Functional delivery of viral miRNAs via exosomes
- PMID: 20304794
- PMCID: PMC2851954
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0914843107
Functional delivery of viral miRNAs via exosomes
Abstract
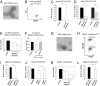
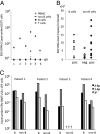
Noncoding regulatory microRNAs (miRNAs) of cellular and viral origin control gene expression by repressing the translation of mRNAs into protein. Interestingly, miRNAs are secreted actively through small vesicles called "exosomes" that protect them from degradation by RNases, suggesting that these miRNAs may function outside the cell in which they were produced. Here we demonstrate that miRNAs secreted by EBV-infected cells are transferred to and act in uninfected recipient cells. Using a quantitative RT-PCR approach, we demonstrate that mature EBV-encoded miRNAs are secreted by EBV-infected B cells through exosomes. These EBV-miRNAs are functional because internalization of exosomes by MoDC results in a dose-dependent, miRNA-mediated repression of confirmed EBV target genes, including CXCL11/ITAC, an immunoregulatory gene down-regulated in primary EBV-associated lymphomas. We demonstrate that throughout coculture of EBV-infected B cells EBV-miRNAs accumulate in noninfected neighboring MoDC and show that this accumulation is mediated by transfer of exosomes. Thus, the exogenous EBV-miRNAs transferred through exosomes are delivered to subcellular sites of gene repression in recipient cells. Finally, we show in peripheral blood mononuclear cells from patients with increased EBV load that, although EBV DNA is restricted to the circulating B-cell population, EBV BART miRNAs are present in both B-cell and non-B-cell fractions, suggestive of miRNA transfer. Taken together our findings are consistent with miRNA-mediated gene silencing as a potential mechanism of intercellular communication between cells of the immune system that may be exploited by the persistent human gamma-herpesvirus EBV.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
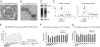

Similar articles
-
Viral miRNAs exploiting the endosomal-exosomal pathway for intercellular cross-talk and immune evasion.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2011 Nov-Dec;1809(11-12):715-21. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagrm.2011.08.002. Epub 2011 Aug 9. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2011. PMID: 21855666
-
Role of exosomes as a proinflammatory mediator in the development of EBV-associated lymphoma.Blood. 2018 Jun 7;131(23):2552-2567. doi: 10.1182/blood-2017-07-794529. Epub 2018 Apr 22. Blood. 2018. PMID: 29685921
-
Clustered microRNAs of the Epstein-Barr virus cooperatively downregulate an epithelial cell-specific metastasis suppressor.J Virol. 2015 Mar;89(5):2684-97. doi: 10.1128/JVI.03189-14. Epub 2014 Dec 17. J Virol. 2015. PMID: 25520514 Free PMC article.
-
Multifunctional non-coding Epstein-Barr virus encoded RNAs (EBERs) contribute to viral pathogenesis.Virus Res. 2016 Jan 2;212:30-8. doi: 10.1016/j.virusres.2015.08.007. Epub 2015 Aug 18. Virus Res. 2016. PMID: 26292159 Review.
-
Regulation of the MIR155 host gene in physiological and pathological processes.Gene. 2013 Dec 10;532(1):1-12. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2012.12.009. Epub 2012 Dec 14. Gene. 2013. PMID: 23246696 Review.
Cited by
-
Hepatitis Viruses Control Host Immune Responses by Modifying the Exosomal Biogenesis Pathway and Cargo.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Sep 17;23(18):10862. doi: 10.3390/ijms231810862. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36142773 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Extracellular Vesicles Tracking and Quantification Using CT and Optical Imaging in Rats.Bio Protoc. 2020 Jun 5;10(11):e3635. doi: 10.21769/BioProtoc.3635. eCollection 2020 Jun 5. Bio Protoc. 2020. PMID: 33659306 Free PMC article.
-
Involvement of extracellular vesicle microRNA clusters in developing healthy and Rett syndrome brain organoids.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2024 Sep 21;81(1):410. doi: 10.1007/s00018-024-05409-7. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2024. PMID: 39305343 Free PMC article.
-
Extracellular vesicles and their convergence with viral pathways.Adv Virol. 2012;2012:767694. doi: 10.1155/2012/767694. Epub 2012 Jul 25. Adv Virol. 2012. PMID: 22888349 Free PMC article.
-
Recent Advances in Understanding of NASH: MicroRNAs as Both Biochemical Markers and Players.Curr Pathobiol Rep. 2014 Sep 1;2(3):109-115. doi: 10.1007/s40139-014-0049-8. Curr Pathobiol Rep. 2014. PMID: 25574453 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

