Proteasome inhibitor PS-341 (bortezomib) induces calpain-dependent IkappaB(alpha) degradation
- PMID: 20335171
- PMCID: PMC2871478
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M109.072694
Proteasome inhibitor PS-341 (bortezomib) induces calpain-dependent IkappaB(alpha) degradation
Erratum in
-
Correction: Proteasome inhibitor PS-341 (bortezomib) induces calpain-dependent IκBα degradation.J Biol Chem. 2020 Jun 26;295(26):8869. doi: 10.1074/jbc.AAC120.014434. J Biol Chem. 2020. PMID: 32591445 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
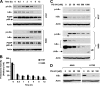
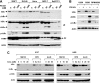
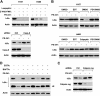
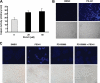
The proteasome, a key component of the ubiquitin-proteasome pathway, has emerged as an important cancer therapeutic target. PS-341 (also called Bortezomib or Velcade) is the first proteasome inhibitor approved for newly diagnosed and relapsed multiple myeloma and is currently being tested in many clinical trials against other types of cancers. One proposed mechanism by which PS-341 exerts its anticancer effect is inactivation of nuclear factor-kappaB (NF-kappaB) through prevention of IkappaB(alpha) degradation. In this study, we show that PS-341 at concentrations that effectively inhibited the growth of human cancer cells, instead of increasing IkappaB(alpha) stability, paradoxically induced IkappaB(alpha) degradation. As a result, PS-341 facilitated p65 nuclear translocation and increased NF-kappaB activity. Moreover, IkappaB(alpha) degradation by PS-341 occurred early before induction of apoptosis and could not be inhibited by a pan-caspase inhibitor or caspase-8 silencing; however, it could be prevented with calpain inhibitors, calcium-chelating agents, calpain knockdown, or calpastatin overexpression. In agreement, PS-341 increased calpain activity. These data together indicate that PS-341 induces a calpain-mediated IkappaB(alpha) degradation independent of caspases. In the presence of a calpain inhibitor, the apoptosis-inducing activity of PS-341 was dramatically enhanced. Collectively, these unexpected findings suggest not only a novel paradigm regarding the relationship between proteasome inhibition and NF-kappaB activity but also a strategy to enhance the anticancer efficacy of PS-341.
Figures

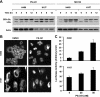
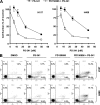
Similar articles
-
The proteasome inhibitor PS-341 markedly enhances sensitivity of multiple myeloma tumor cells to chemotherapeutic agents.Clin Cancer Res. 2003 Mar;9(3):1136-44. Clin Cancer Res. 2003. PMID: 12631619
-
Induction of cell cycle arrest and apoptosis by the proteasome inhibitor PS-341 in Hodgkin disease cell lines is independent of inhibitor of nuclear factor-kappaB mutations or activation of the CD30, CD40, and RANK receptors.Clin Cancer Res. 2004 May 1;10(9):3207-15. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.ccr-03-0494. Clin Cancer Res. 2004. PMID: 15131062
-
The role of nuclear factor-kappaB in the biology and treatment of multiple myeloma.Semin Oncol. 2001 Dec;28(6):626-33. doi: 10.1016/s0093-7754(01)90036-3. Semin Oncol. 2001. PMID: 11740821 Review.
-
Bortezomib induces canonical nuclear factor-kappaB activation in multiple myeloma cells.Blood. 2009 Jul 30;114(5):1046-52. doi: 10.1182/blood-2009-01-199604. Epub 2009 May 12. Blood. 2009. PMID: 19436050 Free PMC article.
-
Proteasome inhibition in cancer: development of PS-341.Semin Oncol. 2001 Dec;28(6):613-9. doi: 10.1016/s0093-7754(01)90034-x. Semin Oncol. 2001. PMID: 11740819 Review.
Cited by
-
Therapeutic trial of metformin and bortezomib in a mouse model of tuberous sclerosis complex (TSC).PLoS One. 2012;7(2):e31900. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0031900. Epub 2012 Feb 21. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22363765 Free PMC article.
-
Macrolide antibiotics block autophagy flux and sensitize to bortezomib via endoplasmic reticulum stress-mediated CHOP induction in myeloma cells.Int J Oncol. 2013 May;42(5):1541-50. doi: 10.3892/ijo.2013.1870. Epub 2013 Mar 28. Int J Oncol. 2013. PMID: 23546223 Free PMC article.
-
Regulatory role of proteasome in determination of platelet life span.J Biol Chem. 2013 Mar 8;288(10):6826-34. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M112.403154. Epub 2013 Jan 17. J Biol Chem. 2013. PMID: 23329846 Free PMC article.
-
Perturbation of proteasome function by bortezomib leading to ER stress-induced apoptotic cell death in cholangiocarcinoma.J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2013 Sep;139(9):1551-62. doi: 10.1007/s00432-013-1473-6. Epub 2013 Jul 23. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2013. PMID: 23877657
-
Obatoclax interacts synergistically with the irreversible proteasome inhibitor carfilzomib in GC- and ABC-DLBCL cells in vitro and in vivo.Mol Cancer Ther. 2012 May;11(5):1122-32. doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-12-0021. Epub 2012 Mar 12. Mol Cancer Ther. 2012. Retraction in: Mol Cancer Ther. 2019 Jun;18(6):1180. doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-19-0470 PMID: 22411899 Free PMC article. Retracted.
References
-
- Adams J. (2004) Nat. Rev. Cancer 4, 349–360 - PubMed
-
- Rajkumar S. V., Richardson P. G., Hideshima T., Anderson K. C. (2005) J. Clin. Oncol. 23, 630–639 - PubMed
-
- Zavrski I., Jakob C., Schmid P., Krebbel H., Kaiser M., Fleissner C., Rosche M., Possinger K., Sezer O. (2005) Anticancer Drugs 16, 475–481 - PubMed
-
- Adams J., Kauffman M. (2004) Cancer Invest. 22, 304–311 - PubMed
-
- Richardson P. G., Mitsiades C., Hideshima T., Anderson K. C. (2006) Annu. Rev. Med. 57, 33–47 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

