Methionine aminopeptidases from Mycobacterium tuberculosis as novel antimycobacterial targets
- PMID: 20142044
- PMCID: PMC3165048
- DOI: 10.1016/j.chembiol.2009.12.014
Methionine aminopeptidases from Mycobacterium tuberculosis as novel antimycobacterial targets
Abstract
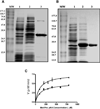
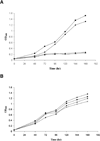
Methionine aminopeptidase (MetAP) is a metalloprotease that removes the N-terminal methionine during protein synthesis. To assess the importance of the two MetAPs in Mycobacterium tuberculosis, we overexpressed and purified each of the MetAPs to near homogeneity and showed that both were active as MetAP enzymes in vitro. We screened a library of 175,000 compounds against MtMetAP1c and identified 2,3-dichloro-1,4-naphthoquinone class of compounds as inhibitors of both MtMetAPs. It was found that the MtMetAP inhibitors were active against replicating and aged nongrowing M. tuberculosis. Overexpression of either MtMetAP1a or MtMetAP1c in M. tuberculosis conferred resistance of bacterial cells to the inhibitors. Moreover, knockdown of MtMetAP1a, but not MtMetAP1c, resulted in decreased viability of M. tuberculosis. These results suggest that MtMetAP1a is a promising target for developing antituberculosis agents.
Copyright (c) 2010 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Characterization of clioquinol and analogues as novel inhibitors of methionine aminopeptidases from Mycobacterium tuberculosis.Tuberculosis (Edinb). 2011 Dec;91 Suppl 1(Suppl 1):S61-5. doi: 10.1016/j.tube.2011.10.012. Epub 2011 Nov 23. Tuberculosis (Edinb). 2011. PMID: 22115541 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of Mycobacterium tuberculosis methionine aminopeptidases by bengamide derivatives.ChemMedChem. 2011 Jun 6;6(6):1041-8. doi: 10.1002/cmdc.201100003. Epub 2011 Apr 4. ChemMedChem. 2011. PMID: 21465667 Free PMC article.
-
Expression and characterization of Mycobacterium tuberculosis methionine aminopeptidase type 1a.Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2010 May 1;20(9):2776-9. doi: 10.1016/j.bmcl.2010.03.067. Epub 2010 Mar 19. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2010. PMID: 20363127 Free PMC article.
-
Methionine aminopeptidases: Potential therapeutic target for microsporidia and other microbes.J Eukaryot Microbiol. 2024 Sep-Oct;71(5):e13036. doi: 10.1111/jeu.13036. Epub 2024 Jul 22. J Eukaryot Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 39036929 Review.
-
Advances in Bacterial Methionine Aminopeptidase Inhibition.Curr Top Med Chem. 2016;16(4):397-414. doi: 10.2174/1568026615666150813145410. Curr Top Med Chem. 2016. PMID: 26268344 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Anti-Tuberculosis Potential of OJT008 against Active and Multi-Drug-Resistant Mycobacterium Tuberculosis: In Silico and In Vitro Inhibition of Methionine Aminopeptidase.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Dec 5;24(24):17142. doi: 10.3390/ijms242417142. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 38138972 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic Approaches to Facilitate Antibacterial Drug Development.Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med. 2015 Feb 13;5(7):a021139. doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a021139. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med. 2015. PMID: 25680982 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeting Mycobacterium tuberculosis pH-driven adaptation.Microbiology (Reading). 2024 May;170(5):001458. doi: 10.1099/mic.0.001458. Microbiology (Reading). 2024. PMID: 38717801 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Characterization of clioquinol and analogues as novel inhibitors of methionine aminopeptidases from Mycobacterium tuberculosis.Tuberculosis (Edinb). 2011 Dec;91 Suppl 1(Suppl 1):S61-5. doi: 10.1016/j.tube.2011.10.012. Epub 2011 Nov 23. Tuberculosis (Edinb). 2011. PMID: 22115541 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting Non-Replicating Mycobacterium tuberculosis and Latent Infection: Alternatives and Perspectives (Mini-Review).Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Dec 10;22(24):13317. doi: 10.3390/ijms222413317. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34948114 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Addlagatta A, Hu X, Liu JO, Matthews BW. Structural Basis for the Functional Differences between Type I and Type II Human Methionine Aminopeptidases. Biochemistry. 2005a;44:14741–14749. - PubMed
-
- Addlagatta A, Quillin ML, Omotoso O, Liu JO, Matthews BW. Identification of an SH3-binding motif in a new class of methionine aminopeptidases from Mycobacterium tuberculosis suggests a mode of interaction with the ribosome. Biochemistry. 2005b;44:7166–7174. - PubMed
-
- Bernier SG, Taghizadeh N, Thompson CD, Westlin WF, Hannig G. Methionine aminopeptidases type I and type II are essential to control cell proliferation. J Cell Biochem. 2005;95:1191–1203. - PubMed
-
- Boxem M, Tsai CW, Zhang Y, Saito RM, Liu JO. The C. elegans methionine aminopeptidase 2 analog map-2 is required for germ cell proliferation. FEBS Lett. 2004;576:245–250. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

