The XBP-Bax1 helicase-nuclease complex unwinds and cleaves DNA: implications for eukaryal and archaeal nucleotide excision repair
- PMID: 20139443
- PMCID: PMC2856306
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M109.094763
The XBP-Bax1 helicase-nuclease complex unwinds and cleaves DNA: implications for eukaryal and archaeal nucleotide excision repair
Abstract
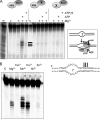
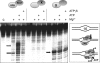
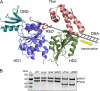
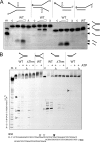
XPB helicase is an integral part of transcription factor TFIIH, required for both transcription initiation and nucleotide excision repair (NER). Along with the XPD helicase, XPB plays a crucial but only partly understood role in defining and extending the DNA repair bubble around lesions in NER. Archaea encode clear homologues of XPB and XPD, and structural studies of these proteins have yielded key insights relevant to the eukaryal system. Here we show that archaeal XPB functions with a structure-specific nuclease, Bax1, as a helicase-nuclease machine that unwinds and cleaves model NER substrates. DNA bubbles are extended by XPB and cleaved by Bax1 at a position equivalent to that cut by the XPG nuclease in eukaryal NER. The helicase activity of archaeal XPB is dependent on the conserved Thumb domain, which may act as the helix breaker. The N-terminal damage recognition domain of XPB is shown to be crucial for XPB-Bax1 activity and may be unique to the archaea. These findings have implications for the role of XPB in both archaeal and eukaryal NER and for the evolution of the NER pathway. XPB is shown to be a very limited helicase that can act on small DNA bubbles and open a defined region of the DNA duplex. The specialized functions of the accessory domains of XPB are now more clearly delineated. This is also the first direct demonstration of a repair function for archaeal XPB and suggests strongly that the role of XPB in transcription occurred later in evolution than that in repair.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Structural basis of the XPB-Bax1 complex as a dynamic helicase-nuclease machinery for DNA repair.Nucleic Acids Res. 2020 Jun 19;48(11):6326-6339. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkaa324. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020. PMID: 32374860 Free PMC article.
-
The archaeal XPB protein is a ssDNA-dependent ATPase with a novel partner.J Mol Biol. 2008 Feb 22;376(3):634-44. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2007.12.019. Epub 2007 Dec 15. J Mol Biol. 2008. PMID: 18177890
-
Bax1 is a novel endonuclease: implications for archaeal nucleotide excision repair.J Biol Chem. 2009 Nov 20;284(47):32272-8. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M109.055913. Epub 2009 Sep 15. J Biol Chem. 2009. PMID: 19759013 Free PMC article.
-
XPB: An unconventional SF2 DNA helicase.Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 2015 Mar;117(2-3):174-181. doi: 10.1016/j.pbiomolbio.2014.12.005. Epub 2015 Jan 30. Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 2015. PMID: 25641424 Review.
-
The evolution and mechanisms of nucleotide excision repair proteins.Res Microbiol. 2011 Jan;162(1):19-26. doi: 10.1016/j.resmic.2010.09.003. Epub 2010 Sep 21. Res Microbiol. 2011. PMID: 20863882 Review.
Cited by
-
Host nucleotide polymorphism in hepatitis B virus-associated hepatocellular carcinoma.World J Hepatol. 2016 Apr 8;8(10):485-98. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v8.i10.485. World J Hepatol. 2016. PMID: 27057306 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Knockout and functional analysis of two DExD/H-box family helicase genes in Sulfolobus islandicus REY15A.Extremophiles. 2016 Jul;20(4):537-46. doi: 10.1007/s00792-016-0847-5. Epub 2016 Jun 11. Extremophiles. 2016. PMID: 27290726
-
Single-stranded DNA binding activity of XPBI, but not XPBII, from Sulfolobus tokodaii causes double-stranded DNA melting.Extremophiles. 2011 Jan;15(1):67-76. doi: 10.1007/s00792-010-0338-z. Epub 2010 Dec 5. Extremophiles. 2011. PMID: 21132514
-
Structural basis of the XPB-Bax1 complex as a dynamic helicase-nuclease machinery for DNA repair.Nucleic Acids Res. 2020 Jun 19;48(11):6326-6339. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkaa324. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020. PMID: 32374860 Free PMC article.
-
The complete structure of the human TFIIH core complex.Elife. 2019 Mar 12;8:e44771. doi: 10.7554/eLife.44771. Elife. 2019. PMID: 30860024 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

