant Src with an impaired Src homology 2 (SH2) domain bound to RPTPalpha, illustrating that Src binding to RPTPalpha is not mediated by a pTyr-SH2 interaction. Mutation of RPTPalpha Ser204 to Asp, mimicking phosphorylation, reduced coimmunoprecipitation with Src, suggesting that phosphorylation of Ser204 prohibits binding to Src. Based on our results, we propose a new model for mitotic activation of Src in which PP2A-mediated dephosphorylation of RPTPalpha pSer204 facilitates Src binding, leading to RPTPalpha-mediated dephosphorylation of Src pTyr527 and pTyr416 and hence modest activation of Src.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Mitotic activation of protein-tyrosine phosphatase alpha and regulation of its Src-mediated transforming activity by its sites of protein kinase C phosphorylation.J Biol Chem. 2002 Jun 14;277(24):21922-9. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M201394200. Epub 2002 Mar 28. J Biol Chem. 2002. PMID: 11923305 Free PMC article.
-
Suppression of the phosphorylation of receptor tyrosine phosphatase-alpha on the Src-independent site tyrosine 789 by reactive oxygen species.Mol Pharmacol. 2006 Jun;69(6):1938-44. doi: 10.1124/mol.105.020115. Epub 2006 Feb 27. Mol Pharmacol. 2006. PMID: 16505154
-
Tight association of GRB2 with receptor protein-tyrosine phosphatase alpha is mediated by the SH2 and C-terminal SH3 domains.EMBO J. 1996 Jun 17;15(12):3016-27. EMBO J. 1996. PMID: 8670803 Free PMC article.
-
Meeting at mitosis: cell cycle-specific regulation of c-Src by RPTPalpha.Sci STKE. 2002 Jan 15;2002(115):pe3. doi: 10.1126/stke.2002.115.pe3. Sci STKE. 2002. PMID: 11796915 Review.
-
c-Src and mitosis.Ciba Found Symp. 1992;170:248-65; discussion 265-75. doi: 10.1002/9780470514320.ch15. Ciba Found Symp. 1992. PMID: 1282857 Review.
Cited by
-
Development of FRET Biosensor to Characterize CSK Subcellular Regulation.Biosensors (Basel). 2024 Apr 20;14(4):206. doi: 10.3390/bios14040206. Biosensors (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38667199 Free PMC article.
-
Alcohol-dependent molecular adaptations of the NMDA receptor system.Genes Brain Behav. 2017 Jan;16(1):139-148. doi: 10.1111/gbb.12363. Genes Brain Behav. 2017. PMID: 27906494 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Clustering of phosphatase RPTPα promotes Src signaling and the arthritogenic action of synovial fibroblasts.Sci Signal. 2023 Jul 4;16(792):eabn8668. doi: 10.1126/scisignal.abn8668. Epub 2023 Jul 4. Sci Signal. 2023. PMID: 37402225 Free PMC article.
-
Glucose-mediated N-glycosylation of RPTPα affects its subcellular localization and Src activation.Oncogene. 2023 Mar;42(14):1058-1071. doi: 10.1038/s41388-023-02622-9. Epub 2023 Feb 10. Oncogene. 2023. PMID: 36765146
-
Helicobacter pylori VacA, acting through receptor protein tyrosine phosphatase α, is crucial for CagA phosphorylation in human duodenum carcinoma cell line AZ-521.Dis Model Mech. 2016 Dec 1;9(12):1473-1481. doi: 10.1242/dmm.025361. Dis Model Mech. 2016. PMID: 27935824 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alonso, A., J. Sasin, N. Bottini, I. Friedberg, A. Osterman, A. Godzik, T. Hunter, J. Dixon, and T. Mustelin. 2004. Protein tyrosine phosphatases in the human genome. Cell 117:699-711. - PubMed
-
- Bagrodia, S., I. Chackalaparampil, T. E. Kmiecik, and D. Shalloway. 1991. Altered tyrosine 527 phosphorylation and mitotic activation of p60c-src. Nature 349:172-175. - PubMed
-
- Bhandari, V., K. L. Lim, and C. J. Pallen. 1998. Physical and functional interactions between receptor-like protein-tyrosine phosphatase alpha and p59fyn. J. Biol. Chem. 273:8691-8698. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
