Delayed onset of positive feedback activation of Rab5 by Rabex-5 and Rabaptin-5 in endocytosis
- PMID: 20169068
- PMCID: PMC2821916
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0009226
Delayed onset of positive feedback activation of Rab5 by Rabex-5 and Rabaptin-5 in endocytosis
Abstract
Background: Rabex-5 is a guanine nucleotide exchange factor (GEF) that specifically activates Rab5, i.e., converting Rab5-GDP to Rab5-GTP, through two distinct pathways to promote endosome fusion and endocytosis. The direct pathway involves a pool of membrane-associated Rabex-5 that targets to the membrane via an early endosomal targeting (EET) domain. The indirect pathway, on the other hand, involves a cytosolic pool of Rabex-5/Rabaptin-5 complex. The complex is recruited to the membrane via Rabaptin-5 binding to Rab5-GTP, suggesting a positive feedback mechanism. The relationship of these two pathways for Rab5 activation in the cell is unclear.
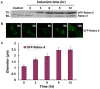
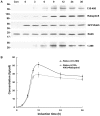
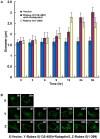
Methodology/principal findings: We dissect the relative contribution of each pathway to Rab5 activation via mathematical modeling and kinetic analysis in the cell. These studies show that the indirect pathway constitutes a positive feedback loop for converting Rab5-GDP to Rab5-GTP on the endosomal membrane and allows sensitive regulation of endosome fusion activity by the levels of Rab5 and Rabex-5 in the cell. The onset of this positive feedback effect, however, contains a threshold, which requires above endogenous levels of Rab5 or Rabex-5 in the cell. We term this novel phenomenon "delayed response". The presence of the direct pathway reduces the delay by increasing the basal level of Rab5-GTP, thus facilitates the function of the Rabex-5/Rabaptin-5-mediated positive feedback loop.
Conclusion: Our data support the mathematical model. With the model's guidance, the data reveal the affinity of Rabex-5/Rabaptin-5/Rab5-GTP interaction in the cell, which is quantitatively related to the Rabex-5 concentration for the onset of the indirect positive feedback pathway. The presence of the direct pathway and increased Rab5 concentration can reduce the Rabex-5 concentration required for the onset of the positive feedback loop. Thus the direct and indirect pathways cooperate in the regulation of early endosome fusion.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

Similar articles
-
Rabaptin-5-independent membrane targeting and Rab5 activation by Rabex-5 in the cell.Mol Biol Cell. 2007 Oct;18(10):4119-28. doi: 10.1091/mbc.e07-02-0100. Epub 2007 Aug 15. Mol Biol Cell. 2007. PMID: 17699593 Free PMC article.
-
Rabex-5 is a Rab22 effector and mediates a Rab22-Rab5 signaling cascade in endocytosis.Mol Biol Cell. 2009 Nov;20(22):4720-9. doi: 10.1091/mbc.e09-06-0453. Epub 2009 Sep 16. Mol Biol Cell. 2009. PMID: 19759177 Free PMC article.
-
Functional synergy between Rab5 effector Rabaptin-5 and exchange factor Rabex-5 when physically associated in a complex.Mol Biol Cell. 2001 Jul;12(7):2219-28. doi: 10.1091/mbc.12.7.2219. Mol Biol Cell. 2001. PMID: 11452015 Free PMC article.
-
[Effectors of GTPase Rab5 in endocytosis and signal transduction].Postepy Biochem. 2009;55(2):171-80. Postepy Biochem. 2009. PMID: 19824473 Review. Polish.
-
Who's in control? Principles of Rab GTPase activation in endolysosomal membrane trafficking and beyond.J Cell Biol. 2021 Sep 6;220(9):e202105120. doi: 10.1083/jcb.202105120. Epub 2021 Aug 12. J Cell Biol. 2021. PMID: 34383013 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Signal transduction: RABGEF1 fingers RAS for ubiquitination.Curr Biol. 2010 Aug 10;20(15):R630-2. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2010.06.019. Curr Biol. 2010. PMID: 20692608 Free PMC article.
-
A Rab8 guanine nucleotide exchange factor-effector interaction network regulates primary ciliogenesis.J Biol Chem. 2012 May 4;287(19):15602-9. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M111.333245. Epub 2012 Mar 19. J Biol Chem. 2012. PMID: 22433857 Free PMC article.
-
Interlinked GTPase cascades provide a motif for both robust switches and oscillators.J R Soc Interface. 2019 Aug 30;16(157):20190198. doi: 10.1098/rsif.2019.0198. Epub 2019 Aug 7. J R Soc Interface. 2019. PMID: 31387482 Free PMC article.
-
The chemical master equation approach to nonequilibrium steady-state of open biochemical systems: linear single-molecule enzyme kinetics and nonlinear biochemical reaction networks.Int J Mol Sci. 2010 Sep 20;11(9):3472-500. doi: 10.3390/ijms11093472. Int J Mol Sci. 2010. PMID: 20957107 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Stochastic activation and bistability in a Rab GTPase regulatory network.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2020 Mar 24;117(12):6540-6549. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1921027117. Epub 2020 Mar 11. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2020. PMID: 32161136 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Horiuchi H, Lippe R, McBride HM, Rubino M, Woodman P, et al. A novel Rab5 GDP/GTP exchange factor complexed to Rabaptin-5 links nucleotide exchange to effector recruitment and function. Cell. 1997;90:1149–1159. - PubMed
-
- Bucci C, Parton RG, Mather IM, Stunnenberg H, Simons K, et al. The small GTPase Rab5 functions as a regulatory factor in the early endocytic pathway. Cell. 1992;70:715–728. - PubMed
-
- Gorvel J-P, Chavrier P, Zerial M, Gruenberg J. rab5 controls early endosome fusion in vitro. Cell. 1991;64:915–925. - PubMed
-
- Li G, Barbieri MA, Colombo MI, Stahl PD. Structural features of the GTP-binding defective Rab5 mutants required for their inhibitory activity on endocytosis. J Biol Chem. 1994;269:14631–14635. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

