Allosteric drug discrimination is coupled to mechanochemical changes in the kinesin-5 motor core
- PMID: 20299460
- PMCID: PMC2881790
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M109.092072
Allosteric drug discrimination is coupled to mechanochemical changes in the kinesin-5 motor core
Abstract
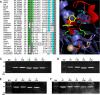
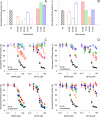
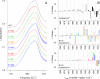
Essential in mitosis, the human Kinesin-5 protein is a target for >80 classes of allosteric compounds that bind to a surface-exposed site formed by the L5 loop. Not established is why there are differing efficacies in drug inhibition. Here we compare the ligand-bound states of two L5-directed inhibitors against 15 Kinesin-5 mutants by ATPase assays and IR spectroscopy. Biochemical kinetics uncovers functional differences between individual residues at the N or C termini of the L5 loop. Infrared evaluation of solution structures and multivariate analysis of the vibrational spectra reveal that mutation and/or ligand binding not only can remodel the allosteric binding surface but also can transmit long range effects. Changes in L5-localized 3(10) helix and disordered content, regardless of substitution or drug potency, are experimentally detected. Principal component analysis couples these local structural events to two types of rearrangements in beta-sheet hydrogen bonding. These transformations in beta-sheet contacts are correlated with inhibitory drug response and are corroborated by wild type Kinesin-5 crystal structures. Despite considerable evolutionary divergence, our data directly support a theorized conserved element for long distance mechanochemical coupling in kinesin, myosin, and F(1)-ATPase. These findings also suggest that these relatively rapid IR approaches can provide structural biomarkers for clinical determination of drug sensitivity and drug efficacy in nucleotide triphosphatases.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Novel Allosteric Pathway of Eg5 Regulation Identified through Multivariate Statistical Analysis of Hydrogen-Exchange Mass Spectrometry (HX-MS) Ligand Screening Data.Mol Cell Proteomics. 2017 Mar;16(3):428-437. doi: 10.1074/mcp.M116.064246. Epub 2017 Jan 5. Mol Cell Proteomics. 2017. PMID: 28062800 Free PMC article.
-
An allosteric transition trapped in an intermediate state of a new kinesin-inhibitor complex.Biochem J. 2009 Dec 14;425(1):55-60. doi: 10.1042/BJ20091207. Biochem J. 2009. PMID: 19793049
-
Structural basis of new allosteric inhibition in Kinesin spindle protein Eg5.ACS Chem Biol. 2015 Apr 17;10(4):1128-36. doi: 10.1021/cb500939x. Epub 2015 Feb 3. ACS Chem Biol. 2015. PMID: 25622007
-
Kinesin and myosin ATPases: variations on a theme.Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1992 Apr 29;336(1276):13-7; discussion 17-8. doi: 10.1098/rstb.1992.0038. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1992. PMID: 1351290 Review.
-
Structure-mutation analysis of the ATPase site of Dictyostelium discoideum myosin II.Adv Biophys. 1998;35:1-24. Adv Biophys. 1998. PMID: 9949764 Review.
Cited by
-
Microtubule capture by mitotic kinesin centromere protein E (CENP-E).J Biol Chem. 2012 Jul 20;287(30):24894-904. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M112.376830. Epub 2012 May 27. J Biol Chem. 2012. PMID: 22637578 Free PMC article.
-
Loop 5-directed compounds inhibit chimeric kinesin-5 motors: implications for conserved allosteric mechanisms.J Biol Chem. 2011 Feb 25;286(8):6201-10. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.154989. Epub 2010 Dec 2. J Biol Chem. 2011. PMID: 21127071 Free PMC article.
-
Insights into the Molecular Mechanisms of Eg5 Inhibition by (+)-Morelloflavone.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2019 Apr 16;12(2):58. doi: 10.3390/ph12020058. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2019. PMID: 30995725 Free PMC article.
-
Src family kinase phosphorylation of the motor domain of the human kinesin-5, Eg5.Cytoskeleton (Hoboken). 2017 Sep;74(9):317-330. doi: 10.1002/cm.21380. Epub 2017 Jul 25. Cytoskeleton (Hoboken). 2017. PMID: 28646493 Free PMC article.
-
Drug resistance dependent on allostery: A P-loop rigor Eg5 mutant exhibits resistance to allosteric inhibition by STLC.Front Oncol. 2022 Oct 12;12:965455. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.965455. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 36313676 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Gunasekaran K., Ma B., Nussinov R. (2004) Proteins 57, 433–443 - PubMed
-
- Monod J., Wyman J., Changeux J. P. (1965) J. Mol. Biol. 12, 88–118 - PubMed
-
- Kern D., Zuiderweg E. R. (2003) Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 13, 748–757 - PubMed
-
- Cooper A., Dryden D. T. (1984) Eur. Biophys. J. 11, 103–109 - PubMed
-
- Hotha S., Yarrow J. C., Yang J. G., Garrett S., Renduchintala K. V., Mayer T. U., Kapoor T. M. (2003) Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 42, 2379–2382 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

