The sodium pump and cardiotonic steroids-induced signal transduction protein kinases and calcium-signaling microdomain in regulation of transporter trafficking
- PMID: 20144708
- PMCID: PMC5375027
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bbadis.2010.01.013
The sodium pump and cardiotonic steroids-induced signal transduction protein kinases and calcium-signaling microdomain in regulation of transporter trafficking
Abstract
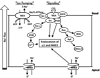
The Na/K-ATPase was discovered as an energy transducing ion pump. A major difference between the Na/K-ATPase and other P-type ATPases is its ability to bind a group of chemicals called cardiotonic steroids (CTS). The plant-derived CTS such as digoxin are valuable drugs for the management of cardiac diseases, whereas ouabain and marinobufagenin (MBG) have been identified as a new class of endogenous hormones. Recent studies have demonstrated that the endogenous CTS are important regulators of renal Na(+) excretion and blood pressure. The Na/K-ATPase is not only an ion pump, but also an important receptor that can transduce the ligand-like effect of CTS on intracellular protein kinases and Ca(2+) signaling. Significantly, these CTS-provoked signaling events are capable of reducing the surface expression of apical NHE3 (Na/H exchanger isoform 3) and basolateral Na/K-ATPase in renal proximal tubular cells. These findings suggest that endogenous CTS may play an important role in regulation of tubular Na(+) excretion under physiological conditions; conversely, a defect at either the receptor level (Na/K-ATPase) or receptor-effector coupling would reduce the ability of renal proximal tubular cells to excrete Na(+), thus culminating/resulting in salt-sensitive hypertension.
Copyright © 2010 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Regulation of apical NHE3 trafficking by ouabain-induced activation of the basolateral Na+-K+-ATPase receptor complex.Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2008 Feb;294(2):C555-63. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00475.2007. Epub 2007 Dec 12. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2008. PMID: 18077602
-
Impairment of Na/K-ATPase signaling in renal proximal tubule contributes to Dahl salt-sensitive hypertension.J Biol Chem. 2011 Jul 1;286(26):22806-13. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M111.246249. Epub 2011 May 9. J Biol Chem. 2011. PMID: 21555512 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of cardiotonic steroids on isolated perfused kidney and NHE3 activity in renal proximal tubules.Biochim Biophys Acta Gen Subj. 2017 Aug;1861(8):1943-1950. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagen.2017.05.012. Epub 2017 May 12. Biochim Biophys Acta Gen Subj. 2017. PMID: 28506883
-
Cardiotonic steroids in adaptation to dietary salt intake.Curr Clin Pharmacol. 2014;9(3):298-309. doi: 10.2174/1574884708666131111204031. Curr Clin Pharmacol. 2014. PMID: 24219001 Review.
-
Endogenous and exogenous cardiac glycosides: their roles in hypertension, salt metabolism, and cell growth.Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2007 Aug;293(2):C509-36. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00098.2007. Epub 2007 May 9. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2007. PMID: 17494630 Review.
Cited by
-
Cardiac Oxidative Signaling and Physiological Hypertrophy in the Na/K-ATPase α1s/sα2s/s Mouse Model of High Affinity for Cardiotonic Steroids.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Mar 27;22(7):3462. doi: 10.3390/ijms22073462. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33801629 Free PMC article.
-
Critical role of the α1-Na(+), K(+)-ATPase subunit in insensitivity of rodent cells to cytotoxic action of ouabain.Apoptosis. 2015 Sep;20(9):1200-10. doi: 10.1007/s10495-015-1144-y. Apoptosis. 2015. PMID: 26067145 Free PMC article.
-
ATP1A1 Integrates AKT and ERK Signaling via Potential Interaction With Src to Promote Growth and Survival in Glioma Stem Cells.Front Oncol. 2019 Apr 30;9:320. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2019.00320. eCollection 2019. Front Oncol. 2019. PMID: 31114755 Free PMC article.
-
The Na/K-ATPase α1 and c-Src form signaling complex under native condition: A crosslinking approach.Sci Rep. 2020 Apr 7;10(1):6006. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-61920-4. Sci Rep. 2020. PMID: 32265464 Free PMC article.
-
Salt and gene expression: evidence for [Na+]i/[K+]i-mediated signaling pathways.Pflugers Arch. 2015 Mar;467(3):489-98. doi: 10.1007/s00424-014-1650-8. Epub 2014 Dec 6. Pflugers Arch. 2015. PMID: 25479826 Review.
References
-
- Feraille E, Doucet A. Sodium-potassium-adenosinetriphosphatase-dependent sodium transport in the kidney: hormonal control. Physiol Rev. 2001;81(1):345–418. - PubMed
-
- Schoner W, Scheiner-Bobis G. Endogenous and exogenous cardiac glycosides: their roles in hypertension, salt metabolism, and cell growth. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2007;293(2):C509–C536. - PubMed
-
- Xie Z, Cai T. Na+-K+--ATPase-mediated signal transduction: from protein interaction to cellular function. Mol Interv. 2003;3(3):157–168. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous