Cancer therapies utilizing the camptothecins: a review of the in vivo literature
- PMID: 20108971
- PMCID: PMC3733266
- DOI: 10.1021/mp900243b
Cancer therapies utilizing the camptothecins: a review of the in vivo literature
Abstract
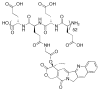
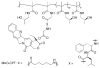
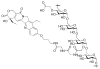
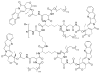
This review summarizes the in vivo assessment-preliminary, preclinical, and clinical-of chemotherapeutics derived from camptothecin or a derivative. Camptothecin is a naturally occurring, pentacyclic quinoline alkaloid that possesses high cytotoxic activity in a variety of cell lines. Major limitations of the drug, including poor solubility and hydrolysis under physiological conditions, prevent full clinical utilization. Camptothecin remains at equilibrium in an active lactone form and inactive hydrolyzed carboxylate form. The active lactone binds to DNA topoisomerase I cleavage complex, believed to be the single site of activity. Binding inhibits DNA religation, resulting in apoptosis. A series of small molecule camptothecin derivatives have been developed that increase solubility, lactone stability and bioavailability to varying levels of success. A number of macromolecular agents have also been described wherein camptothecin(s) are covalently appended or noncovalently associated with the goal of improving solubility and lactone stability, while taking advantage of the tumor physiology to deliver larger doses of drug to the tumor with lower systemic toxicity. With the increasing interest in drug delivery and polymer therapeutics, additional constructs are anticipated. The goal of this review is to summarize the relevant literature for others interested in the field of camptothecin-based therapeutics, specifically in the context of biodistribution, dosing regimens, and pharmacokinetics with the desire of providing a useful source of comparative data. To this end, only constructs where in vivo data is available are reported. The review includes published reports in English through mid-2009.
Figures
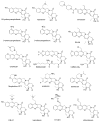
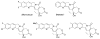
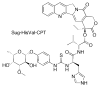
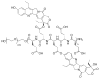
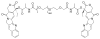
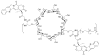
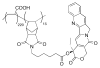

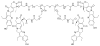

Similar articles
-
Current perspectives on the clinical experience, pharmacology, and continued development of the camptothecins.Clin Cancer Res. 2002 Mar;8(3):641-61. Clin Cancer Res. 2002. PMID: 11895891 Review.
-
The clinical pharmacology of topoisomerase I inhibitors.Semin Hematol. 1998 Jul;35(3 Suppl 4):13-21. Semin Hematol. 1998. PMID: 9779877 Review.
-
Lactone Stabilization is Not a Necessary Feature for Antibody Conjugates of Camptothecins.Mol Pharm. 2018 Sep 4;15(9):4063-4072. doi: 10.1021/acs.molpharmaceut.8b00477. Epub 2018 Aug 14. Mol Pharm. 2018. PMID: 30067902
-
Rubitecan.Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 2006 Jan;15(1):71-9. doi: 10.1517/13543784.15.1.71. Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 2006. PMID: 16370935 Review.
-
Strategies Targeting DNA Topoisomerase I in Cancer Chemotherapy: Camptothecins, Nanocarriers for Camptothecins, Organic Non-Camptothecin Compounds and Metal Complexes.Curr Drug Targets. 2016;17(16):1928-1939. doi: 10.2174/1389450117666160502151707. Curr Drug Targets. 2016. PMID: 27138759 Review.
Cited by
-
Cancer nanomedicines: so many papers and so few drugs!Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2013 Jan;65(1):80-8. doi: 10.1016/j.addr.2012.09.038. Epub 2012 Oct 1. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2013. PMID: 23036224 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Accurate mass-time tag library for LC/MS-based metabolite profiling of medicinal plants.Phytochemistry. 2013 Jul;91:187-97. doi: 10.1016/j.phytochem.2013.02.018. Epub 2013 Apr 16. Phytochemistry. 2013. PMID: 23597491 Free PMC article.
-
A Tumor-Homing Peptide Platform Enhances Drug Solubility, Improves Blood-Brain Barrier Permeability and Targets Glioblastoma.Cancers (Basel). 2022 Apr 28;14(9):2207. doi: 10.3390/cancers14092207. Cancers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35565337 Free PMC article.
-
Synergism of cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitors with camptothecin derivatives in small cell lung cancer cell lines.Molecules. 2014 Feb 17;19(2):2077-88. doi: 10.3390/molecules19022077. Molecules. 2014. PMID: 24549232 Free PMC article.
-
PEAMOtecan, a novel chronotherapeutic polymeric drug for brain cancer.J Control Release. 2020 May 10;321:36-48. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2020.02.003. Epub 2020 Feb 3. J Control Release. 2020. PMID: 32027939 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Wall ME, Wani MC, Cooke CE, Palmer KH, McPhail AT, Sim GA. Plant antitumor agents. I. The isolation and structure of camptothecin, a novel alkaloidal leukemia and tumor inhibitor from Camptotheca acuminata. J Am Chem Soc. 1966;88:3888–3890.
-
- Wani MC, Taylor HL, Wall ME, Coggon P, McPhail AT. Plant antitumor agentsVI The isolation and structure of taxol, a novel antileukemic and antitumor agent from taxus brevifolia. J Am Chem Soc. 1971;93:2325–2327. - PubMed
-
- Slichenmyer WJ, Von Hoff DD. New natural products in cancer chemotherapy. J Clin Pharmacol. 1990;30:770–788. - PubMed
-
- Wall ME. Camptothecin and taxol: discovery to clinic. Med Res Rev. 1998;18:299–314. - PubMed
-
- Hsiang Y-H, Hertzberg R, Hecht S, Liu LF. Camptothecin induces protein-linked DNA breaks via mammalian DNA topoisomerase I. J Biol Chem. 1985;260:14873–14878. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

