A transcriptional signature and common gene networks link cancer with lipid metabolism and diverse human diseases
- PMID: 20385360
- PMCID: PMC2854678
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ccr.2010.01.022
A transcriptional signature and common gene networks link cancer with lipid metabolism and diverse human diseases
Abstract
Transcriptional profiling of two isogenic models of transformation identifies a gene signature linking cancer with inflammatory and metabolic diseases. In accord with this common transcriptional program, many drugs used for treatment of diabetes and cardiovascular diseases inhibit transformation and tumor growth. Unexpectedly, lipid metabolism genes are important for transformation and are upregulated in cancer tissues. As in atherosclerosis, oxidized LDL and its receptor OLR1 activate the inflammatory pathway through NF-kappaB, leading to transformation. OLR1 is important for maintaining the transformed state in developmentally diverse cancer cell lines and for tumor growth, suggesting a molecular connection between cancer and atherosclerosis. We suggest that the interplay between this common transcriptional program and cell-type-specific factors gives rise to phenotypically disparate human diseases.
Copyright 2010 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
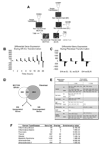
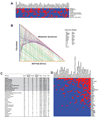
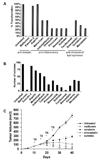
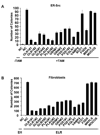
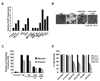
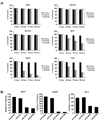
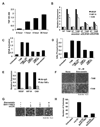
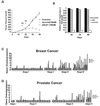
Comment in
-
Transcriptomics: Common disease pathogenesis pathways.Nat Rev Genet. 2010 Jun;11(6):386. doi: 10.1038/nrg2799. Nat Rev Genet. 2010. PMID: 20479770 No abstract available.
-
Transcriptomics: Common disease pathogenesis pathways.Nat Rev Cancer. 2010 Jun;10(6):387. doi: 10.1038/nrc2860. Nat Rev Cancer. 2010. PMID: 20509175 No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Oxidized LDL receptor 1 (OLR1) as a possible link between obesity, dyslipidemia and cancer.PLoS One. 2011;6(5):e20277. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0020277. Epub 2011 May 26. PLoS One. 2011. PMID: 21637860 Free PMC article.
-
Oxidative stress and lectin-like ox-LDL-receptor LOX-1 in atherogenesis and tumorigenesis.Antioxid Redox Signal. 2011 Oct 15;15(8):2301-33. doi: 10.1089/ars.2010.3792. Epub 2011 May 25. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2011. PMID: 21338316 Review.
-
LOX-1 and Its Splice Variants: A New Challenge for Atherosclerosis and Cancer-Targeted Therapies.Int J Mol Sci. 2017 Jan 29;18(2):290. doi: 10.3390/ijms18020290. Int J Mol Sci. 2017. PMID: 28146073 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Functional characterization and expression analysis of novel alternative splicing isoforms of Olr1 gene during mouse embryogenesis.Gene. 2012 Jan 1;491(1):5-12. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2011.09.030. Epub 2011 Oct 2. Gene. 2012. PMID: 22001547
-
LOX-1 receptor: A potential link in atherosclerosis and cancer.Life Sci. 2018 Apr 1;198:79-86. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2018.02.024. Epub 2018 Feb 17. Life Sci. 2018. PMID: 29462603 Review.
Cited by
-
GEO Data Mining Identifies OLR1 as a Potential Biomarker in NSCLC Immunotherapy.Front Oncol. 2021 Apr 20;11:629333. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2021.629333. eCollection 2021. Front Oncol. 2021. PMID: 33959497 Free PMC article.
-
Phytochemical Targeting of STAT3 Orchestrated Lipid Metabolism in Therapy-Resistant Cancers.Biomolecules. 2020 Jul 28;10(8):1118. doi: 10.3390/biom10081118. Biomolecules. 2020. PMID: 32731620 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Human sterol 14α-demethylase as a target for anticancer chemotherapy: towards structure-aided drug design.J Lipid Res. 2016 Aug;57(8):1552-63. doi: 10.1194/jlr.M069229. Epub 2016 Jun 16. J Lipid Res. 2016. PMID: 27313059 Free PMC article.
-
Role of six single nucleotide polymorphisms, risk factors in coronary disease, in OLR1 alternative splicing.RNA. 2015 Jun;21(6):1187-202. doi: 10.1261/rna.049890.115. Epub 2015 Apr 22. RNA. 2015. PMID: 25904137 Free PMC article.
-
STAT3 activation of miR-21 and miR-181b-1 via PTEN and CYLD are part of the epigenetic switch linking inflammation to cancer.Mol Cell. 2010 Aug 27;39(4):493-506. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2010.07.023. Mol Cell. 2010. PMID: 20797623 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Balkwill F, Mantovani A. Inflammation and cancer: back to Virchow? Lancet. 2001;357:539–545. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
- HG2966/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HG002966-03/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA057436-10/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA107486-01A3/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HG002966-04/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA057436-11/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA107486/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA107486-03/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HG004069/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- HG4069-02/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA057436/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HG004069-01/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HG004069-02/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- CA107486/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HG004069-03/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HG002966-05/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- CA57486/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HG002966/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA107486-02/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA057436-09/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

