Jane: a new tool for the cophylogeny reconstruction problem
- PMID: 20181081
- PMCID: PMC2830923
- DOI: 10.1186/1748-7188-5-16
Jane: a new tool for the cophylogeny reconstruction problem
Abstract
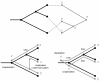
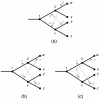
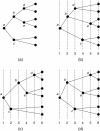
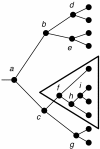
Background: This paper describes the theory and implementation of a new software tool, called Jane, for the study of historical associations. This problem arises in parasitology (associations of hosts and parasites), molecular systematics (associations of orderings and genes), and biogeography (associations of regions and orderings). The underlying problem is that of reconciling pairs of trees subject to biologically plausible events and costs associated with these events. Existing software tools for this problem have strengths and limitations, and the new Jane tool described here provides functionality that complements existing tools.
Results: The Jane software tool uses a polynomial time dynamic programming algorithm in conjunction with a genetic algorithm to find very good, and often optimal, solutions even for relatively large pairs of trees. The tool allows the user to provide rich timing information on both the host and parasite trees. In addition the user can limit host switch distance and specify multiple host switch costs by specifying regions in the host tree and costs for host switches between pairs of regions. Jane also provides a graphical user interface that allows the user to interactively experiment with modifications to the solutions found by the program.
Conclusions: Jane is shown to be a useful tool for cophylogenetic reconstruction. Its functionality complements existing tools and it is therefore likely to be of use to researchers in the areas of parasitology, molecular systematics, and biogeography.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Reconstruction of the cophylogenetic history of related phylogenetic trees with divergence timing information.Theory Biosci. 2005 Apr;123(4):277-99. doi: 10.1016/j.thbio.2005.01.003. Theory Biosci. 2005. PMID: 18202869
-
The co phylogeny reconstruction problem is NP-complete.J Comput Biol. 2011 Jan;18(1):59-65. doi: 10.1089/cmb.2009.0240. Epub 2010 Aug 17. J Comput Biol. 2011. PMID: 20715926
-
A geography-aware reconciliation method to investigate diversification patterns in host/parasite interactions.Mol Ecol Resour. 2018 Apr 26. doi: 10.1111/1755-0998.12897. Online ahead of print. Mol Ecol Resour. 2018. PMID: 29697894
-
Recent results in cophylogeny mapping.Adv Parasitol. 2003;54:303-30. doi: 10.1016/s0065-308x(03)54007-6. Adv Parasitol. 2003. PMID: 14711089 Review.
-
Cophylogeny of the Ficus microcosm.Biol Rev Camb Philos Soc. 2004 Nov;79(4):751-68. doi: 10.1017/s1464793104006463. Biol Rev Camb Philos Soc. 2004. PMID: 15682869 Review.
Cited by
-
The nature of interspecific interactions and co-diversification patterns, as illustrated by the fig microcosm.New Phytol. 2019 Nov;224(3):1304-1315. doi: 10.1111/nph.16176. Epub 2019 Oct 4. New Phytol. 2019. PMID: 31494940 Free PMC article.
-
A Missing Link between Retrotransposons and Retroviruses.mBio. 2022 Apr 26;13(2):e0018722. doi: 10.1128/mbio.00187-22. Epub 2022 Mar 15. mBio. 2022. PMID: 35289644 Free PMC article.
-
Novel Polyomaviruses in Mammals from Multiple Orders and Reassessment of Polyomavirus Evolution and Taxonomy.Viruses. 2019 Oct 10;11(10):930. doi: 10.3390/v11100930. Viruses. 2019. PMID: 31658738 Free PMC article.
-
Discovery and Evolution of a Divergent Coronavirus in the Plateau Pika From China That Extends the Host Range of Alphacoronaviruses.Front Microbiol. 2021 Oct 7;12:755599. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2021.755599. eCollection 2021. Front Microbiol. 2021. PMID: 34691006 Free PMC article.
-
Divergent Viruses Discovered in Swine Alter the Understanding of Evolutionary History and Genetic Diversity of the Respirovirus Genus and Related Porcine Parainfluenza Viruses.Microbiol Spectr. 2022 Jun 29;10(3):e0024222. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.00242-22. Epub 2022 Jun 1. Microbiol Spectr. 2022. PMID: 35647875 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Conow C, Fielder D, Ovadia Y, Libeskind-Hadas R. The Cophylogeny Reticulation Problem is NP-complete. http://www.cs.hmc.edu/~hadas/research/CophyNPC.pdf Harvey Mudd College Technical Report 2009-01.
-
- Ronquist F. TreeFitter. http://www.ebc.uu.se/systzoo/research/treefitter/treefitter.html
-
- Page RDM. COMPONENT User's Manual. http://taxonomy.zoology.gla.ac.uk/rod/cpw.html
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

