Heterodimerization of Lrrk1-Lrrk2: Implications for LRRK2-associated Parkinson disease
- PMID: 20144646
- PMCID: PMC2847049
- DOI: 10.1016/j.mad.2010.01.009
Heterodimerization of Lrrk1-Lrrk2: Implications for LRRK2-associated Parkinson disease
Abstract
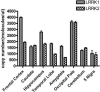
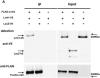
LRRK2 mutations are recognized as the most frequent genetic cause of both familial and sporadic parkinsonism identified to date. A remarkable feature of this form of parkinsonism is the variable penetrance of symptom manifestation resulting in a wide range of age-at-onset in patients. Herein we use a functional approach to identify the Lrrk1 protein as a potential disease modifier demonstrating an interaction and heterodimer formation with Lrrk2. In addition, evaluation of LRRK1 variants in our large Lrrk2 p.G2019S-parkinsonism series from a Tunisian (n=145) identified a missense mutation (p.L416M) resulting in an average 6.2 years younger age at disease onset. In conclusion we show that the interaction of Lrrk1-Lrrk2 can form protein dimers and this interaction may influence the age of symptomatic manifestation in Lrrk2-parkinsonism patients.
2010 Elsevier Ireland Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures
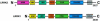

Similar articles
-
Disease penetrance of late-onset parkinsonism: a meta-analysis.JAMA Neurol. 2014 Dec;71(12):1535-9. doi: 10.1001/jamaneurol.2014.1909. JAMA Neurol. 2014. PMID: 25330418
-
Genetic and Environmental Factors Influence the Pleomorphy of LRRK2 Parkinsonism.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Jan 21;22(3):1045. doi: 10.3390/ijms22031045. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33494262 Free PMC article. Review.
-
LRRK2 mutations in Spanish patients with Parkinson disease: frequency, clinical features, and incomplete penetrance.Arch Neurol. 2006 Mar;63(3):377-82. doi: 10.1001/archneur.63.3.377. Arch Neurol. 2006. PMID: 16533964
-
Comparative study of Parkinson's disease and leucine-rich repeat kinase 2 p.G2019S parkinsonism.Neurobiol Aging. 2014 May;35(5):1125-31. doi: 10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2013.11.015. Epub 2013 Nov 22. Neurobiol Aging. 2014. PMID: 24355527
-
Co-occurrence of sporadic parkinsonism and late-onset Alzheimer's disease in a Brazilian male with the LRRK2 p.G2019S mutation.Genet Test. 2008 Dec;12(4):471-3. doi: 10.1089/gte.2008.0042. Genet Test. 2008. PMID: 19072560 Review.
Cited by
-
Differential protein-protein interactions of LRRK1 and LRRK2 indicate roles in distinct cellular signaling pathways.J Neurochem. 2014 Oct;131(2):239-50. doi: 10.1111/jnc.12798. Epub 2014 Jul 14. J Neurochem. 2014. PMID: 24947832 Free PMC article.
-
The function of orthologues of the human Parkinson's disease gene LRRK2 across species: implications for disease modelling in preclinical research.Biochem J. 2016 Feb 1;473(3):221-32. doi: 10.1042/BJ20150985. Biochem J. 2016. PMID: 26811536 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Comparative and evolutionary analysis of RIP kinases in immune responses.Front Genet. 2022 Oct 3;13:796291. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2022.796291. eCollection 2022. Front Genet. 2022. PMID: 36263437 Free PMC article.
-
Suppression of Presymptomatic Oxidative Stress and Inflammation in Neurodegeneration by Grape-Derived Polyphenols.Front Pharmacol. 2018 Aug 28;9:867. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2018.00867. eCollection 2018. Front Pharmacol. 2018. PMID: 30210334 Free PMC article. Review.
-
LRRK2 pathobiology in Parkinson's disease.J Neurochem. 2014 Dec;131(5):554-65. doi: 10.1111/jnc.12949. Epub 2014 Oct 10. J Neurochem. 2014. PMID: 25251388 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Haugarvoll K, Rademakers R, Kachergus JM, Nuytemans K, Ross OA, Gibson JM, Tan EK, Gaig C, Tolosa E, Goldwurm S, Guidi M, Riboldazzi G, Brown L, Walter U, Benecke R, Berg D, Gasser T, Theuns J, Pals P, Cras P, De Deyn PP, Engelborghs S, Pickut B, Uitti RJ, Foroud T, Nichols WC, Hagenah J, Klein C, Samii A, Zabetian CP, Bonifati V, Van Broeckhoven C, Farrer MJ, Wszolek ZK. Lrrk2 R1441C parkinsonism is clinically similar to sporadic Parkinson disease. Neurology. 2008;70:1456–1460. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Hulihan MM, Ishihara-Paul L, Kachergus J, Warren L, Amouri R, Elango R, Prinjha RK, Upmanyu R, Kefi M, Zouari M, Sassi SB, Yahmed SB, El Euch-Fayeche G, Matthews PM, Middleton LT, Gibson RA, Hentati F, Farrer MJ. LRRK2 Gly2019Ser penetrance in Arab-Berber patients from Tunisia: a casecontrol genetic study. Lancet Neurol. 2008;7:591–594. - PubMed
-
- Kaltenbach LS, Romero E, Becklin RR, Chettier R, Bell R, Phansalkar A, Strand A, Torcassi C, Savage J, Hurlburt A, Cha GH, Ukani L, Chepanoske CL, Zhen Y, Sahasrabudhe S, Olson J, Kurschner C, Ellerby LM, Peltier JM, Botas J, Hughes RE. Huntingtin interacting proteins are genetic modifiers of neurodegeneration. PLoS Genet. 2007;3:e82. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Gloeckner CJ, Kinkl N, Schumacher A, Braun RJ, O'Neill E, Meitinger T, Kolch W, Prokisch H, Ueffing M. The Parkinson disease causing LRRK2 mutation I2020T is associated with increased kinase activity. Hum Mol Genet. 2006;15:223–232. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

