Flavokawain B, a kava chalcone, induces apoptosis via up-regulation of death-receptor 5 and Bim expression in androgen receptor negative, hormonal refractory prostate cancer cell lines and reduces tumor growth
- PMID: 20112340
- PMCID: PMC2888737
- DOI: 10.1002/ijc.25210
Flavokawain B, a kava chalcone, induces apoptosis via up-regulation of death-receptor 5 and Bim expression in androgen receptor negative, hormonal refractory prostate cancer cell lines and reduces tumor growth
Abstract
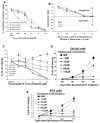
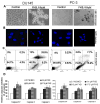
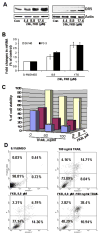
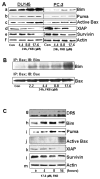
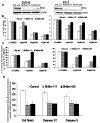
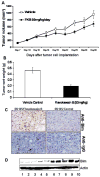
Limited success has been achieved in extending the survival of patients with metastatic and hormone-refractory prostate cancer (HRPC). There is a strong need for novel agents in the treatment and prevention of HRPC. We have shown that flavokawain B (FKB), a kava chalcone, is about 4- to 12-fold more effective in reducing the cell viabilities of androgen receptor (AR)-negative, HRPC cell lines DU145 and PC-3 than AR-positive, hormone-sensitive prostate cancer cell lines LAPC4 and LNCaP, with minimal effect on normal prostatic epithelial and stromal cells. FKB induces apoptosis with an associated increased expression of proapoptotic proteins: death receptor-5, Bim and Puma and a decreased expression of inhibitors of apoptosis protein: XIAP and survivin. Among them, Bim expression was significantly induced by FKB as early as 4 hr of the treatment. Knockdown of Bim expression by short-hairpin RNAs attenuates the inhibitory effect on anchorage-dependent and -independent growth and caspase cleavages induced by FKB. These findings suggest that the effect of FKB, at least in part, requires Bim expression. In addition, FKB synergizes with TRAIL for markedly enhanced induction of apoptosis. Furthermore, FKB treatment of mice bearing DU145 xenograft tumors results in tumor growth inhibition and increases Bim expression in tumor tissues. Together, these results suggest robust mechanisms for FKB induction of apoptosis preferentially for HRPC and the potential usefulness of FKB for prevention and treatment of HRPC in an adjuvant setting.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Flavokawain B induces apoptosis of human oral adenoid cystic cancer ACC-2 cells via up-regulation of Bim and down-regulation of Bcl-2 expression.Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 2011 Dec;89(12):875-83. doi: 10.1139/y11-088. Epub 2011 Nov 24. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 2011. PMID: 22115332
-
Flavokawain B, a kava chalcone, induces apoptosis in synovial sarcoma cell lines.J Orthop Res. 2012 Jul;30(7):1045-50. doi: 10.1002/jor.22050. Epub 2011 Dec 29. J Orthop Res. 2012. PMID: 22213202 Free PMC article.
-
Flavokawain B, a kava chalcone, inhibits growth of human osteosarcoma cells through G2/M cell cycle arrest and apoptosis.Mol Cancer. 2013 Jun 10;12:55. doi: 10.1186/1476-4598-12-55. Mol Cancer. 2013. PMID: 23764122 Free PMC article.
-
The proteasome inhibitor bortezomib sensitizes cells to killing by death receptor ligand TRAIL via BH3-only proteins Bik and Bim.Mol Cancer Ther. 2005 Mar;4(3):443-9. doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-04-0260. Mol Cancer Ther. 2005. PMID: 15767553
-
Flavokawain B targets protein neddylation for enhancing the anti-prostate cancer effect of Bortezomib via Skp2 degradation.Cell Commun Signal. 2019 Mar 18;17(1):25. doi: 10.1186/s12964-019-0338-2. Cell Commun Signal. 2019. PMID: 30885218 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Targeting death receptor TRAIL-R2 by chalcones for TRAIL-induced apoptosis in cancer cells.Int J Mol Sci. 2012 Nov 20;13(11):15343-59. doi: 10.3390/ijms131115343. Int J Mol Sci. 2012. PMID: 23203129 Free PMC article.
-
Dietary chalcones with chemopreventive and chemotherapeutic potential.Genes Nutr. 2011 May;6(2):125-47. doi: 10.1007/s12263-011-0210-5. Epub 2011 Feb 4. Genes Nutr. 2011. PMID: 21484163 Free PMC article.
-
Pharmacological Small Molecules against Prostate Cancer by Enhancing Function of Death Receptor 5.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2022 Aug 21;15(8):1029. doi: 10.3390/ph15081029. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36015177 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The role of chalcones in suppression of NF-κB-mediated inflammation and cancer.Int Immunopharmacol. 2011 Mar;11(3):295-309. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2010.12.006. Epub 2010 Dec 22. Int Immunopharmacol. 2011. PMID: 21184860 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cancer cell growth inhibitory effect of bee venom via increase of death receptor 3 expression and inactivation of NF-kappa B in NSCLC cells.Toxins (Basel). 2014 Jul 25;6(8):2210-28. doi: 10.3390/toxins6082210. Toxins (Basel). 2014. PMID: 25068924 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hsing AW, Devesa SS. Trends and patterns of prostate cancer: what do they suggest? Epidemiol Rev. 2001;23:3–13. - PubMed
-
- Feldman BJ, Feldman D. The development of androgen-independent prostate cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 2001;1:34–45. - PubMed
-
- Dagher R, Li N, Abraham S, Rahman A, Sridhara R, Pazdur R. Approval summary: Docetaxel in combination with prednisone for the treatment of androgen-independent hormone-refractory prostate cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 2004;10:8147–51. - PubMed
-
- Kasper S, Cookson MS. Mechanisms leading to the development of hormone-resistant prostate cancer. Urol Clin North Am. 2006;33:201–210. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

