Neutrophils in a mouse model of autoantibody-mediated arthritis: critical producers of Fc receptor gamma, the receptor for C5a, and lymphocyte function-associated antigen 1
- PMID: 20191628
- PMCID: PMC3057458
- DOI: 10.1002/art.27238
Neutrophils in a mouse model of autoantibody-mediated arthritis: critical producers of Fc receptor gamma, the receptor for C5a, and lymphocyte function-associated antigen 1
Abstract
Objective: Neutrophils represent a prominent component of inflammatory joint effusions and are required for synovial inflammation in mouse models, but the mechanisms are poorly understood. In this study, we developed a system with which to test the importance of the production of specific factors by neutrophils in a mouse model of arthritis.
Methods: Neutrophil-deficient Gfi-1(-/-) mice were administered sublethal doses of radiation and were then engrafted with donor bone marrow cells (BMCs), which resulted in the production of mature neutrophils within 2 weeks. By reconstituting with BMCs from mice lacking selected proinflammatory factors, we generated mice that specifically lacked these factors on their neutrophils. Arthritis was initiated by transfer of K/BxN serum to identify the role of defined neutrophil factors on the incidence and severity of arthritis.
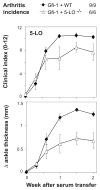
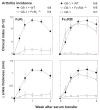
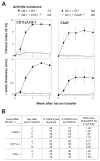
Results: Neutrophils lacking the signaling chain of stimulatory Fc receptors (FcRgamma(-/-)) were unable to elicit arthritis, but neutrophils lacking FcgammaRIII still did so. Neutrophils lacking the chemotactic or adhesion receptor C5a receptor (C5aR) or CD11a/lymphocyte function-associated antigen 1 (LFA-1) also failed to initiate arthritis but could enter joints in which inflammation had been initiated by wild-type neutrophils. Neutrophils unable to produce interleukin-1alpha (IL-1alpha) and IL-1beta (IL-1alpha/beta(-/-)) or leukotrienes (5-lipoxygenase [5-LOX(-/-)]) produced arthritis of intermediate severity. The inability of neutrophils to make tumor necrosis factor or to express receptors for tumor necrosis factor or IL-1 had no effect on arthritis.
Conclusion: A novel transfer system was developed to identify neutrophil production of FcRgamma, C5aR, and CD11a/LFA-1 as critical components of autoantibody-mediated arthritis. Neutrophil production of IL-1 and leukotriene B(4) likely contributes to inflammation but is not essential. Molecular requirements for neutrophil influx into joints become more permissive after inflammation is initiated.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Regulation of human neutrophil Fcγ receptor IIa by C5a receptor promotes inflammatory arthritis in mice.Arthritis Rheum. 2011 Feb;63(2):467-78. doi: 10.1002/art.30141. Arthritis Rheum. 2011. PMID: 21280001 Free PMC article.
-
Neutrophils orchestrate their own recruitment in murine arthritis through C5aR and FcγR signaling.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012 Nov 13;109(46):E3177-85. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1213797109. Epub 2012 Oct 29. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012. PMID: 23112187 Free PMC article.
-
C5a receptor enables participation of mast cells in immune complex arthritis independently of Fcγ receptor modulation.Arthritis Rheum. 2010 Nov;62(11):3322-33. doi: 10.1002/art.27659. Arthritis Rheum. 2010. PMID: 20662064 Free PMC article.
-
The critical role of C5a as an initiator of neutrophil-mediated autoimmune inflammation of the joint and skin.Semin Immunol. 2018 Jun;37:21-29. doi: 10.1016/j.smim.2018.03.002. Epub 2018 Mar 27. Semin Immunol. 2018. PMID: 29602515 Review.
-
The immunoglobulin, IgG Fc receptor and complement triangle in autoimmune diseases.Immunobiology. 2012 Nov;217(11):1067-79. doi: 10.1016/j.imbio.2012.07.015. Immunobiology. 2012. PMID: 22964232 Review.
Cited by
-
TLR2 deletion promotes arthritis through reduction of IL-10.J Leukoc Biol. 2013 May;93(5):751-9. doi: 10.1189/jlb.0912473. Epub 2013 Feb 27. J Leukoc Biol. 2013. PMID: 23446149 Free PMC article.
-
Endothelium-neutrophil interactions in ANCA-associated diseases.J Am Soc Nephrol. 2012 Sep;23(9):1449-61. doi: 10.1681/ASN.2012020119. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2012. PMID: 22942199 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Saposin C coupled lipid nanovesicles specifically target arthritic mouse joints for optical imaging of disease severity.PLoS One. 2012;7(3):e33966. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0033966. Epub 2012 Mar 28. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22470501 Free PMC article.
-
The selective inhibition of the Syk tyrosine kinase ameliorates experimental autoimmune arthritis.Front Immunol. 2023 Dec 4;14:1279155. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1279155. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 38111569 Free PMC article.
-
Defining the Signature of VISTA on Myeloid Cell Chemokine Responsiveness.Front Immunol. 2019 Nov 19;10:2641. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.02641. eCollection 2019. Front Immunol. 2019. PMID: 31803182 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Monach PA, Benoist C, Mathis D. The role of antibodies in mouse models of rheumatoid arthritis, and relevance to human disease. Adv Immunol. 2004;82:217–48. - PubMed
-
- Korganow AS, Ji H, Mangialaio S, Duchatelle V, Pelanda R, Martin T, et al. From systemic T cell self-reactivity to organ-specific autoimmune disease via immunoglobulins. Immunity. 1999;10(4):451–61. - PubMed
-
- Wipke BT, Allen PM. Essential role of neutrophils in the initiation and progression of a murine model of rheumatoid arthritis. J Immunol. 2001;167(3):1601–8. - PubMed
-
- Lee DM, Friend DS, Gurish MF, Benoist C, Mathis D, Brenner MB. Mast cells: a cellular link between autoantibodies and inflammatory arthritis. Science. 2002;297(5587):1689–92. - PubMed
-
- Corr M, Crain B. The role of FcgammaR signaling in the K/B x N serum transfer model of arthritis. J Immunol. 2002;169(11):6604–9. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

