Cellular stress responses: cell survival and cell death
- PMID: 20182529
- PMCID: PMC2825543
- DOI: 10.1155/2010/214074
Cellular stress responses: cell survival and cell death
Abstract
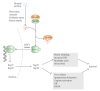
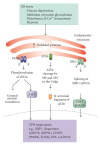
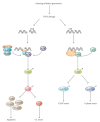
Cells can respond to stress in various ways ranging from the activation of survival pathways to the initiation of cell death that eventually eliminates damaged cells. Whether cells mount a protective or destructive stress response depends to a large extent on the nature and duration of the stress as well as the cell type. Also, there is often the interplay between these responses that ultimately determines the fate of the stressed cell. The mechanism by which a cell dies (i.e., apoptosis, necrosis, pyroptosis, or autophagic cell death) depends on various exogenous factors as well as the cell's ability to handle the stress to which it is exposed. The implications of cellular stress responses to human physiology and diseases are manifold and will be discussed in this review in the context of some major world health issues such as diabetes, Parkinson's disease, myocardial infarction, and cancer.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Misfolded proteins bind and activate death receptor 5 to trigger apoptosis during unresolved endoplasmic reticulum stress.Elife. 2020 Jan 6;9:e52291. doi: 10.7554/eLife.52291. Elife. 2020. PMID: 31904339 Free PMC article.
-
Cell Stress Signaling Cascades Regulating Cell Fate.Curr Pharm Des. 2018;24(27):3176-3183. doi: 10.2174/1381612824666180711122753. Curr Pharm Des. 2018. PMID: 29992877 Review.
-
RIP1, a kinase on the crossroads of a cell's decision to live or die.Cell Death Differ. 2007 Mar;14(3):400-10. doi: 10.1038/sj.cdd.4402085. Cell Death Differ. 2007. PMID: 17301840 Review.
-
Cell death and autophagy: cytokines, drugs, and nutritional factors.Toxicology. 2008 Dec 30;254(3):147-57. doi: 10.1016/j.tox.2008.07.048. Epub 2008 Jul 23. Toxicology. 2008. PMID: 18694801 Review.
-
Repairing plasma membrane damage in regulated necrotic cell death.Mol Biol Rep. 2021 Mar;48(3):2751-2759. doi: 10.1007/s11033-021-06252-w. Epub 2021 Mar 9. Mol Biol Rep. 2021. PMID: 33687702 Review.
Cited by
-
Divergent Heat Stress Responses in Bactrocera tryoni and Ceratitis capitata.Insects. 2024 Sep 30;15(10):759. doi: 10.3390/insects15100759. Insects. 2024. PMID: 39452334 Free PMC article.
-
SLC38A10 Transporter Plays a Role in Cell Survival Under Oxidative Stress and Glutamate Toxicity.Front Mol Biosci. 2021 May 5;8:671865. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2021.671865. eCollection 2021. Front Mol Biosci. 2021. PMID: 34026845 Free PMC article.
-
Autophagy regulates colistin-induced apoptosis in PC-12 cells.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2015 Apr;59(4):2189-97. doi: 10.1128/AAC.04092-14. Epub 2015 Feb 2. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2015. PMID: 25645826 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of Oxidative Stress-Associated Molecular Subtypes and Signature for Predicting Survival Outcome of Cervical Squamous Cell Carcinoma.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2022 Oct 3;2022:1056825. doi: 10.1155/2022/1056825. eCollection 2022. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2022. Retraction in: Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2023 Aug 2;2023:9795318. doi: 10.1155/2023/9795318 PMID: 36225179 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
Oxidative stress induces transient O-GlcNAc elevation and tau dephosphorylation in SH-SY5Y cells.J Cell Mol Med. 2016 Dec;20(12):2269-2277. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.12910. Epub 2016 Jul 26. J Cell Mol Med. 2016. PMID: 27456536 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lockshin RA, Zakeri Z. Programmed cell death and apoptosis: origins of the theory. Nature Reviews Molecular Cell Biology. 2001;2(7):545–550. - PubMed
-
- Lockshin RA, Williams CM. Programmed cell death—I. Cytology of degeneration in the intersegmental muscles of the Pernyi silkmoth. Journal of Insect Physiology. 1965;11(2):123–133. - PubMed
-
- Lockshin RA, Williams CM. Programmed cell death—IV. The influence of drugs on the breakdown of the intersegmental muscles of silkmoths. Journal of Insect Physiology. 1965;11(6):803–809. - PubMed
-
- Lockshin RA, Williams CM. Programmed cell death—V. Cytolytic enzymes in relation to the breakdown of the intersegmental muscles of silkmoths. Journal of Insect Physiology. 1965;11(7):831–844. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

