KMUP-1 attenuates isoprenaline-induced cardiac hypertrophy in rats through NO/cGMP/PKG and ERK1/2/calcineurin A pathways
- PMID: 20132211
- PMCID: PMC2839273
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.2009.00587.x
KMUP-1 attenuates isoprenaline-induced cardiac hypertrophy in rats through NO/cGMP/PKG and ERK1/2/calcineurin A pathways
Abstract
Background and purpose: To determine whether KMUP-1, a novel xanthine-based derivative, attenuates isoprenaline (ISO)-induced cardiac hypertrophy in rats, and if so, whether the anti-hypertrophic effect is mediated by the nitric oxide (NO) pathway.
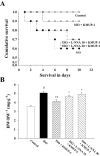
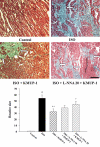
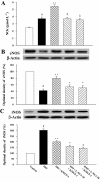
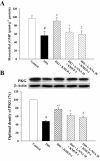
Experimental approach: In vivo, cardiac hypertrophy was induced by injection of ISO (5 mg.kg(-1).day(-1), s.c.) for 10 days in Wistar rats. In the treatment group, KMUP-1 was administered 1 h before ISO. After 10 days, effects of KMUP-1 on survival, cardiac hypertrophy and fibrosis, the NO/guanosine 3'5'-cyclic monophosphate (cGMP)/protein kinase G (PKG) and hypertrophy signalling pathways [calcineurin A and extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK)1/2] were examined. To investigate the role of nitric oxide synthase (NOS) in the effects of KMUP-1, a NOS inhibitor, N(omega)-nitro-L-arginine (L-NNA) was co-administered with KMUP-1. In vitro, anti-hypertrophic effects of KMUP-1 were studied in ISO-induced hypertrophic neonatal rat cardiomyocytes.
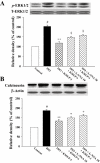
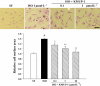
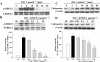
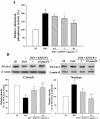
Key results: In vivo, KMUP-1 pretreatment attenuated the cardiac hypertrophy and fibrosis and improved the survival of ISO-treated rats. Plasma NOx (nitrite and nitrate) and cardiac endothelial NOS, cGMP and PKG were all increased by KMUP-1. The activation of hypertrophic signalling by calcineurin A and ERK1/2 in ISO-treated rats was also attenuated by KMUP-1. All these effects of KMUP-1 were inhibited by simultaneous administration of L-NNA. Similarly, in vitro, KMUP-1 attenuated hypertrophic responses and signalling induced by ISO in neonatal rat cardiomyocytes.
Conclusions and implications: KMUP-1 attenuates the cardiac hypertrophy in rats induced by administration of ISO. These effects are mediated, at least in part, by NOS activation. This novel agent, which targets the NO/cGMP pathway, has a potential role in the prevention of cardiac hypertrophy.
Figures
Similar articles
-
KMUP-1 inhibits hypertension-induced left ventricular hypertrophy through regulation of nitric oxide synthases, ERK1/2, and calcineurin.Kaohsiung J Med Sci. 2012 Nov;28(11):567-76. doi: 10.1016/j.kjms.2012.04.022. Epub 2012 Jul 25. Kaohsiung J Med Sci. 2012. PMID: 23140764
-
KMUP-1 regulates the vascular calcification in chronic renal failure by mediating NO/cGMP/PKG signaling pathway.Life Sci. 2020 Jul 15;253:117683. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2020.117683. Epub 2020 Apr 18. Life Sci. 2020. PMID: 32315727
-
KMUP-1 Attenuates Endothelin-1-Induced Cardiomyocyte Hypertrophy through Activation of Heme Oxygenase-1 and Suppression of the Akt/GSK-3β, Calcineurin/NFATc4 and RhoA/ROCK Pathways.Molecules. 2015 Jun 5;20(6):10435-49. doi: 10.3390/molecules200610435. Molecules. 2015. PMID: 26056815 Free PMC article.
-
KMUP-1 Ameliorates Ischemia-Induced Cardiomyocyte Apoptosis through the NO⁻cGMP⁻MAPK Signaling Pathways.Molecules. 2019 Apr 8;24(7):1376. doi: 10.3390/molecules24071376. Molecules. 2019. PMID: 30965668 Free PMC article.
-
Regression of pathological cardiac hypertrophy: signaling pathways and therapeutic targets.Pharmacol Ther. 2012 Sep;135(3):337-54. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2012.06.006. Epub 2012 Jun 29. Pharmacol Ther. 2012. PMID: 22750195 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Inhibition of the TGFβ signalling pathway by cGMP and cGMP-dependent kinase I in renal fibrosis.FEBS Open Bio. 2017 Mar 1;7(4):550-561. doi: 10.1002/2211-5463.12202. eCollection 2017 Apr. FEBS Open Bio. 2017. PMID: 28396839 Free PMC article.
-
BKCa Channel Inhibition by Peripheral Nerve Injury Is Restored by the Xanthine Derivative KMUP-1 in Dorsal Root Ganglia.Cells. 2021 Apr 20;10(4):949. doi: 10.3390/cells10040949. Cells. 2021. PMID: 33923953 Free PMC article.
-
A xanthine-derivative K(+)-channel opener protects against serotonin-induced cardiomyocyte hypertrophy via the modulation of protein kinases.Int J Biol Sci. 2013 Dec 17;10(1):64-72. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.7894. eCollection 2013. Int J Biol Sci. 2013. PMID: 24391452 Free PMC article.
-
Cardioprotective Effect of Ulmus wallichiana Planchon in β-Adrenergic Agonist Induced Cardiac Hypertrophy.Front Pharmacol. 2016 Dec 21;7:510. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2016.00510. eCollection 2016. Front Pharmacol. 2016. PMID: 28066255 Free PMC article.
-
KMUP-3 attenuates ventricular remodelling after myocardial infarction through eNOS enhancement and restoration of MMP-9/TIMP-1 balance.Br J Pharmacol. 2011 Jan;162(1):126-35. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.2010.01024.x. Br J Pharmacol. 2011. PMID: 20840538 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aaronson KD, Sackner-Bernstein J. Risk of death associated with nesiritide in patients with acutely decompensated heart failure. JAMA. 2006;296:1465–1466. - PubMed
-
- Bueno OF, Molkentin JD. Involvement of extracellular signal-regulated kinases 1/2 in cardiac hypertrophy and cell death. Circ Res. 2002;91:776–781. - PubMed
-
- Fiedler B, Wollert KC. Interference of antihypertrophic molecules and signaling pathways with the Ca2+-calcineurin-NFAT cascade in cardiac myocytes. Cardiovasc Res. 2004;63:450–457. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

