Gene transfer in the nervous system and implications for transsynaptic neuronal tracing
- PMID: 20367126
- PMCID: PMC2866520
- DOI: 10.1517/14712591003796538
Gene transfer in the nervous system and implications for transsynaptic neuronal tracing
Abstract
Importance of the field: Neuronal circuitries are determined by specific synaptic connections and they provide the cellular basis of cognitive processes and behavioral functions. To investigate neuronal circuitries, tracers are typically used to identify the original neurons and their projection targets.
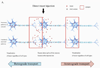
Areas covered in this review: Traditional tracing methods using chemical tracers have major limitations such as non-specificity. In this review, we highlight novel genetic tracing approaches that enable visualization of specific neuronal pathways by introducing cDNA encoding a transsynaptic tracer. In contrast to conventional tracing methods, these genetic approaches use cell-type-specific promoters to express transsynaptic tracers such as wheat germ agglutinin and C-terminal fragment of tetanus toxin, which allows labeling of either the input or output populations and connections of specific neuronal type.
What the reader will gain: Specific neuronal circuit information by these genetic approaches will allow more precise, comprehensive and novel information about individual neural circuits and their function in normal and diseased brains.
Take home message: Using tracer gene transfer, neuronal circuit plasticity after traumatic injury or neurodegenerative diseases can be visualized. Also, this can provide a good marker for evaluation of therapeutic effects of neuroprotective or neurotrophic agents.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Triggering genetically-expressed transneuronal tracers by peripheral axotomy reveals convergent and segregated sensory neuron-spinal cord connectivity.Neuroscience. 2009 Nov 10;163(4):1220-32. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2009.07.051. Epub 2009 Jul 30. Neuroscience. 2009. PMID: 19647044 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of WGA-Cre-dependent topological transgene expression in the rodent brain.Brain Struct Funct. 2017 Mar;222(2):717-733. doi: 10.1007/s00429-016-1241-x. Epub 2016 Jun 3. Brain Struct Funct. 2017. PMID: 27259586
-
Conditional genetic transsynaptic tracing in the embryonic mouse brain.J Vis Exp. 2014 Dec 22;(94):52487. doi: 10.3791/52487. J Vis Exp. 2014. PMID: 25549135 Free PMC article.
-
[Visualization of selective transsynaptic neural pathways using a genetic method].Brain Nerve. 2010 Mar;62(3):233-42. Brain Nerve. 2010. PMID: 20297728 Review. Japanese.
-
Viral Vectors for Neural Circuit Mapping and Recent Advances in Trans-synaptic Anterograde Tracers.Neuron. 2020 Sep 23;107(6):1029-1047. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2020.07.010. Epub 2020 Aug 4. Neuron. 2020. PMID: 32755550 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Viral vector-based tools advance knowledge of basal ganglia anatomy and physiology.J Neurophysiol. 2016 Apr;115(4):2124-46. doi: 10.1152/jn.01131.2015. Epub 2016 Feb 17. J Neurophysiol. 2016. PMID: 26888111 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Towards new uses of botulinum toxin as a novel therapeutic tool.Toxins (Basel). 2011 Jan;3(1):63-81. doi: 10.3390/toxins3010063. Epub 2011 Jan 12. Toxins (Basel). 2011. PMID: 22069690 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dietary Plant Lectins Appear to Be Transported from the Gut to Gain Access to and Alter Dopaminergic Neurons of Caenorhabditis elegans, a Potential Etiology of Parkinson's Disease.Front Nutr. 2016 Mar 7;3:7. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2016.00007. eCollection 2016. Front Nutr. 2016. PMID: 27014695 Free PMC article.
-
Profiling metabolites and peptides in single cells.Nat Methods. 2011 Apr;8(4 Suppl):S20-9. doi: 10.1038/nmeth.1549. Epub 2011 Mar 30. Nat Methods. 2011. PMID: 21451513 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Intranasal Delivery of Targeted Nanoparticles Loaded With miR-132 to Brain for the Treatment of Neurodegenerative Diseases.Front Pharmacol. 2020 Aug 6;11:1165. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2020.01165. eCollection 2020. Front Pharmacol. 2020. PMID: 32848773 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Boldogkoi Z, Sik A, Denes A, et al. Novel tracing paradigms-genetically engineered herpes viruses as tools for mapping functional circuits within the CNS: present status and future prospects. Prog. Neurobiol. 2004;72(6):417–445. - PubMed
-
- Yoshihara Y. Visualizing selective neural pathways with WGA transgene: combination of neuroanatomy with gene technology. Neurosci. Res. 2002;44(2):133–140. - PubMed
-
-
Kobbert C, Apps R, Bechmann I, et al. Current concepts in neuroanatomical tracing. Prog. Neurobiol. 2000;62(4):327–351. · · Review on the conventional tracing method
-
-
- Thanos S, Vidal-Sanz M, Aguayo AJ. The use of rhodamine-B-isothiocyanate (RITC) as an anterograde and retrograde tracer in the adult rat visual system. Brain Res. 1987;406(1–2):317–321. - PubMed
-
- Godement P, Vanselow J, Thanos S, Bonhoeffer F. A study in developing visual systems with a new method of staining neurones and their processes in fixed tissue. Development. 1987;101(4):697–713. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
