Highly pathogenic avian influenza A virus H5N1 NS1 protein induces caspase-dependent apoptosis in human alveolar basal epithelial cells
- PMID: 20196872
- PMCID: PMC2854112
- DOI: 10.1186/1743-422X-7-51
Highly pathogenic avian influenza A virus H5N1 NS1 protein induces caspase-dependent apoptosis in human alveolar basal epithelial cells
Abstract
Background: It is widely considered that the multifunctional NS1 protein of influenza A viruses contributes significantly disease pathogenesis by modulating a number of virus and host-cell processes, but it is highly controversial whether this non-structural protein is a proapoptotic or antiapoptotic factor in infected cells.
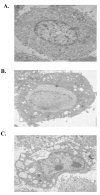
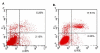
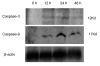
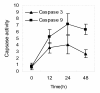
Results: NS1 protein of influenza A/chicken/Jilin/2003 virus, a highly pathogenic H5N1 strain, could induce apoptosis in the carcinomic human alveolar basal epithelial cells (A549) by electron microscopic and flow cytometric analyses. NS1 protein-triggered apoptosis in A549 cells is via caspase-dependent pathway.
Conclusions: Influenza A virus NS1 protein serves as a strong inducer of apoptosis in infected human respiratory epithelial cells and plays a critical role in disease pathogenesis.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Avian influenza virus A/HK/483/97(H5N1) NS1 protein induces apoptosis in human airway epithelial cells.J Virol. 2008 Mar;82(6):2741-51. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01712-07. Epub 2008 Jan 16. J Virol. 2008. PMID: 18199656 Free PMC article.
-
The NS1 protein of influenza A virus interacts with heat shock protein Hsp90 in human alveolar basal epithelial cells: implication for virus-induced apoptosis.Virol J. 2011 Apr 19;8:181. doi: 10.1186/1743-422X-8-181. Virol J. 2011. PMID: 21501532 Free PMC article.
-
A Conserved Residue, Tyrosine (Y) 84, in H5N1 Influenza A Virus NS1 Regulates IFN Signaling Responses to Enhance Viral Infection.Viruses. 2017 May 12;9(5):107. doi: 10.3390/v9050107. Viruses. 2017. PMID: 28498306 Free PMC article.
-
Pathology, molecular biology, and pathogenesis of avian influenza A (H5N1) infection in humans.Am J Pathol. 2008 May;172(5):1155-70. doi: 10.2353/ajpath.2008.070791. Epub 2008 Apr 10. Am J Pathol. 2008. PMID: 18403604 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The NS1 protein: a multitasking virulence factor.Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2015;386:73-107. doi: 10.1007/82_2014_400. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2015. PMID: 25007846 Review.
Cited by
-
mTOR/p70S6K signaling distinguishes routine, maintenance-level autophagy from autophagic cell death during influenza A infection.Virology. 2014 Mar;452-453:175-190. doi: 10.1016/j.virol.2014.01.008. Epub 2014 Feb 5. Virology. 2014. PMID: 24606695 Free PMC article.
-
Host gene expression profiling in influenza A virus-infected lung epithelial (A549) cells: a comparative analysis between highly pathogenic and modified H5N1 viruses.Virol J. 2010 Sep 9;7:219. doi: 10.1186/1743-422X-7-219. Virol J. 2010. PMID: 20828378 Free PMC article.
-
Non structural protein of avian influenza A (H11N1) virus is a weaker suppressor of immune responses but capable of inducing apoptosis in host cells.Virol J. 2012 Aug 6;9:149. doi: 10.1186/1743-422X-9-149. Virol J. 2012. PMID: 22866982 Free PMC article.
-
The roles of apoptosis, autophagy and unfolded protein response in arbovirus, influenza virus, and HIV infections.Virulence. 2019 Dec;10(1):376-413. doi: 10.1080/21505594.2019.1605803. Virulence. 2019. PMID: 30966844 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Effector Domain of the Influenza A Virus Nonstructural Protein NS1 Triggers Host Shutoff by Mediating Inhibition and Global Deregulation of Host Transcription When Associated with Specific Structures in the Nucleus.mBio. 2021 Oct 26;12(5):e0219621. doi: 10.1128/mBio.02196-21. Epub 2021 Sep 7. mBio. 2021. PMID: 34488451 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Price GE, Smith H, Sweet C. Differential induction of cytotoxicity and apoptosis by influenza virus strains of differing virulence. J Gen Virol. 1997;78:2821–2829. - PubMed
-
- Fesq H, Bacher M, Nain M, Gemsa D. Programmed cell death (apoptosis) in human monocytes infected by influenza A virus. Immunobiology. 1994;190:175–182. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

