Interaction of the mu-opioid receptor with GPR177 (Wntless) inhibits Wnt secretion: potential implications for opioid dependence
- PMID: 20214800
- PMCID: PMC2841195
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2202-11-33
Interaction of the mu-opioid receptor with GPR177 (Wntless) inhibits Wnt secretion: potential implications for opioid dependence
Abstract
Background: Opioid agonist drugs produce analgesia. However, long-term exposure to opioid agonists may lead to opioid dependence. The analgesic and addictive properties of opioid agonist drugs are mediated primarily via the mu-opioid receptor (MOR). Opioid agonists appear to alter neuronal morphology in key brain regions implicated in the development of opioid dependence. However, the precise role of the MOR in the development of these neuronal alterations remains elusive. We hypothesize that identifying and characterizing novel MOR interacting proteins (MORIPs) may help to elucidate the underlying mechanisms involved in the development of opioid dependence.
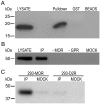
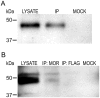
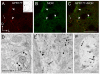
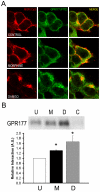
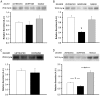
Results: GPR177, the mammalian ortholog of Drosophila Wntless/Evi/Sprinter, was identified as a MORIP in a modified split ubiquitin yeast two-hybrid screen. GPR177 is an evolutionarily conserved protein that plays a critical role in mediating Wnt protein secretion from Wnt producing cells. The MOR/GPR177 interaction was validated in pulldown, coimmunoprecipitation, and colocalization studies using mammalian tissue culture cells. The interaction was also observed in rodent brain, where MOR and GPR177 were coexpressed in close spatial proximity within striatal neurons. At the cellular level, morphine treatment caused a shift in the distribution of GPR177 from cytosol to the cell surface, leading to enhanced MOR/GPR177 complex formation at the cell periphery and the inhibition of Wnt protein secretion.
Conclusions: It is known that chronic morphine treatment decreases dendritic arborization and hippocampal neurogenesis, and Wnt proteins are essential for these processes. We therefore propose that the morphine-mediated MOR/GPR177 interaction may result in decreased Wnt secretion in the CNS, resulting in atrophy of dendritic arbors and decreased neurogenesis. Our results demonstrate a previously unrecognized role for GPR177 in regulating cellular response to opioid drugs.
Figures

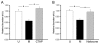

Similar articles
-
Ultrastructural relationship between the mu opioid receptor and its interacting protein, GPR177, in striatal neurons.Brain Res. 2010 Oct 28;1358:71-80. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2010.08.080. Epub 2010 Sep 21. Brain Res. 2010. PMID: 20813097 Free PMC article.
-
Opiate agonist-induced re-distribution of Wntless, a mu-opioid receptor interacting protein, in rat striatal neurons.Exp Neurol. 2012 Jan;233(1):205-13. doi: 10.1016/j.expneurol.2011.09.037. Epub 2011 Oct 6. Exp Neurol. 2012. PMID: 22001156 Free PMC article.
-
Morphine-induced trafficking of a mu-opioid receptor interacting protein in rat locus coeruleus neurons.Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. 2014 Apr 3;50:53-65. doi: 10.1016/j.pnpbp.2013.12.003. Epub 2013 Dec 12. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. 2014. PMID: 24333843 Free PMC article.
-
The mechanism of μ-opioid receptor (MOR)-TRPV1 crosstalk in TRPV1 activation involves morphine anti-nociception, tolerance and dependence.Channels (Austin). 2015;9(5):235-43. doi: 10.1080/19336950.2015.1069450. Epub 2015 Jul 15. Channels (Austin). 2015. PMID: 26176938 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Direct association of Mu-opioid and NMDA glutamate receptors supports their cross-regulation: molecular implications for opioid tolerance.Curr Drug Abuse Rev. 2012 Sep;5(3):199-226. doi: 10.2174/1874473711205030199. Curr Drug Abuse Rev. 2012. PMID: 22920535 Review.
Cited by
-
Morphine Inhibited the Rat Neural Stem Cell Proliferation Rate by Increasing Neuro Steroid Genesis.Neurochem Res. 2016 Jun;41(6):1410-9. doi: 10.1007/s11064-016-1847-7. Epub 2016 Jan 30. Neurochem Res. 2016. PMID: 26830291
-
Ultrastructural relationship between the mu opioid receptor and its interacting protein, GPR177, in striatal neurons.Brain Res. 2010 Oct 28;1358:71-80. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2010.08.080. Epub 2010 Sep 21. Brain Res. 2010. PMID: 20813097 Free PMC article.
-
Opiate agonist-induced re-distribution of Wntless, a mu-opioid receptor interacting protein, in rat striatal neurons.Exp Neurol. 2012 Jan;233(1):205-13. doi: 10.1016/j.expneurol.2011.09.037. Epub 2011 Oct 6. Exp Neurol. 2012. PMID: 22001156 Free PMC article.
-
MOR is not enough: identification of novel mu-opioid receptor interacting proteins using traditional and modified membrane yeast two-hybrid screens.PLoS One. 2013 Jun 28;8(6):e67608. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0067608. Print 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23840749 Free PMC article.
-
Cortical-striatal gene expression in neonatal hippocampal lesion (NVHL)-amplified cocaine sensitization.Genes Brain Behav. 2013 Jul;12(5):564-75. doi: 10.1111/gbb.12051. Epub 2013 Jun 22. Genes Brain Behav. 2013. PMID: 23682998 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

