Radiation dose reduction using a CdZnTe-based computed tomography system: comparison to flat-panel detectors
- PMID: 20384260
- PMCID: PMC2842286
- DOI: 10.1118/1.3312435
Radiation dose reduction using a CdZnTe-based computed tomography system: comparison to flat-panel detectors
Abstract
Purpose: Although x-ray projection mammography has been very effective in early detection of breast cancer, its utility is reduced in the detection of small lesions that are occult or in dense breasts. One drawback is that the inherent superposition of parenchymal structures makes visualization of small lesions difficult. Breast computed tomography using flat-panel detectors has been developed to address this limitation by producing three-dimensional data while at the same time providing more comfort to the patients by eliminating breast compression. Flat panels are charge integrating detectors and therefore lack energy resolution capability. Recent advances in solid state semiconductor x-ray detector materials and associated electronics allow the investigation of x-ray imaging systems that use a photon counting and energy discriminating detector, which is the subject of this article.
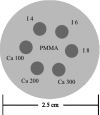
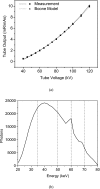
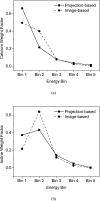
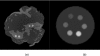
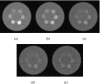
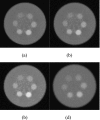
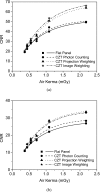
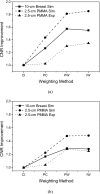
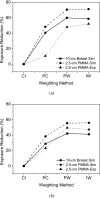
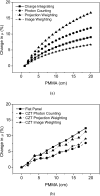
Methods: A small field-of-view computed tomography (CT) system that uses CdZnTe (CZT) photon counting detector was compared to one that uses a flat-panel detector for different imaging tasks in breast imaging. The benefits afforded by the CZT detector in the energy weighting modes were investigated. Two types of energy weighting methods were studied: Projection based and image based. Simulation and phantom studies were performed with a 2.5 cm polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) cylinder filled with iodine and calcium contrast objects. Simulation was also performed on a 10 cm breast specimen.
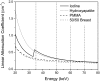
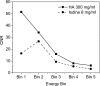
Results: The contrast-to-noise ratio improvements as compared to flat-panel detectors were 1.30 and 1.28 (projection based) and 1.35 and 1.25 (image based) for iodine over PMMA and hydroxylapatite over PMMA, respectively. Corresponding simulation values were 1.81 and 1.48 (projection based) and 1.85 and 1.48 (image based). Dose reductions using the CZT detector were 52.05% and 49.45% for iodine and hydroxyapatite imaging, respectively. Image-based weighting was also found to have the least beam hardening effect.
Conclusions: The results showed that a CT system using an energy resolving detector reduces the dose to the patient while maintaining image quality for various breast imaging tasks.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Tilted angle CZT detector for photon counting/energy weighting x-ray and CT imaging.Phys Med Biol. 2006 Sep 7;51(17):4267-87. doi: 10.1088/0031-9155/51/17/010. Epub 2006 Aug 15. Phys Med Biol. 2006. PMID: 16912381
-
Investigation of energy weighting using an energy discriminating photon counting detector for breast CT.Med Phys. 2013 Aug;40(8):081923. doi: 10.1118/1.4813901. Med Phys. 2013. PMID: 23927337 Free PMC article.
-
Segmentation and quantification of materials with energy discriminating computed tomography: a phantom study.Med Phys. 2011 Jan;38(1):228-37. doi: 10.1118/1.3525835. Med Phys. 2011. PMID: 21361191 Free PMC article.
-
Solid-state, flat-panel, digital radiography detectors and their physical imaging characteristics.Clin Radiol. 2008 May;63(5):487-98. doi: 10.1016/j.crad.2007.10.014. Epub 2008 Jan 31. Clin Radiol. 2008. PMID: 18374710 Review.
-
Tutorial on X-ray photon counting detector characterization.J Xray Sci Technol. 2018;26(1):1-28. doi: 10.3233/XST-16210. J Xray Sci Technol. 2018. PMID: 29154310 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Quantification of breast density with spectral mammography based on a scanned multi-slit photon-counting detector: a feasibility study.Phys Med Biol. 2012 Aug 7;57(15):4719-38. doi: 10.1088/0031-9155/57/15/4719. Epub 2012 Jul 6. Phys Med Biol. 2012. PMID: 22771941 Free PMC article.
-
Tight-frame based iterative image reconstruction for spectral breast CT.Med Phys. 2013 Mar;40(3):031905. doi: 10.1118/1.4790468. Med Phys. 2013. PMID: 23464320 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of energy response for photon-counting detectors using x-ray fluorescence.Med Phys. 2014 Dec;41(12):121902. doi: 10.1118/1.4900820. Med Phys. 2014. PMID: 25471962 Free PMC article.
-
Image-based spectral distortion correction for photon-counting x-ray detectors.Med Phys. 2012 Apr;39(4):1864-76. doi: 10.1118/1.3693056. Med Phys. 2012. PMID: 22482608 Free PMC article.
-
Energy response calibration of photon-counting detectors using x-ray fluorescence: a feasibility study.Phys Med Biol. 2014 Dec 7;59(23):7211-27. doi: 10.1088/0031-9155/59/23/7211. Epub 2014 Nov 4. Phys Med Biol. 2014. PMID: 25369288 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lai C. J., Shaw C. C., Chen L. Y., Altunbas M. C., Liu X. M., Han T., Wang T. P., Yang W. T., Whitman G. J., and Tu S. J., “Visibility of microcalcification in cone beam breast CT: Effects of x-ray tube voltage and radiation dose,” Med. Phys. MPHYA6 34(7), 2995–3004 (2007).10.1118/1.2745921 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Schlomka J. P., Roessl E., Dorscheid R., Dill S., Martens G., Istel T., Baumer C., Herrmann C., Steadman R., Zeitler G., Livne A., and Proksa R., “Experimental feasibility of multi-energy photon-counting K-edge imaging in pre-clinical computed tomography,” Phys. Med. Biol. PHMBA7 53(15), 4031–4047 (2008).10.1088/0031-9155/53/15/002 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

