Pharmacokinetics and enhanced oral bioavailability in beagle dogs of cyclosporine A encapsulated in glyceryl monooleate/poloxamer 407 cubic nanoparticles
- PMID: 20161984
- PMCID: PMC2819904
Pharmacokinetics and enhanced oral bioavailability in beagle dogs of cyclosporine A encapsulated in glyceryl monooleate/poloxamer 407 cubic nanoparticles
Abstract
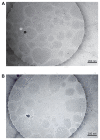
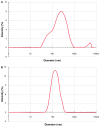
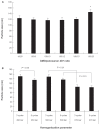
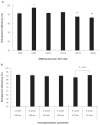
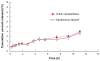
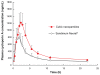
Efforts to improve the oral bioavailability of cyclosporine A (CyA) remains a challenge in the field of drug delivery. In this study, glyceryl monooleate (GMO)/poloxamer 407 cubic nanoparticles were evaluated as potential vehicles to improve the oral bioavailability of CyA. Cubic nanoparticles were prepared via the fragmentation of a bulk GMO/poloxamer 407 cubic phase gel by sonication and homogenization. The cubic inner structure formed was verified using Cryo-TEM. The mean diameters of the nanoparticles were about 180 nm, and the entrapment efficiency of these particles for CyA was over 85%. The in vitro release of CyA from these nanoparticles was less than 5% at 12 h. The results of a pharmacokinetic study in beagle dogs showed improved absorption of CyA from cubic nanoparticles as compared to microemulsion-based Neoral((R)); higher C(max) (1371.18 +/- 37.34 vs 969.68 +/- 176.3 ng mL(-1)), higher AUC(0-t) (7757.21 +/- 1093.64 vs 4739.52 +/- 806.30 ng h mL(-1)) and AUC(0-infinity) (9004.77 +/- 1090.38 vs 5462.31 +/- 930.76 ng h mL(-1)). The relative oral bioavailability of CyA cubic nanoparticles calculated on the basis of AUC(0-infinity) was about 178% as compared to Neoral((R)). The enhanced bioavailability of CyA is likely due to facilitated absorption by cubic nanoparticles rather than improved release.
Keywords: beagle dogs; bioavailability; cubosomes; cyclosporine A; glyceryl monooleate; nanoparticles; oral drug delivery.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Oral cyclosporine treatment in dogs: a review of the literature.J Vet Intern Med. 2014 Jan-Feb;28(1):1-20. doi: 10.1111/jvim.12265. Epub 2013 Dec 16. J Vet Intern Med. 2014. PMID: 24341787 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Glyceryl monooleate/poloxamer 407 cubic nanoparticles as oral drug delivery systems: I. In vitro evaluation and enhanced oral bioavailability of the poorly water-soluble drug simvastatin.AAPS PharmSciTech. 2009;10(3):960-6. doi: 10.1208/s12249-009-9292-4. Epub 2009 Jul 28. AAPS PharmSciTech. 2009. PMID: 19636709 Free PMC article.
-
Ocular delivery of cyclosporine A based on glyceryl monooleate/poloxamer 407 liquid crystalline nanoparticles: preparation, characterization, in vitro corneal penetration and ocular irritation.J Drug Target. 2012 Dec;20(10):856-63. doi: 10.3109/1061186X.2012.723214. Epub 2012 Oct 11. J Drug Target. 2012. PMID: 23050903
-
pH-sensitive nanoparticles for improving the oral bioavailability of cyclosporine A.Int J Pharm. 2004 Aug 6;280(1-2):229-40. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpharm.2004.05.006. Int J Pharm. 2004. PMID: 15265562
-
Cyclosporin A (Neoral) in pediatric organ transplantation. Neoral Pediatric Study Group.Pediatr Transplant. 1998 Feb;2(1):35-9. Pediatr Transplant. 1998. PMID: 10084758 Review.
Cited by
-
Effect of cell-penetrating peptide-coated nanostructured lipid carriers on the oral absorption of tripterine.Int J Nanomedicine. 2012;7:4581-91. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S34991. Epub 2012 Aug 20. Int J Nanomedicine. 2012. PMID: 22942642 Free PMC article.
-
Drug transport by red blood cells.Front Physiol. 2023 Dec 11;14:1308632. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2023.1308632. eCollection 2023. Front Physiol. 2023. PMID: 38148901 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Oral cyclosporine treatment in dogs: a review of the literature.J Vet Intern Med. 2014 Jan-Feb;28(1):1-20. doi: 10.1111/jvim.12265. Epub 2013 Dec 16. J Vet Intern Med. 2014. PMID: 24341787 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Engineered nanoparticulate drug delivery systems: the next frontier for oral administration?AAPS J. 2012 Dec;14(4):688-702. doi: 10.1208/s12248-012-9377-y. Epub 2012 Jul 6. AAPS J. 2012. PMID: 22767270 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nano composite emulsion for sustained drug release and improved bioavailability.Pharm Res. 2014 Oct;31(10):2774-83. doi: 10.1007/s11095-014-1374-7. Epub 2014 Apr 22. Pharm Res. 2014. PMID: 24752481
References
-
- Dunn CJ, Wagstaff AJ, Perry CM, et al. Cyclosporin: an updated review of the pharmacokinetic properties, clinical efficacy and tolerability of a microemulsion-based formulation (Neoral®) in organ transplantation. Drugs. 2001;61:1957–2016. - PubMed
-
- Hebert MF. Contributions of hepatic and intestinal matabolism and Pglycoprotein to cyclosporin ans tacrolimus oral drug delivery. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 1997;27:201–214. - PubMed
-
- Noble S, Markham A. Cyclosporin: a review of the pharmacokinetic properties, clinical efficacy and tolerability of a microemulsion-based formulation (Neoral®) Drugs. 1995;50:924–941. - PubMed
-
- Vonderscher J, Meinzer A. Rationale for the development of Sandimmun Neoral. Transplant Proc. 1994;26:2925–2927. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

