Down regulation of the PEDF gene in human lens epithelium cells changed the expression of proteins vimentin and alphaB-crystallin
- PMID: 20104255
- PMCID: PMC2810874
Down regulation of the PEDF gene in human lens epithelium cells changed the expression of proteins vimentin and alphaB-crystallin
Abstract
Purpose: To study the relationship of pigment epithelium-derived factor (PEDF) expression with the expression of vimentin and alphaB-crystallin by lens epithelial cells.
Methods: Lens epithelial cells adhering to anterior capsules taken from young donor eyes aged from 20 to 35 years were cultured and passaged. We designed small interfering RNA (siRNA) constructs to specifically downregulate the expression of PEDF by these primary lens epithelial cells. Quantitative PCR was used to confirm the downregulation of PEDF RNA expression following infection of lens epithelial cells. To determine whether altering the expression of PEDF would effect the expression of vimentin or alphaB-crystallin, we performed western blotting 48 h after expression of the PEDF-directed siRNA.
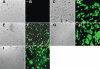
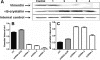
Results: PEDF RNA expression in the human lens epithelial cells was strongly downregulated by the three separate siRNA constructs. Western blotting revealed that the downregulation of PEDF expression resulted in a concomitant decrease in expression of vimentin and an increase in alphaB-crystallin protein.
Conclusions: Decreased expression of PEDF in primary human lens epithelial cells resulted in a decrease in the expression of vimentin and the increase of alphaB-crystallin expression, two proteins critical for maintaining lens clarity.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Expression of Neovascular Associated Factors PEDF and αB-crystallin in Human Lens Epithelial Cells.Curr Eye Res. 2020 Nov;45(11):1385-1389. doi: 10.1080/02713683.2020.1746813. Epub 2020 Mar 30. Curr Eye Res. 2020. PMID: 32208037
-
alpha-Crystallin localizes to the leading edges of migrating lens epithelial cells.Exp Cell Res. 2005 May 15;306(1):203-15. doi: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2005.01.026. Epub 2005 Mar 17. Exp Cell Res. 2005. PMID: 15878345
-
Expression of pigment epithelium-derived factor in normal adult rat eye and experimental choroidal neovascularization.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2002 Apr;43(4):1168-75. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2002. PMID: 11923262
-
Downregulation of gene expression in the ageing lens: a possible contributory factor in senile cataract.Eye (Lond). 2005 Jan;19(1):80-5. doi: 10.1038/sj.eye.6701423. Eye (Lond). 2005. PMID: 15105821
-
A comparative analysis of alphaA- and alphaB-crystallin expression during the cell cycle in primary mouse lens epithelial cultures.Exp Eye Res. 2004 Dec;79(6):795-805. doi: 10.1016/j.exer.2004.05.006. Exp Eye Res. 2004. PMID: 15642316
Cited by
-
Cross-reactivity of antibodies against leptospiral recurrent uveitis-associated proteins A and B (LruA and LruB) with eye proteins.PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2010 Aug 3;4(8):e778. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0000778. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2010. PMID: 20689825 Free PMC article.
-
Lens Biology and Biochemistry.Prog Mol Biol Transl Sci. 2015;134:169-201. doi: 10.1016/bs.pmbts.2015.04.007. Epub 2015 Jun 4. Prog Mol Biol Transl Sci. 2015. PMID: 26310155 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Growth inhibition of human lens epithelial cells by short hairpin RNA in transcription factor forkhead box E3 (FOXE3).Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2012 Jul;250(7):999-1007. doi: 10.1007/s00417-012-1944-5. Epub 2012 Apr 18. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2012. PMID: 22527307
-
The human lens is capable of trilineage differentiation towards osteo-, chondro-, and adipogenesis-a model for studying cataract pathogenesis.Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2023 May 31;11:1164795. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2023.1164795. eCollection 2023. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2023. PMID: 37324433 Free PMC article.
-
Changes in PEDF, MMP-2, and TGF-β2 levels in the aqueous humor of cataract patients and their correlation with disease severity.Clinics (Sao Paulo). 2024 Oct 15;79:100402. doi: 10.1016/j.clinsp.2024.100402. eCollection 2024. Clinics (Sao Paulo). 2024. PMID: 39413500 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Wu YQ, Becerra SP. Proteolytic activity directed toward pigment epithelium-derived factor in vitreous bovine eyes. Implications of proteolytic processing. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 1996;37:1984–93. - PubMed
-
- Kuszak JR. Embryology and histology of the lens. Duane’s Clinical Ophthalmology Vol 1. Philadelphia; Lippincot-Raven: 1995. p. 1–9.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
