Dicer's helicase domain is required for accumulation of some, but not all, C. elegans endogenous siRNAs
- PMID: 20354150
- PMCID: PMC2856884
- DOI: 10.1261/rna.2122010
Dicer's helicase domain is required for accumulation of some, but not all, C. elegans endogenous siRNAs
Abstract
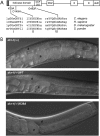
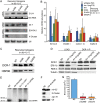
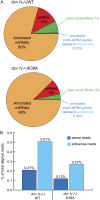
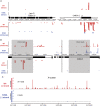
Years after the discovery that Dicer is a key enzyme in gene silencing, the role of its helicase domain remains enigmatic. Here we show that this domain is critical for accumulation of certain endogenous small interfering RNAs (endo-siRNAs) in Caenorhabditis elegans. The domain is required for the production of the direct products of Dicer, or primary endo-siRNAs, and consequently affects levels of downstream intermediates, the secondary endo-siRNAs. Consistent with the role of endo-siRNAs in silencing, their loss correlates with an increase in cognate mRNA levels. We find that the helicase domain of Dicer is not necessary for microRNA (miRNA) processing, or RNA interference following exposure to exogenous double-stranded RNA. Comparisons of wild-type and helicase-defective strains using deep-sequencing analyses show that the helicase domain is required by a subset of annotated endo-siRNAs, in particular, those associated with the slightly longer 26-nucleotide small RNA species containing a 5' guanosine.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Dicer's helicase domain discriminates dsRNA termini to promote an altered reaction mode.Mol Cell. 2011 Mar 4;41(5):589-99. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2011.02.005. Mol Cell. 2011. PMID: 21362554 Free PMC article.
-
A role for the Dicer helicase domain in the processing of thermodynamically unstable hairpin RNAs.Nucleic Acids Res. 2008 Nov;36(20):6511-22. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkn687. Epub 2008 Oct 15. Nucleic Acids Res. 2008. PMID: 18927112 Free PMC article.
-
Biology and Mechanisms of Short RNAs in Caenorhabditis elegans.Adv Genet. 2013;83:1-69. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-407675-4.00001-8. Adv Genet. 2013. PMID: 23890211 Review.
-
In vitro analyses of the production and activity of secondary small interfering RNAs in C. elegans.EMBO J. 2007 Dec 12;26(24):5007-19. doi: 10.1038/sj.emboj.7601910. Epub 2007 Nov 15. EMBO J. 2007. PMID: 18007599 Free PMC article.
-
Short silencing RNA: the dark matter of genetics?Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 2006;71:13-20. doi: 10.1101/sqb.2006.71.052. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 2006. PMID: 17381275 Review.
Cited by
-
Recognition of the pre-miRNA structure by Drosophila Dicer-1.Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2011 Sep 18;18(10):1153-8. doi: 10.1038/nsmb.2125. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2011. PMID: 21926993
-
A conserved PHD finger protein and endogenous RNAi modulate insulin signaling in Caenorhabditis elegans.PLoS Genet. 2011 Sep;7(9):e1002299. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1002299. Epub 2011 Sep 29. PLoS Genet. 2011. PMID: 21980302 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of ADARs on small RNA processing pathways in C. elegans.Genome Res. 2012 Aug;22(8):1488-98. doi: 10.1101/gr.134841.111. Epub 2012 Jun 6. Genome Res. 2012. PMID: 22673872 Free PMC article.
-
Dual roles for nuclear RNAi Argonautes in Caenorhabditis elegans dosage compensation.Genetics. 2022 May 5;221(1):iyac033. doi: 10.1093/genetics/iyac033. Genetics. 2022. PMID: 35234908 Free PMC article.
-
Evolutionarily conserved roles of the dicer helicase domain in regulating RNA interference processing.J Biol Chem. 2014 Oct 10;289(41):28352-62. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M114.589051. Epub 2014 Aug 18. J Biol Chem. 2014. PMID: 25135636 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ambros V, Lee RC, Lavanway A, Williams PT, Jewell D 2003. MicroRNAs and other tiny endogenous RNAs in C. elegans. Curr Biol 13: 807–818 - PubMed
-
- Bernstein E, Caudy AA, Hammond SM, Hannon GJ 2001. Role for a bidentate ribonuclease in the initiation step of RNA interference. Nature 409: 363–366 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
