Water-soluble triarylphosphines as biomarkers for protein S-nitrosation
- PMID: 20146502
- PMCID: PMC2863053
- DOI: 10.1021/cb900302u
Water-soluble triarylphosphines as biomarkers for protein S-nitrosation
Abstract
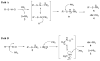
S-Nitrosothiols (RSNOs) represent an important class of post-translational modifications that preserve and amplify the actions of nitric oxide and regulate enzyme activity. Several regulatory proteins are now verified targets of cellular S-nitrosation, and the direct detection of S-nitrosated residues in proteins has become essential to better understand RSNO-mediated signaling. Current RSNO detection depends on indirect assays that limit their overall specificity and reliability. Herein, we report the reaction of S-nitrosated cysteine, glutathione, and a mutated C165S alkyl hydroperoxide reductase with the water-soluble phosphine tris(4,6-dimethyl-3-sulfonatophenyl)phosphine trisodium salt hydrate (TXPTS). A combination of NMR and MS techniques reveals that these reactions produce covalent S-alkylphosphonium ion adducts (with S-P(+) connectivity), TXPTS oxide, and a TXPTS-derived aza-ylide. Mechanistically, this reaction may proceed through an S-substituted aza-ylide or the direct displacement of nitroxyl from the RSNO group. This work provides a new means for detecting and quantifying S-nitrosated species in solution and suggests that phosphines may be useful tools for understanding the complex physiological roles of S-nitrosation and its implications in cell signaling and homeostasis.
Figures
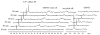
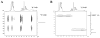

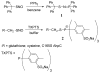
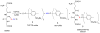
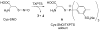
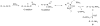
Similar articles
-
Chemical methods for the direct detection and labeling of S-nitrosothiols.Antioxid Redox Signal. 2012 Oct 1;17(7):981-91. doi: 10.1089/ars.2012.4570. Epub 2012 Mar 23. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2012. PMID: 22356122 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The role of a formaldehyde dehydrogenase-glutathione pathway in protein S-nitrosation in mammalian cells.Nitric Oxide. 2003 Nov;9(3):172-81. doi: 10.1016/j.niox.2003.11.003. Nitric Oxide. 2003. PMID: 14732341
-
Mechanism-based triarylphosphine-ester probes for capture of endogenous RSNOs.J Am Chem Soc. 2013 May 22;135(20):7693-704. doi: 10.1021/ja401565w. Epub 2013 May 8. J Am Chem Soc. 2013. PMID: 23614769 Free PMC article.
-
Visible photolysis and amperometric detection of S-nitrosothiols.Anal Chem. 2012 Jan 17;84(2):851-6. doi: 10.1021/ac2031805. Epub 2011 Dec 27. Anal Chem. 2012. PMID: 22201553 Free PMC article.
-
Chemical methods to detect S-nitrosation.Curr Opin Chem Biol. 2011 Feb;15(1):32-7. doi: 10.1016/j.cbpa.2010.10.006. Epub 2010 Oct 29. Curr Opin Chem Biol. 2011. PMID: 21036657 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Developing Photoactive Coumarin-Caged N-Hydroxysulfonamides for Generation of Nitroxyl (HNO).Molecules. 2024 Aug 19;29(16):3918. doi: 10.3390/molecules29163918. Molecules. 2024. PMID: 39202997 Free PMC article.
-
Covalent Chemical Tools for Profiling Post-Translational Modifications.Front Chem. 2022 Jul 4;10:868773. doi: 10.3389/fchem.2022.868773. eCollection 2022. Front Chem. 2022. PMID: 35860626 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mass spectrometry in studies of protein thiol chemistry and signaling: opportunities and caveats.Free Radic Biol Med. 2015 Mar;80:191-211. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2014.09.016. Epub 2014 Sep 28. Free Radic Biol Med. 2015. PMID: 25261734 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nitroxyl (HNO): A Reduced Form of Nitric Oxide with Distinct Chemical, Pharmacological, and Therapeutic Properties.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2016;2016:4867124. doi: 10.1155/2016/4867124. Epub 2015 Dec 7. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2016. Retraction in: Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2016;2016:4018417. doi: 10.1155/2016/4018417. PMID: 26770654 Free PMC article. Retracted. Review.
-
Protein S-Nitrosylation: A Chemical Modification with Ubiquitous Biological Activities.Protein J. 2024 Aug;43(4):639-655. doi: 10.1007/s10930-024-10223-y. Epub 2024 Jul 28. Protein J. 2024. PMID: 39068633 Review.
References
-
- Davies MJ, Fu S, Wang H, Dean RT. Stable markers of oxidant damage to proteins and their application in the study of human disease. Free Radic Biol Med. 1999;27:1151–1163. - PubMed
-
- Poole LB, Karplus PA, Claiborne A. Protein sulfenic acids in redox signaling. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 2004;44:325–347. - PubMed
-
- Deem S, Kim SS, Min JH, Eveland R, Moulding J, Martyr S, Wang X, Swenson ER, Gladwin MT. Pulmonary vascular effects of red blood cells containing S-nitrosated hemoglobin. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2004;287:H2561–2568. - PubMed
-
- Kobayashi-Miura M, Shioji K, Hoshino Y, Masutani H, Nakamura H, Yodoi J. Oxygen sensing and redox signaling: the role of thioredoxin in embryonic development and cardiac diseases. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2007;292:H2040–2050. - PubMed
-
- Haendeler J, Weiland U, Zeiher AM, Dimmeler S. Effects of redox-related congeners of NO on apoptosis and caspase-3 activity. Nitric Oxide. 1997;1:282–293. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

