Tyrosine kinase Btk regulates E-selectin-mediated integrin activation and neutrophil recruitment by controlling phospholipase C (PLC) gamma2 and PI3Kgamma pathways
- PMID: 20167705
- PMCID: PMC2858472
- DOI: 10.1182/blood-2009-11-254185
Tyrosine kinase Btk regulates E-selectin-mediated integrin activation and neutrophil recruitment by controlling phospholipase C (PLC) gamma2 and PI3Kgamma pathways
Abstract
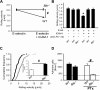
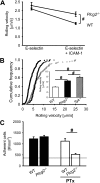
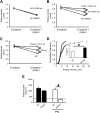
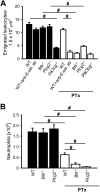
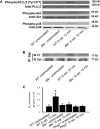
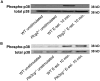
Selectins mediate leukocyte rolling, trigger beta(2)-integrin activation, and promote leukocyte recruitment into inflamed tissue. E-selectin binding to P-selectin glycoprotein ligand 1 (PSGL-1) leads to activation of an immunoreceptor tyrosine-based activation motif (ITAM)-dependent pathway, which in turn activates the spleen tyrosine kinase (Syk). However, the signaling pathway linking Syk to integrin activation after E-selectin engagement is unknown. To identify the pathway, we used different gene-deficient mice in autoperfused flow chamber, intravital microscopy, peritonitis, and biochemical studies. We report here that the signaling pathway downstream of Syk divides into a phospholipase C (PLC) gamma2- and phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI3K) gamma-dependent pathway. The Tec family kinase Bruton tyrosine kinase (Btk) is required for activating both pathways, generating inositol-3,4,5-trisphosphate (IP(3)), and inducing E-selectin-mediated slow rolling. Inhibition of this signal-transduction pathway diminished Galpha(i)-independent leukocyte adhesion to and transmigration through endothelial cells in inflamed postcapillary venules of the cremaster. Galpha(i)-independent neutrophil recruitment into the inflamed peritoneal cavity was reduced in Btk(-/-) and Plcg2(-/-) mice. Our data demonstrate the functional importance of this newly identified signaling pathway mediated by E-selectin engagement.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Rap1a activation by CalDAG-GEFI and p38 MAPK is involved in E-selectin-dependent slow leukocyte rolling.Eur J Immunol. 2011 Jul;41(7):2074-85. doi: 10.1002/eji.201041196. Epub 2011 Jun 7. Eur J Immunol. 2011. PMID: 21480213 Free PMC article.
-
PSGL-1 engagement by E-selectin signals through Src kinase Fgr and ITAM adapters DAP12 and FcR gamma to induce slow leukocyte rolling.J Exp Med. 2008 Sep 29;205(10):2339-47. doi: 10.1084/jem.20072660. Epub 2008 Sep 15. J Exp Med. 2008. PMID: 18794338 Free PMC article.
-
E-selectin engages PSGL-1 and CD44 through a common signaling pathway to induce integrin alphaLbeta2-mediated slow leukocyte rolling.Blood. 2010 Jul 22;116(3):485-94. doi: 10.1182/blood-2009-12-259556. Epub 2010 Mar 18. Blood. 2010. PMID: 20299514 Free PMC article.
-
Reprint of Neutrophil cell surface receptors and their intracellular signal transduction pathways.Int Immunopharmacol. 2013 Dec;17(4):1185-97. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2013.11.010. Epub 2013 Nov 18. Int Immunopharmacol. 2013. PMID: 24263067 Review.
-
Neutrophil cell surface receptors and their intracellular signal transduction pathways.Int Immunopharmacol. 2013 Nov;17(3):638-50. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2013.06.034. Epub 2013 Aug 30. Int Immunopharmacol. 2013. PMID: 23994464 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
A Comparative Review of Equine SIRS, Sepsis, and Neutrophils.Front Vet Sci. 2019 Mar 12;6:69. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2019.00069. eCollection 2019. Front Vet Sci. 2019. PMID: 30931316 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mediation of transitional B cell maturation in the absence of functional Bruton's tyrosine kinase.Sci Rep. 2017 Apr 5;7:46029. doi: 10.1038/srep46029. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 28378771 Free PMC article.
-
Modulating proximal cell signaling by targeting Btk ameliorates humoral autoimmunity and end-organ disease in murine lupus.Arthritis Res Ther. 2012 Nov 8;14(6):R243. doi: 10.1186/ar4086. Arthritis Res Ther. 2012. PMID: 23136880 Free PMC article.
-
Bruton's tyrosine kinase inhibition attenuates disease progression by reducing renal immune cell invasion in mice with hemolytic-uremic syndrome.Front Immunol. 2023 Feb 23;14:1105181. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1105181. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 36911665 Free PMC article.
-
Ibrutinib blocks Btk-dependent NF-ĸB and NFAT responses in human macrophages during Aspergillus fumigatus phagocytosis.Blood. 2018 Nov 1;132(18):1985-1988. doi: 10.1182/blood-2017-12-823393. Epub 2018 Jul 18. Blood. 2018. PMID: 30021784 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ley K, Laudanna C, Cybulsky MI, Nourshargh S. Getting to the site of inflammation: the leukocyte adhesion cascade updated. Nat Rev Immunol. 2007;7(9):678–689. - PubMed
-
- Matsumoto M, Shigeta A, Miyasaka M, Hirata T. CD43 plays both antiadhesive and proadhesive roles in neutrophil rolling in a context-dependent manner. J Immunol. 2008;181(5):3628–3635. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

