Genotoxic stress causes the accumulation of the splicing regulator Sam68 in nuclear foci of transcriptionally active chromatin
- PMID: 20110258
- PMCID: PMC2875014
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkq004
Genotoxic stress causes the accumulation of the splicing regulator Sam68 in nuclear foci of transcriptionally active chromatin
Abstract
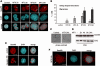
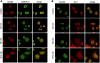
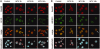
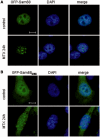
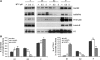
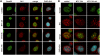
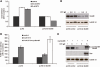
DNA-damaging agents cause a multifaceted cellular stress response. Cells set in motion either repair mechanisms or programmed cell death pathways, depending on the extent of the damage and on their ability to withstand it. The RNA-binding protein (RBP) Sam68, which is up-regulated in prostate carcinoma, promotes prostate cancer cell survival to genotoxic stress. Herein, we have investigated the function of Sam68 in this cellular response. Mitoxantrone (MTX), a topoisomerase II inhibitor, induced relocalization of Sam68 from the nucleoplasm to nuclear granules, together with several other RBPs involved in alternative splicing, such as TIA-1, hnRNP A1 and the SR proteins SC35 and ASF/SF2. Sam68 accumulation in nuclear stress granules was independent of signal transduction pathways activated by DNA damage. Using BrU labelling and immunofluorescence, we demonstrate that MTX-induced nuclear stress granules are transcriptionally active foci where Sam68 and the phosphorylated form of RNA polymerase II accumulate. Finally, we show that MTX-induced relocalization of Sam68 correlates with changes in alternative splicing of its mRNA target CD44, and that MTX-induced CD44 splicing depends on Sam68 expression. These results strongly suggest that Sam68 is part of a RNA-mediated stress response of the cell that modulates alternative splicing in response to DNA damage.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Role of Sam68 in post-transcriptional gene regulation.Int J Mol Sci. 2013 Nov 28;14(12):23402-19. doi: 10.3390/ijms141223402. Int J Mol Sci. 2013. PMID: 24287914 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The transcriptional co-activator SND1 is a novel regulator of alternative splicing in prostate cancer cells.Oncogene. 2014 Jul 17;33(29):3794-802. doi: 10.1038/onc.2013.360. Epub 2013 Sep 2. Oncogene. 2014. PMID: 23995791
-
The RNA-binding and adaptor protein Sam68 modulates signal-dependent splicing and transcriptional activity of the androgen receptor.J Pathol. 2008 May;215(1):67-77. doi: 10.1002/path.2324. J Pathol. 2008. PMID: 18273831
-
Proteomic identification of heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein L as a novel component of SLM/Sam68 Nuclear Bodies.BMC Cell Biol. 2009 Nov 13;10:82. doi: 10.1186/1471-2121-10-82. BMC Cell Biol. 2009. PMID: 19912651 Free PMC article.
-
The RNA-binding protein Sam68 is a multifunctional player in human cancer.Endocr Relat Cancer. 2011 Jul 1;18(4):R91-R102. doi: 10.1530/ERC-11-0041. Print 2011 Aug. Endocr Relat Cancer. 2011. PMID: 21565971 Review.
Cited by
-
Inhibition of HSF1 and SAFB Granule Formation Enhances Apoptosis Induced by Heat Stress.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 May 7;22(9):4982. doi: 10.3390/ijms22094982. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34067147 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of HuR by DNA Damage Response Kinases.J Nucleic Acids. 2010 Jul 25;2010:981487. doi: 10.4061/2010/981487. J Nucleic Acids. 2010. PMID: 20798862 Free PMC article.
-
Role of Sam68 in post-transcriptional gene regulation.Int J Mol Sci. 2013 Nov 28;14(12):23402-19. doi: 10.3390/ijms141223402. Int J Mol Sci. 2013. PMID: 24287914 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Splicing alterations in healthy aging and disease.Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA. 2021 Jul;12(4):e1643. doi: 10.1002/wrna.1643. Epub 2021 Feb 9. Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA. 2021. PMID: 33565261 Free PMC article. Review.
-
RBM45 associates with nuclear stress bodies and forms nuclear inclusions during chronic cellular stress and in neurodegenerative diseases.Acta Neuropathol Commun. 2020 Jun 26;8(1):91. doi: 10.1186/s40478-020-00965-y. Acta Neuropathol Commun. 2020. PMID: 32586379 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Crighton D, Ryan KM. Splicing DNA-damage responses to tumour cell death. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 2004;1705:3–15. - PubMed
-
- Muñoz MJ, Pérez Santangelo MS, Paronetto MP, de la Mata M, Pelisch F, Boireau S, Glover-Cutter K, Ben-Dov C, Blaustein M, Lozano JJ, et al. DNA damage regulates alternative splicing through inhibition of RNA polymerase II elongation. Cell. 2009;137:708–720. - PubMed
-
- Black DL. Mechanisms of alternative pre-messenger RNA splicing. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2003;72:291–336. - PubMed
-
- Matlin AJ, Clark F, Smith CW. Understanding alternative splicing: towards a cellular code. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2005;6:386–398. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

