In the Staphylococcus aureus two-component system sae, the response regulator SaeR binds to a direct repeat sequence and DNA binding requires phosphorylation by the sensor kinase SaeS
- PMID: 20172998
- PMCID: PMC2849438
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.01524-09
In the Staphylococcus aureus two-component system sae, the response regulator SaeR binds to a direct repeat sequence and DNA binding requires phosphorylation by the sensor kinase SaeS
Abstract
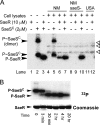
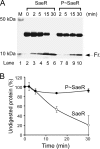
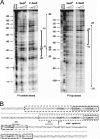
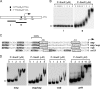
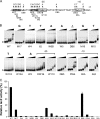
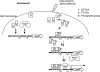
Staphylococcus aureus uses the SaeRS two-component system to control the expression of many virulence factors such as alpha-hemolysin and coagulase; however, the molecular mechanism of this signaling has not yet been elucidated. Here, using the P1 promoter of the sae operon as a model target DNA, we demonstrated that the unphosphorylated response regulator SaeR does not bind to the P1 promoter DNA, while its C-terminal DNA binding domain alone does. The DNA binding activity of full-length SaeR could be restored by sensor kinase SaeS-induced phosphorylation. Phosphorylated SaeR is more resistant to digestion by trypsin, suggesting conformational changes. DNase I footprinting assays revealed that the SaeR protection region in the P1 promoter contains a direct repeat sequence (GTTAAN(6)GTTAA [where N is any nucleotide]). This sequence is critical to the binding of phosphorylated SaeR. Mutational changes in the repeat sequence greatly reduced both the in vitro binding of SaeR and the in vivo function of the P1 promoter. From these results, we concluded that SaeR recognizes the direct repeat sequence as a binding site and that binding requires phosphorylation by SaeS.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The SaeRS Two-Component System of Staphylococcus aureus.Genes (Basel). 2016 Oct 3;7(10):81. doi: 10.3390/genes7100081. Genes (Basel). 2016. PMID: 27706107 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Organizational requirements of the SaeR binding sites for a functional P1 promoter of the sae operon in Staphylococcus aureus.J Bacteriol. 2012 Jun;194(11):2865-76. doi: 10.1128/JB.06771-11. Epub 2012 Mar 23. J Bacteriol. 2012. PMID: 22447906 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of the P3 promoter and distinct roles of the two promoters of the SaeRS two-component system in Staphylococcus aureus.J Bacteriol. 2011 Sep;193(18):4672-84. doi: 10.1128/JB.00353-11. Epub 2011 Jul 15. J Bacteriol. 2011. PMID: 21764914 Free PMC article.
-
Nutritional Regulation of the Sae Two-Component System by CodY in Staphylococcus aureus.J Bacteriol. 2018 Mar 26;200(8):e00012-18. doi: 10.1128/JB.00012-18. Print 2018 Apr 15. J Bacteriol. 2018. PMID: 29378891 Free PMC article.
-
Differential target gene activation by the Staphylococcus aureus two-component system saeRS.J Bacteriol. 2010 Feb;192(3):613-23. doi: 10.1128/JB.01242-09. Epub 2009 Nov 20. J Bacteriol. 2010. PMID: 19933357 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
The SaeRS Two-Component System of Staphylococcus aureus.Genes (Basel). 2016 Oct 3;7(10):81. doi: 10.3390/genes7100081. Genes (Basel). 2016. PMID: 27706107 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Regulation of the Staphylococcal Superantigen-Like Protein 1 Gene of Community-Associated Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus in Murine Abscesses.Toxins (Basel). 2019 Jul 4;11(7):391. doi: 10.3390/toxins11070391. Toxins (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31277443 Free PMC article.
-
The SaeRS Two-Component System Is a Direct and Dominant Transcriptional Activator of Toxic Shock Syndrome Toxin 1 in Staphylococcus aureus.J Bacteriol. 2016 Sep 9;198(19):2732-42. doi: 10.1128/JB.00425-16. Print 2016 Oct 1. J Bacteriol. 2016. PMID: 27457715 Free PMC article.
-
Expression of multidrug resistance efflux pump gene norA is iron responsive in Staphylococcus aureus.J Bacteriol. 2012 Apr;194(7):1753-62. doi: 10.1128/JB.06582-11. Epub 2012 Jan 20. J Bacteriol. 2012. PMID: 22267518 Free PMC article.
-
Calprotectin Increases the Activity of the SaeRS Two Component System and Murine Mortality during Staphylococcus aureus Infections.PLoS Pathog. 2015 Jul 6;11(7):e1005026. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1005026. eCollection 2015 Jul. PLoS Pathog. 2015. PMID: 26147796 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Adhikari, R. P., and R. P. Novick. 2008. Regulatory organization of the staphylococcal sae locus. Microbiology 154:949-959. - PubMed
-
- Archer, G. L. 1998. Staphylococcus aureus: a well-armed pathogen. Clin. Infect. Dis. 26:1179-1181. - PubMed
-
- Bae, T., T. Baba, K. Hiramatsu, and O. Schneewind. 2006. Prophages of Staphylococcus aureus Newman and their contribution to virulence. Mol. Microbiol. 62:1035-1047. - PubMed
-
- Barnard, A., A. Wolfe, and S. Busby. 2004. Regulation at complex bacterial promoters: how bacteria use different promoter organizations to produce different regulatory outcomes. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 7:102-108. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

