Activity of retinoic acid receptor-alpha is directly regulated at its protein kinase A sites in response to follicle-stimulating hormone signaling
- PMID: 20215566
- PMCID: PMC2869257
- DOI: 10.1210/en.2009-1338
Activity of retinoic acid receptor-alpha is directly regulated at its protein kinase A sites in response to follicle-stimulating hormone signaling
Abstract
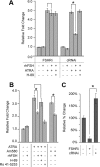
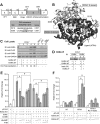
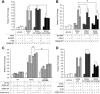
Retinoic acid receptor-alpha (RARA) is crucial for germ cell development in the testis, as shown by the degenerated testis in Rara gene knockout mice, which are sterile. Similarly, FSH is known to regulate Sertoli cell proliferation and differentiation, indirectly controlling the quantity of the spermatogenic output. Interestingly, FSH inhibited, via activation of FSH receptor, cAMP, and protein kinase A (PKA), the nuclear localization and transcriptional activity of RARA. Given that retinoic acid, the ligand for RARA, is known to regulate cell proliferation and differentiation, we investigated whether FSH regulates RARA by a direct posttranslational phosphorylation mechanism. Mutagenesis of serine 219 (S219) and S369 at the PKA sites on RARA to either double alanines or double glutamic acids showed that both PKA sites are important for RARA activity. The negative charges at the PKA sites, whether they are from glutamic acids or phosphorylation of serines, decreased the nuclear localization of RARA, heterodimerization with retinoid X receptor-alpha, and the transcriptional activity of the receptor. On the other hand, the double-alanine mutant that cannot be phosphorylated at the 219 and 369 amino acid positions did not respond to cAMP and PKA activation. Wild-type and double-mutant RARA interacted with PKA, but only in the presence of cAMP or FSH. These results together suggest that FSH may regulate cell proliferation and differentiation of Sertoli cells, at least partially, by directly affecting the PKA sites of RARA and controlling the transcriptional function of the receptor.
Figures
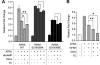


Similar articles
-
Small ubiquitin-like modifier-2 modification of retinoic acid receptor-alpha regulates its subcellular localization and transcriptional activity.Endocrinology. 2009 Dec;150(12):5586-95. doi: 10.1210/en.2009-0868. Epub 2009 Oct 22. Endocrinology. 2009. PMID: 19850744 Free PMC article.
-
Follicle-stimulating hormone inhibits all-trans-retinoic acid-induced retinoic acid receptor alpha nuclear localization and transcriptional activation in mouse Sertoli cell lines.J Biol Chem. 2000 Feb 11;275(6):4145-51. doi: 10.1074/jbc.275.6.4145. J Biol Chem. 2000. PMID: 10660575
-
Follicle-stimulating hormone activates p70 ribosomal protein S6 kinase by protein kinase A-mediated dephosphorylation of Thr 421/Ser 424 in primary Sertoli cells.Mol Endocrinol. 2005 Jul;19(7):1812-20. doi: 10.1210/me.2004-0289. Epub 2005 Mar 17. Mol Endocrinol. 2005. PMID: 15774499
-
[Molecular mechanisms of stimulation and desensitization of Sertoli cells by follicle-stimulating hormone].Reprod Nutr Dev. 1995;35(2):213-35. Reprod Nutr Dev. 1995. PMID: 7734057 Review. French.
-
FSH and testosterone signaling in Sertoli cells.Reproduction. 2005 Jul;130(1):15-28. doi: 10.1530/rep.1.00358. Reproduction. 2005. PMID: 15985628 Review.
Cited by
-
The Role of Retinoic Acid in Spermatogenesis and Its Application in Male Reproduction.Cells. 2024 Jun 24;13(13):1092. doi: 10.3390/cells13131092. Cells. 2024. PMID: 38994945 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mechanistic insight into how gonadotropin hormone receptor complexes direct signaling†.Biol Reprod. 2020 Apr 15;102(4):773-783. doi: 10.1093/biolre/ioz228. Biol Reprod. 2020. PMID: 31882999 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Vitamin A and retinoid signaling: genomic and nongenomic effects.J Lipid Res. 2013 Jul;54(7):1761-75. doi: 10.1194/jlr.R030833. Epub 2013 Feb 24. J Lipid Res. 2013. PMID: 23440512 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Maternal smoking and the retinoid pathway in the developing lung.Respir Res. 2012 Jun 1;13(1):42. doi: 10.1186/1465-9921-13-42. Respir Res. 2012. PMID: 22651576 Free PMC article.
-
Overview of follicle stimulating hormone and its receptors in reproduction and in stem cells and cancer stem cells.Int J Biol Sci. 2022 Jan 1;18(2):675-692. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.63721. eCollection 2022. Int J Biol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35002517 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Griswold MD 1998 The central role of Sertoli cells in spermatogenesis. Semin Cell Dev Biol 9:411–416 - PubMed
-
- Sharpe RM 1994 Regulation of spermatogenesis. In: Knobil E, Neill JD, eds. The physiology of reproduction. 2nd ed. New York: Raven Press; 1363–1434
-
- Kerr J 1999 Male reproductive system. In: Kerr JB, ed. Atlas of functional histology. London: Mosby; 339–353
-
- Russell LD, Ettlin RA, SinhaHikim AP, Clegg ED 1990 Mammalian spermatogenesis. In: Russell LD, Ettlin RA, SinhaHikim AP, Clegg ED, eds. Histological and histopathological evaluation of the testis. Clearwater: Cache River Press; 1–38
-
- Orth J, Christensen AK 1977 Localization of 125I-labeled FSH in the testes of hypophysectomized rats by autoradiography at the light and electron microscope levels. Endocrinology 101:262–278 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

