Widespread circulation of echovirus type 13 demonstrated by increased seroprevalence in Toyama, Japan, between 2000 and 2003
- PMID: 20335430
- PMCID: PMC2863381
- DOI: 10.1128/CVI.00239-09
Widespread circulation of echovirus type 13 demonstrated by increased seroprevalence in Toyama, Japan, between 2000 and 2003
Abstract
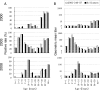
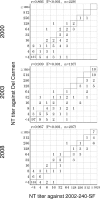
To confirm the magnitude of an echovirus type 13 (E13) outbreak in 2002 and to evaluate whether genetic and antigenic changes in E13 influenced the occurrence of the outbreak, we measured titers of neutralizing (NT) antibody against the Toyama, 2002-240-SF, and prototype Del Carmen E13 strains among inhabitants of Toyama before and after 2002. The rate of positivity for NT antibodies against both 2002-240-SF and Del Carmen in 2003 made a remarkable upturn in children 0 to 14 years old, compared to that in 2000. Titers of NT antibody against strain 2002-240-SF of inhabitants were slightly higher than those against Del Carmen, whereas anti-E13 rabbit serum raised against either strain Del Carmen or 2002-240-SF showed almost the same titer of NT antibody against both strains. These data indicate that the antigenic properties of the strains may be slightly different. Differences in amino acids between strains 2002-240-SF and Del Carmen in the VP4, VP2, VP3, and VP1 regions may affect both antigenic and receptor binding properties, even though they do not seem to be significant enough to escape widespread immunity. One of the factors of the outbreak was thought to be the increase in susceptibility in the young generation.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Epidemiological studies on echovirus type 18 infection in Toyama Prefecture.Microbiol Immunol. 1983;27(4):359-68. doi: 10.1111/j.1348-0421.1983.tb00594.x. Microbiol Immunol. 1983. PMID: 6888292
-
[Epidemic of aseptic meningitis with echovirus type 18 in Gifu Prefecture in 1988].Kansenshogaku Zasshi. 1990 Jul;64(7):815-21. doi: 10.11150/kansenshogakuzasshi1970.64.815. Kansenshogaku Zasshi. 1990. PMID: 2230370 Japanese.
-
Outbreak of aseptic meningitis caused by echovirus 30 in Kushiro, Japan in 2017.J Clin Virol. 2019 Jul;116:34-38. doi: 10.1016/j.jcv.2019.05.001. Epub 2019 May 6. J Clin Virol. 2019. PMID: 31082730
-
Re-emergence of echovirus type 13 infections in 2002 in Yamagata, Japan.J Infect. 2003 Oct;47(3):243-7. doi: 10.1016/s0163-4453(03)00081-1. J Infect. 2003. PMID: 12963387
-
[Epidemic of aseptic meningitis with echovirus type 30 in Gifu Prefecture].Kansenshogaku Zasshi. 1993 Nov;67(11):1068-75. doi: 10.11150/kansenshogakuzasshi1970.67.1068. Kansenshogaku Zasshi. 1993. PMID: 8270799 Japanese.
Cited by
-
Recombination among human non-polio enteroviruses: implications for epidemiology and evolution.Virus Genes. 2015 Apr;50(2):177-88. doi: 10.1007/s11262-014-1152-y. Epub 2014 Dec 24. Virus Genes. 2015. PMID: 25537948 Review.
-
Environmental surveillance of poliovirus in sewage water around the introduction period for inactivated polio vaccine in Japan.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2015 Mar;81(5):1859-64. doi: 10.1128/AEM.03575-14. Epub 2015 Jan 2. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2015. PMID: 25556189 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic characterization of a novel recombinant echovirus 30 strain causing a regional epidemic of aseptic meningitis in Hokkaido, Japan, 2017.Arch Virol. 2020 Feb;165(2):433-438. doi: 10.1007/s00705-019-04484-7. Epub 2019 Dec 11. Arch Virol. 2020. PMID: 31828510 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bingjun, T., H. Yoshida, Y. Wu, L. Lu, T. Tsuji, H. Shimizu, and T. Miyamura. 2008. Molecular typing and epidemiology of non-polio enteroviruses isolated from Yunnan Province, the People's Republic of China. J. Med. Virol. 80:670-679. - PubMed
-
- Buttinelli, G., V. Donati, F. M. Ruggeri, P. Joki-Korpela, T. Hyypia, and L. Fiore. 2003. Antigenic sites of coxsackie A9 virus inducing neutralizing monoclonal antibodies protective in mice. Virology 312:74-83. - PubMed
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. 2001. Echovirus type 13—United States, 2001. MMWR 50:777-780. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

