Reversible N epsilon-lysine acetylation regulates the activity of acyl-CoA synthetases involved in anaerobic benzoate catabolism in Rhodopseudomonas palustris
- PMID: 20345662
- PMCID: PMC2913386
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.2010.07127.x
Reversible N epsilon-lysine acetylation regulates the activity of acyl-CoA synthetases involved in anaerobic benzoate catabolism in Rhodopseudomonas palustris
Abstract
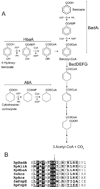
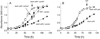
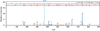
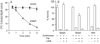
Rhodopseudomonas palustris grows photoheterotrophically on aromatic compounds available in aquatic environments rich in plant-derived lignin. Benzoate degradation is regulated at the transcriptional level in R. palustris in response to anoxia and the presence of benzoate and/or benzoyl-CoA (Bz-CoA). Here, we report evidence that anaerobic benzoate catabolism in this bacterium is also regulated at the post-translational level. In this pathway, benzoate is activated to Bz-CoA by the AMP-forming Bz-CoA synthetase (BadA) enzyme. Mass spectrometry and mutational analysis data indicate that residue Lys512 is critical to BadA activity. Acetylation of Lys512 inactivated BadA; deacetylation reactivated BadA. Likewise, 4-hydroxybenzoyl-CoA (HbaA) and cyclohexanecarboxyl-CoA (AliA) synthetases were also reversibly acetylated. We identified one acetyltransferase that modified BadA, Hba and AliA in vitro. The acetyltransferase enzyme is homologous to the protein acetyltransferase (Pat) enzyme of Salmonella enterica sv Typhimurium LT2, thus we refer to it as RpPat. RpPat also modified acetyl-CoA (Ac-CoA) synthetase (Acs) from R. palustris. In vivo data indicate that at least two deacetylases reactivate BadA(Ac). One is SrtN (encoded by srtN, formerly rpa2524), a sirtuin-type NAD(+)-dependent deacetylase (O-acetyl-ADPribose-forming); the other deacetylase is LdaA (encoded by ldaA, for lysine deacetylase A; formerly rpa0954), an acetate-forming protein deacetylase. LdaA reactivated Hba(Ac) and AliA(Ac)in vitro.
Figures



Similar articles
-
The acetylation motif in AMP-forming Acyl coenzyme A synthetases contains residues critical for acetylation and recognition by the protein acetyltransferase pat of Rhodopseudomonas palustris.J Bacteriol. 2014 Apr;196(8):1496-504. doi: 10.1128/JB.00004-14. Epub 2014 Jan 31. J Bacteriol. 2014. PMID: 24488314 Free PMC article.
-
Benzoate-coenzyme A ligase, encoded by badA, is one of three ligases able to catalyze benzoyl-coenzyme A formation during anaerobic growth of Rhodopseudomonas palustris on benzoate.J Bacteriol. 1995 Nov;177(22):6545-51. doi: 10.1128/jb.177.22.6545-6551.1995. J Bacteriol. 1995. PMID: 7592432 Free PMC article.
-
System-wide studies of N-lysine acetylation in Rhodopseudomonas palustris reveal substrate specificity of protein acetyltransferases.J Biol Chem. 2012 May 4;287(19):15590-601. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M112.352104. Epub 2012 Mar 13. J Biol Chem. 2012. PMID: 22416131 Free PMC article.
-
The bacterial degradation of benzoic acid and benzenoid compounds under anaerobic conditions: unifying trends and new perspectives.FEMS Microbiol Rev. 1994 Apr;13(4):441-68. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6976.1994.tb00061.x. FEMS Microbiol Rev. 1994. PMID: 8011356 Review.
-
Post-translational Lysine Ac(et)ylation in Bacteria: A Biochemical, Structural, and Synthetic Biological Perspective.Front Microbiol. 2021 Oct 11;12:757179. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2021.757179. eCollection 2021. Front Microbiol. 2021. PMID: 34721364 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Bacterial protein acetylation: mechanisms, functions, and methods for study.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2024 Jul 4;14:1408947. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2024.1408947. eCollection 2024. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 39027134 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Staphylococcus aureus modulates the activity of acetyl-Coenzyme A synthetase (Acs) by sirtuin-dependent reversible lysine acetylation.Mol Microbiol. 2019 Aug;112(2):588-604. doi: 10.1111/mmi.14276. Epub 2019 May 27. Mol Microbiol. 2019. PMID: 31099918 Free PMC article.
-
Functional Insights Into Protein Acetylation in the Hyperthermophilic Archaeon Sulfolobus islandicus.Mol Cell Proteomics. 2019 Aug;18(8):1572-1587. doi: 10.1074/mcp.RA119.001312. Epub 2019 Jun 9. Mol Cell Proteomics. 2019. PMID: 31182439 Free PMC article.
-
Acetylation of acetyl-CoA synthetase from Mycobacterium tuberculosis leads to specific inactivation of the adenylation reaction.Arch Biochem Biophys. 2014 May 15;550-551:42-9. doi: 10.1016/j.abb.2014.04.004. Epub 2014 Apr 18. Arch Biochem Biophys. 2014. PMID: 24751484 Free PMC article.
-
Protein acetylation affects acetate metabolism, motility and acid stress response in Escherichia coli.Mol Syst Biol. 2014 Nov 27;10(11):762. doi: 10.15252/msb.20145227. Mol Syst Biol. 2014. PMID: 25518064 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bains J, Boulanger MJ. Biochemical and structural characterization of the paralogous benzoate CoA ligases from Burkholderia xenovorans LB400: defining the entry point into the novel benzoate oxidation (box) pathway. J. Mol. Biol. 2007;373:965–977. - PubMed
-
- Barragan MJ, Blazquez B, Zamarro MT, Mancheno JM, Garcia JL, Diaz E, Carmona M. BzdR, a repressor that controls the anaerobic catabolism of benzoate in Azoarcus sp. CIB, is the first member of a new subfamily of transcriptional regulators. J. Biol. Chem. 2005;280:10683–10694. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

