Ultrasound-enhanced microfluidic synthesis of liposomes
- PMID: 20332455
- PMCID: PMC3789511
Ultrasound-enhanced microfluidic synthesis of liposomes
Abstract
Background: Liposomes have been successfully used as delivery vehicles for anticancer drugs. Both sonication and microfluidic technologies have been used to produce liposomes. The combination of the two methods was evaluated in this study.
Materials and methods: The microfluidic devices, mainly comprising micro-dispensers and a sonicator, were used to produce liposomal nanoparticles. Sonication was used to enhance the reduction of liposome size.
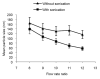
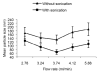
Results: Sonication significantly reduced the size of the liposomes. The particle size also decreased as the buffer to solvent flow rate ratio increased. The smallest particle sizes were achieved with a volumetric flow rate of lipids at 0.374 ml/min.
Conclusion: The microfluidic devices in combination with ultrasound are simple and may be used to produce liposomal nanoparticles with narrow size distribution.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Microfluidic synthesis of PEG- and folate-conjugated liposomes for one-step formation of targeted stealth nanocarriers.Pharm Res. 2013 Jun;30(6):1597-607. doi: 10.1007/s11095-013-0998-3. Epub 2013 Feb 6. Pharm Res. 2013. PMID: 23386106 Free PMC article.
-
Microfluidic directed formation of liposomes of controlled size.Langmuir. 2007 May 22;23(11):6289-93. doi: 10.1021/la070051a. Epub 2007 Apr 24. Langmuir. 2007. PMID: 17451256
-
Microfluidic methods for production of liposomes.Methods Enzymol. 2009;465:129-41. doi: 10.1016/S0076-6879(09)65007-2. Methods Enzymol. 2009. PMID: 19913165 Free PMC article.
-
Liposome production by microfluidics: potential and limiting factors.Sci Rep. 2016 May 19;6:25876. doi: 10.1038/srep25876. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 27194474 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Microfluidics-mediated Liposomal Nanoparticles for Cancer Therapy: Recent Developments on Advanced Devices and Technologies.Curr Top Med Chem. 2024;24(14):1185-1211. doi: 10.2174/0115680266286460240220073334. Curr Top Med Chem. 2024. PMID: 38424436 Review.
Cited by
-
Controlled nucleation of lipid nanoparticles.Pharm Res. 2012 Aug;29(8):2236-48. doi: 10.1007/s11095-012-0752-2. Epub 2012 Apr 28. Pharm Res. 2012. PMID: 22544683
-
pH-responsive high-density lipoprotein-like nanoparticles to release paclitaxel at acidic pH in cancer chemotherapy.Int J Nanomedicine. 2012;7:2805-16. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S29817. Epub 2012 Jun 6. Int J Nanomedicine. 2012. PMID: 22745543 Free PMC article.
-
Microfluidic Hydrodynamic Focusing for Synthesis of Nanomaterials.Nano Today. 2016 Dec;11(6):778-792. doi: 10.1016/j.nantod.2016.10.006. Epub 2016 Nov 12. Nano Today. 2016. PMID: 30337950 Free PMC article.
-
DoE-derived continuous and robust process for manufacturing of pharmaceutical-grade wide-range LNPs for RNA-vaccine/drug delivery.Sci Rep. 2022 Jun 7;12(1):9394. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-12100-z. Sci Rep. 2022. PMID: 35672337 Free PMC article.
-
Development of Dual Drug Loaded Nanosized Liposomal Formulation by A Reengineered Ethanolic Injection Method and Its Pre-Clinical Pharmacokinetic Studies.Pharmaceutics. 2018 Sep 6;10(3):151. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics10030151. Pharmaceutics. 2018. PMID: 30200557 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Gregoriadis G. Liposome Technology. New York: Taylor & Francis/Informa; 2006.
-
- Torchilin VP. Recent advances with liposomes as pharmaceutical carriers. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2005;4(2):145–160. - PubMed
-
- Fenske DB, Cullis PR. Liposomal nanomedicines. Expert Opin Drug Deliv. 2008;5(1):25–44. - PubMed
-
- Abraham SA, Waterhouse DN, Mayer LD, Cullis PR, Madden TD, Bally MB. The liposomal formulation of doxorubicin. Methods Enzymol. 2005;391:71–97. - PubMed
-
- Pan XQ, Lee RJ. In vivo antitumor activity of folate receptor-targeted liposomal daunorubicin in a murine leukemia model. Anticancer Res. 2005;25(1A):343–346. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
